This is the visible surface of the sun, where sunspots and solar weather occur
Photosphere
___________________ refers to how reflective a surface is, and is measured as a percentage of how much light is reflected by the surface
BONUS: What types of surfaces on Earth are highly reflective?
Albedo
BONUS: Snow/ice -- albedo of 0.8
Stars are born from _____________ _____________, dense nebulas of gas and dust
molecular clouds
True or False: M class stars are likely to have shorter lifespans that O class stars
False
True or False: Solar flares, large outbursts of energy from the sun, can cause mass power outages on Earth
True
Nuclear fusion occurs in the __________ of stars, generating the energy that makes stars luminous
BONUS: What temperature must be reached for nuclear fusion to begin?
Core
BONUS: 15 million K
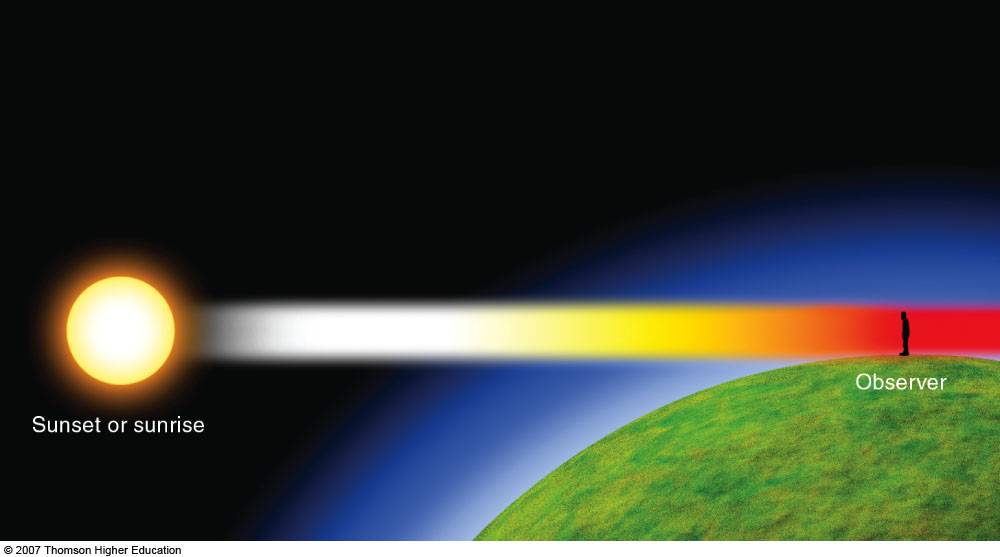
__________________ is the phenomenon by which shorter wavelengths of light bounce off the molecules in our atmosphere, leaving longer wavelengths to pass through and reach our eyes

Scattering
____________ _____________ is how bright a star appears from Earth, and is therefore distance dependent.
_____________ ____________ or luminosity is a measure of how bright the star actually is, independent of distance from Earth
Apparent magnitude
Absolute magnitude
The stellar remnants shown here are the results of the death of a _____-mass star
This remnant could still undergo a type-1 _____________ if it exists in a binary pair
Only massive stars undergo _______ supernovas
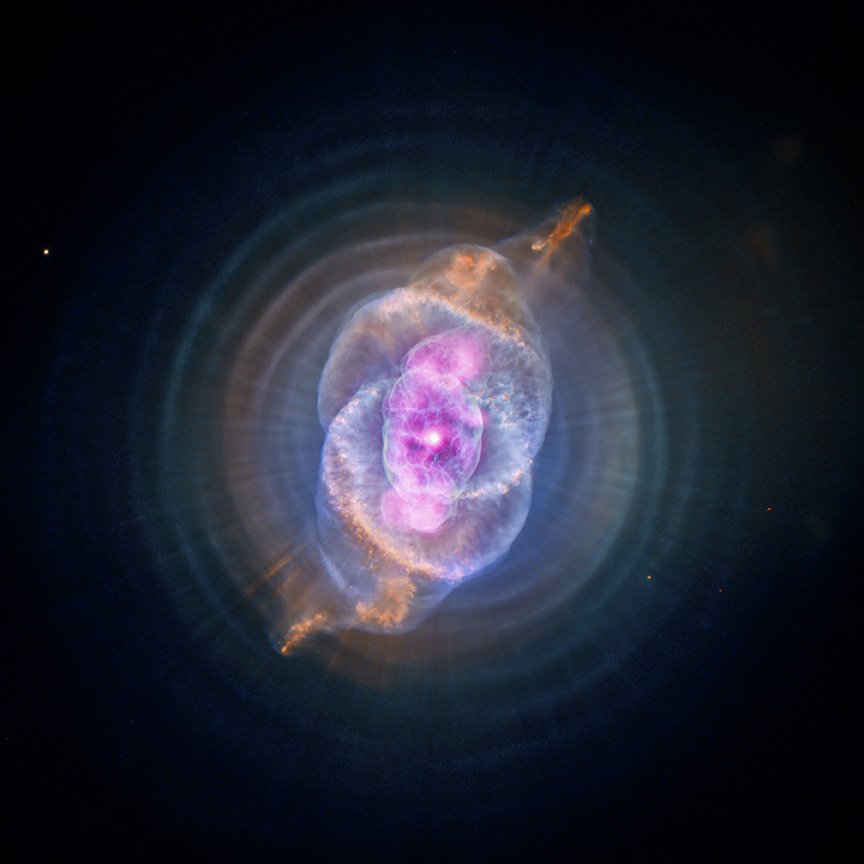

Supernova
Type-2
True or False: Elements heavier than iron can only be created upon the death of a massive star
BONUS: The explosive shockwave created upon the death of a massive star is known as a _____________________
True
Supernova
In this layer of the sun's interior, gamma rays bounce around and lengthen out, becoming less energetic as they transition to the outer layers of the star.
Radiation/radiative zone
_______________ are areas on the surface of the sun that appear dark because of their relatively lower temperatures.
The ___________ ___________ is the constant stream of charged particles that is emitted by the sun.
Sunspots
Solar wind
____-class stars are small, dim, and red
____-class stars are medium sized and yellow
____-class stars are large, blue, and bright
M
G
O
________ _________ stars are those that are still fusing H into He, and are therefore still alive
_________ ________ are stars that are no longer fusing hydrogen into helium; radiation pressure has broken down in the core and the outer layers of the star are now expanding and cooling
__________ __________ are the extremely dense corpses of low mass stars, that can no longer undergo nuclear fusion
Main sequence
Red giants
White dwarfs
A list of apparent magnitudes is given below. Which of the following stars would be brightest?
Star A: -3.5
Star B: 1.0
Star C: 15.0
Star A
In this layer of the sun's interior, heat is transferred from inner layers of the star to outer layers by the following process:
Warm material near the core of the star heats, becoming less dense and rising. This material cools as it transfers energy to outer layers of the star, and sinks back down

Convective/convection zone
The ______________ of the sun radiates most strongly in the UV portion of the EM spectrum. The ______________ radiates most strongly in the X-ray portion of the EM spectrum
BONUS: What may be causing these outer layers to be higher in temperature than more interior layers?
Chromosphere
Corona
BONUS: Electromagnetic field interactions
The color of a star is mainly determined by a star's temperature
_________ stars have the highest temperatures and shortest lifespans
________ stars have the lowest temperatures and longest lifespans
BONUS: Our sun has a lifespan of about 10 _____________ years
Blue
Red
BONUS: 10 billion
1. Dense areas of molecular cloud collapse due to gravitational disturbance (supernova shockwave)
2. As dense areas collapse and heat up, they eventually reach nuclear fusion temps in core (15 million K)
Sunspots typically occur in an _______-year cycle
BONUS: True or false -- the maximum of the sunspot cycle (more sunspots) typically corresponds with calm solar weather
11-year cycle
BONUS: False
Draw a diagram of the sun with all layers labeled. You should have six layers.

BONUS: What causes the different colors of the northern lights?
Charged particles from the solar wind excite electrons in atmospheric gases, causing them to emit light
BONUS: Different gases (with different electron configurations) will emit different wavelengths of light
Utilizing the HR diagram shown below, describe the type of star that would be found at the following points:
A: 3000 K, 0.0001 luminosity
B: 10,000 K, 0.01 luminosity
C: 3500 K, 10,000 luminosity
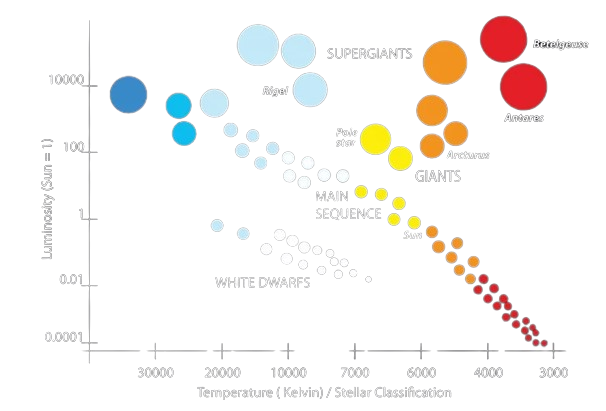
A: Main sequence, red dwarf
B: White dwarf
C: Red giant
List what products will be formed upon the death of each type of star:
A -- low mass star
B -- high mass star
C -- very high mass star
A: white dwarf and planetary nebula
B: Neutron star
C: Neutron star which collapses into a black hole
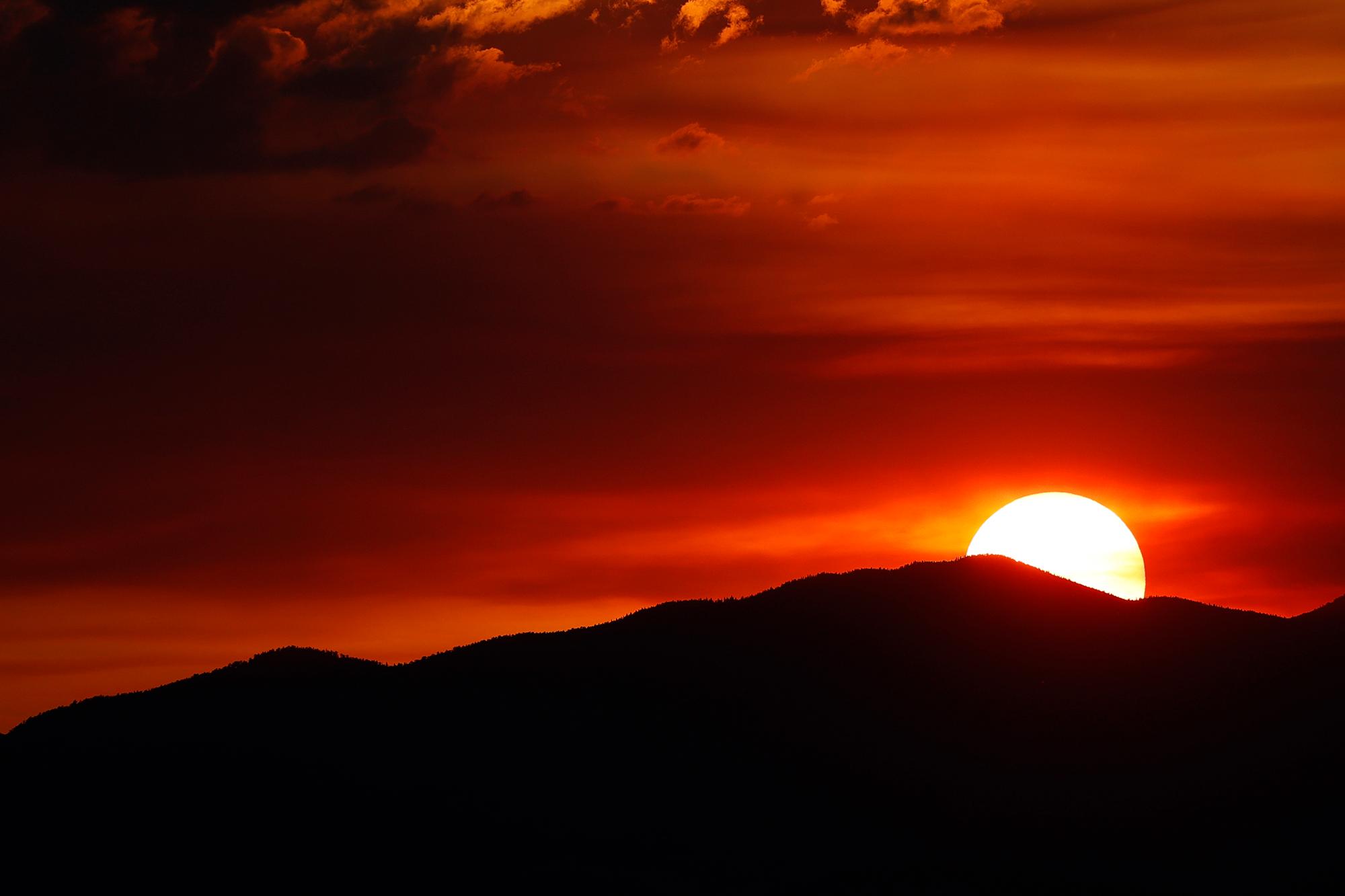
Explain why, during high noon, the sun appears yellow, whereas during sunsets or smoky days it appears red.
The sun has more atmosphere to travel through during sunset, meaning even yellow light is scattered (leaving only red). Smoky days also enhance the scattering effect.