What are enzymes?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms
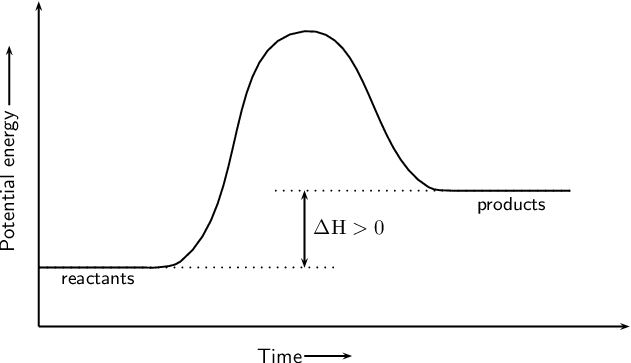
Endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic
What is cell biology?
study of cells, their functions, and interactions
What is the key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells regarding the nucleus?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus; eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
Bacteria
Archae
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed
Which type of reaction releases energy into the surroundings and the products contain less energy than the reactants?
Exothermic
State the three main principles of the cell theory.
All living organisms are made of cells.
The cell is the basic unit of life.
All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
How does the size of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ?
Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryote
What type of macromolecule are enzymes made of?
Proteins
What happens to the reaction rate when enzyme concentration increases?
Decreases
What role does surface area to volume ratio play in determining cell size?
Cells need a high surface area-to-volume ratio to efficiently exchange materials with their environment.
How is DNA stored in prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic: DNA is stored in a single circular chromosome in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic: DNA is stored in the nucleus in double-stranded chromosomes.
Animal
Eukaroyte
What would happen to an enzyme if extreme heat was added?
Denature
What does this image show in relation to enzymes and reactions?
Activation energy is lowered by presence of enzyme thereby speeding up the reaction
How do cell size and shape relate to their functions?
The shape and size of a cell are adapted to its specific function, such as flat epithelial cells for covering surfaces.
What is the function of ribosomes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Ribosomes synthesize proteins by translating mRNA into amino acid sequences.
Fungi
Eukaryote
Explain the lock and key model of enzyme-substrate interaction.
The lock and key model explains how the enzyme's active site (lock) fits perfectly with the substrate (key), allowing the enzyme to catalyze the reaction.
How does increasing enzyme concentration lower the activation energy of a reaction?
More enzyme molecules are available to bind substrates, allowing more reactions to occur simultaneously and lowering the overall activation energy needed.
Give an example of how the structure of a neuron relates to its function.
Neurons are long and branched to efficiently transmit signals across long distances in the body.
How does the locomotion structure in prokaryotic cells differ from that in eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells use simpler flagella for movement, while eukaryotic cells have more complex flagella or cilia, which are composed of microtubules.
Virus
NEITHER (NON-LIVING)