Preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms, like bones or imprints
What are fossils?
List the equation for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and what each variable represents
What is p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1, where p is the frequency of the dominant allele and q is the frequency of the recessive allele?
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its specific environment
What is adaptation?
This force, which is a discovery of Sewall Wright, involves random changes in allele frequencies, especially in small populations.
What is Genetic Drift?
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry, such as the wing of a bat and the arm of a human.
What are homologous structures?
A population of small fish starts with 40 red-spotted fish. In the next generation, they produce 50 red-spotted fish. What is their Absolute Fitness (W)?
What is 1.25 (W = 50/40 = 1.25)?
The evolutionary process by which one ancestral species splits and diverges into two or more species.
What is speciation?
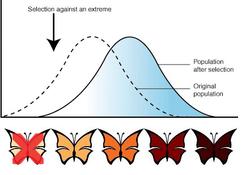
This type of natural selection favors one extreme phenotype, causing the population’s average trait value to shift over generations.
What is Directional Selection?
A structure that has lost its original function over time, such as the appendix in humans or tiny leg bones in some snakes.
What are Vestigial Structures?
The most successful genotype in a population has an Absolute Fitness of 1.5. A less successful genotype has an Absolute Fitness of 0.6. What is the less successful genotype’s Relative Fitness (w)?
What is 0.4 (w = 0.6/1.5 = 0.4)?
These 3D or contour-style graphs are used to visualize the fitness of different trait combinations.
What is Fitness Landscapes?
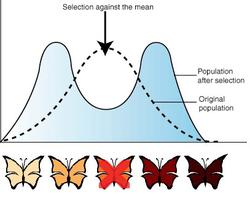
This type of natural selection favors both extreme phenotypes, selecting against the average speciation.
What is Disruptive or Diversifying Selection?
This category of evolutionary evidence documents changes in allele frequencies or average traits within a population that are measurable over a few years or generations, such as pesticide resistance in insects.
A population of moths has a genotype with a Relative Fitness (w) of 0.92. What is the Selection Coefficient (s) for this genotype?
What is 0.08 (s = 1-0.92 = 0.08)?
On a fitness landscape, the “peaks” represent trait combinations with this level of fitness.
What is High(or Optimal) Fitness?
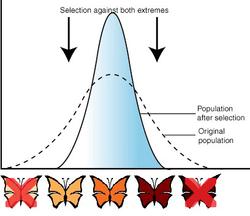
This type of natural selection favors the intermediate phenotype, selecting against both extremes and causing the population distribution to narrow.
What is Stabilizing Selection?
The study of the geographic distribution of organisms, which provided key evidence for Darwin’s theories
What is Biogeography?
In a population of lizards, the AA genotype has an Absolute Fitness (W) of 1.0, and the Aa genotype has an Absolute Fitness (W) of 1.5. What is the Selection Coefficient (s) for the AA genotype?
What is 0.333 (Wmax = 1.5, wAA = 1.0/1.5 = 0.667, s = 1-0.667 - 0.333)?
This type of speciation occurs when two groups are separated by a physical barrier, like a mountain range, and evolve independently.
What is Allopatric Speciation?
These two researchers, along with others, were key architects of the Modern Synthesis, integrating Mendelian genetics with Darwinian natural selection (only need to name one to get points).
Who are Sewall Wright and Theodosius Dobzhansky?