f
frequency
E
joules or J
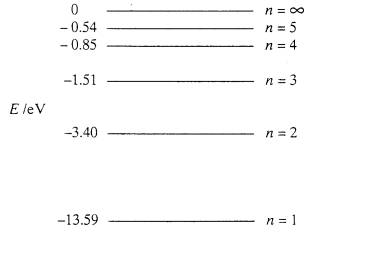 In the figure, the amount of energy absorbed when an electron goes from the n=1 to n=3 level
In the figure, the amount of energy absorbed when an electron goes from the n=1 to n=3 level
12.08 eV
mass number of a beta particle
0
In beta decay, this force converts a neutron to a proton
weak nuclear force
lambda
wavelength
K
joules or J
The energy of a photon with a frequency of 2 x 1015 Hz.
1.3x10-18 J
atomic number of an alpha particle
2
This force is always attractive and partially explains why electrons are attracted to protons.
gravitational force
h
Planck's constant
c
m/s
The energy of a green photon (440 nm)
4.5 x 10-19 J
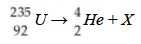 What element is X and what is the mass number?
What element is X and what is the mass number?
Thorium-231
What two forces could exist between an electron and a proton?
gravitational and electrostatic
c
speed of light
lambda
m
On the picture, which transition emits light with the longest wavelength?
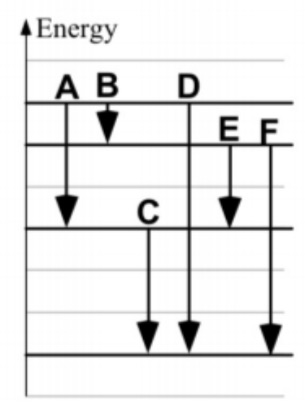
B
In radioactive decay, a particle is emitted from the nucleus of an atom, and the atom's atomic number increases by one. What is the emitted particle?
an electron
What three forces could exist between a proton and a proton?
gravitational, electrostatic and strong nuclear
Phi
work function
m
kg or kilogram
A certain metal is illuminated with light of a frequency of 1.7x1015 Hz. Electrons are ejected with a speed of 8.4x105 m/s. What is the work function of the metal?
8.03x10-19 J
In the radioactive decay equation given below, what is X?
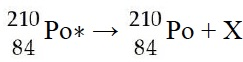
gamma ray (or photon)
The primary reason that very large nuclei are unstable is due to
repulsive force of the protons