When energy is released from a chemical reaction, is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic.
NOTE:
Exo- (prefix): outside, outer, external
Endo- (prefix): within, inner, absorbing
What is the name of the phase change where a solid turns into a liquid?
Melting.
What does “c” stand for? What are units of c?
C = specific heat. Units: cal/g℃ or J/g℃
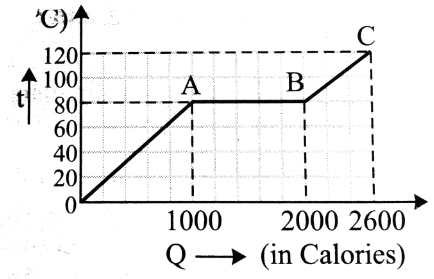
If 1500 Calories are added into a system, what will happen to the substance?
Phase change.
What is the vocab word that represents the energy needed to be overcome in order for reactants to become products?
Activation energy.
What two things happen to particles in an endothermic reaction?
Speed up and spread out.
Identify an exothermic phase change.
Freezing, condensing, deposition.
What does it mean if something has a low specific heat? How will it heat up compared to something with a high specific heat?
Low specific heat means it takes a low amount of energy to heat a substance up. Substances with low specific heats can be heated more quickly than substances with high specific heats.
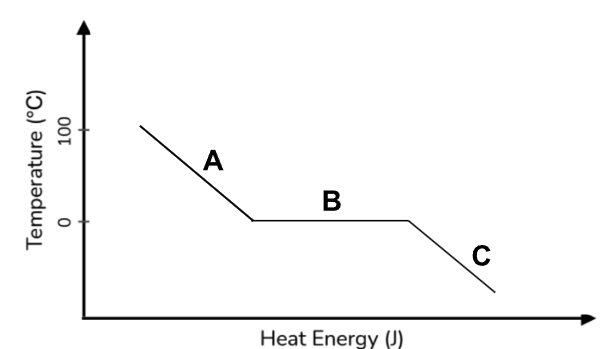
In the cooling curve for water, what is happening at Part A? Make sure you identify the state(s) of matter.
Liquid water is cooled from 100 ℃ to 0℃.
In a CER, what information goes in the “Reasoning” section?
Reasoning explains why the evidence supports the claim
In a chemical reaction, 245 kJ of energy is absorbed to break the reactants. 134 kJ of energy is released when the products form. Will the reaction surroundings feel hot or cold?
Cold.
What happens to the temperature of a substance undergoing a phase change?
Temperature does NOT change during phase changes.
How does a calorimeter work?
Food is burned underneath water and the energy from the food transfers into the water, causing the temperature to heat up.

In the cooling curve for water, what is happening to the particles at Point B? Make sure you identify the state(s) of matter(s)
Liquid water is freezing into solid water (ice). Particles are moving closer together. Temperature does NOT change.
After studying chemistry for a few weeks, you are finding yourself curious about the world around you. You notice that you sleep better on days you play sports. Write a hypothesis you can test in an experiment.
"IF"... "THEN" ...
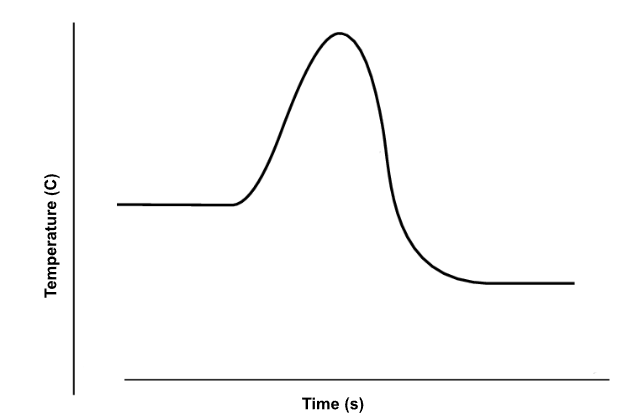
Is the enthalpy change (ΔH) positive or negative? Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Negative, exothermic.
If you had a sample of ice at -5℃ and want to boil it, what steps will the particles go through?
Heat ice from -5℃ to 0℃.
Melt the ice at 0℃.
Heat the water to 100
Boil the water. (Must have 4 steps for full credit).
How much energy is absorbed by a calorimeter if 1440 mL of water heats up from 33.4℃ to 56.3℃? Recall the specific heat of water is 4.18J/g℃ or 1 cal/g℃. Report your energy in Calories.
q=32,978cal → 32.9 Cal
On your whiteboard, label the reactants, products, activation energy, and enthalpy
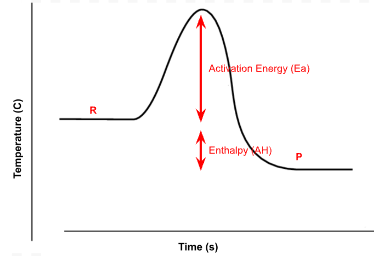
Plate tectonics (volcanoes, earthquakes, etc.) are caused by the movement of Earth’s crust. Rocks warmed by the Earth’s core rise to the top as cooler rocks sink to the bottom. What kind of energy transfer is occurring here?
Convection.
When water vaporizes into steam, what happens to the energy in the system? Is this an endothermic or exothermic phase change?
Energy goes into the system, endothermic.
From the lab, we determined that substances like lauric acid undergo phase changes at a constant rate. What evidence did we find from the lab that supported this?
The slope of the graph flattened out during phase changes, showing the temperature does not change while a substance undergoes a phase change.
What is the energy density of 11.5 grams of crackers if they cause a calorimeter with 1890 mL of water to heat up by 33℃? Recall the specific heat of water is 4.18J/g℃ or 1 cal/g℃. Report your answer in Cal/g.
q = 62,370 cal → 62.37 Cal → 5.4 Cal/g
Draw out a graph of gaseous ethanol cooling from 105℃ to liquid ethanol at 13℃. The condensation/vaporization point of ethanol 73℃ and the melting/freezing point is -113℃
Ms. Murtha will check your answers.
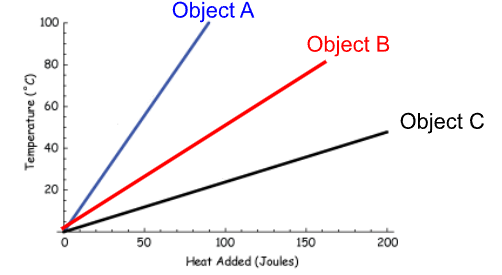
Which substance has the higher specific heat?
Object C.