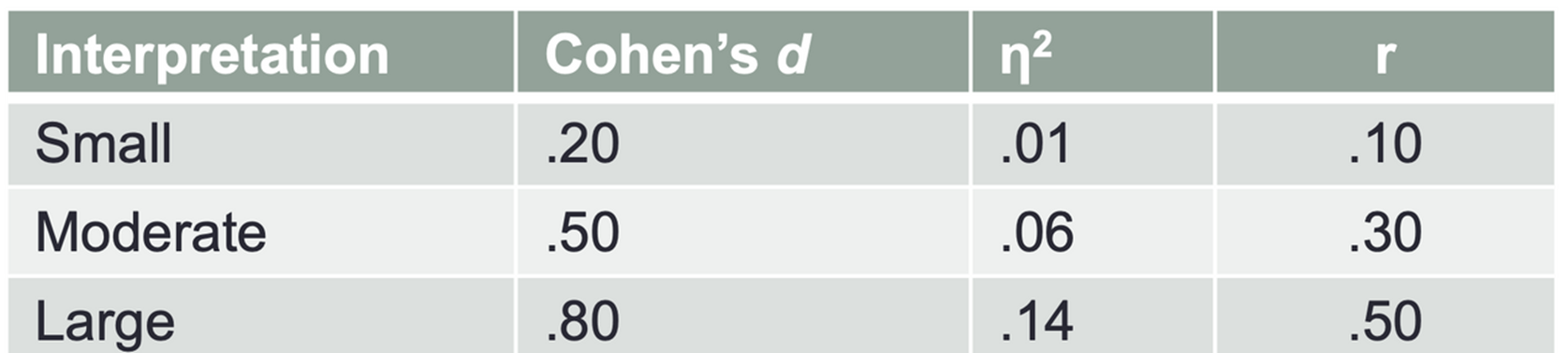
Which of the following is not a recommended strategy for minimizing researcher bias in an experimental study?
A. Implementing double-blind procedures
B. Standardizing instructions and testing environments across participants
C. Selecting participants who are especially likely to engage with the intervention
D. Providing training to data collectors to ensure consistent coding and scoring
C. Selecting participants who are especially likely to engage with the intervention
In a study comparing two math curricula, students in the experimental group receive more one-on-one time with the teacher than those in the control group.
Which type of validity is most at risk here?
Internal validity
Name three measures of central tendency.
Mean, Median, and Mode.
True or False
Fewer subjects are needed in a within subject design compared to a between subject design?
True
True or False
An experiment can never be "overpowered" (i.e. have too big of a sample)
False
What is the key distinction between true experimental designs and quasi-experimental designs?
True experimental designs use Random Assignment. In quasi-experimental designs, participants are assigned to groups based on pre-existing characteristics or non-random criteria.
When the results obtained from an unrepresentative sample cannot generalize to a population, it can be said that the study has poor ______________________
External Validity
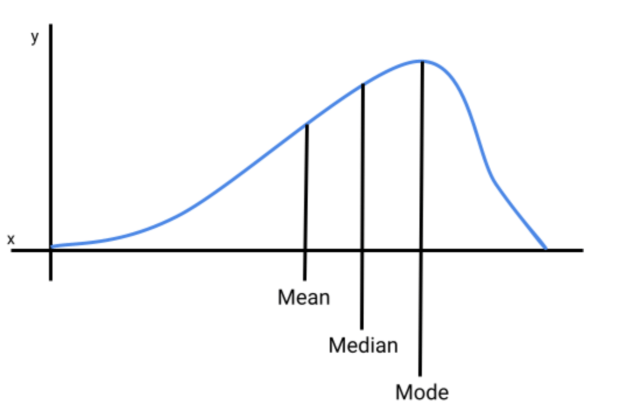
What does a negatively skewed distribution look like? (You may draw a picture)
The data's tail extends towards the lower values, with most data points clustered towards the higher values, resulting in the mean being less than the median.
A speech-language researcher wants to examine whether children produce more correct /s/ sounds when given visual feedback versus no feedback. All 25 children complete the same articulation task twice—once with visual feedback and once without. The order of the conditions is counterbalanced.
Is this a between or within-subject design?
Within-subjects design
(Each participant experiences both conditions.)
What type of error occurs when you reject the null hypothesis, but you shouldn't have rejected it.
Type I error
Imagine you are designing an experiment and suspect experimenter bias might occur. Propose a modification that could address this concern while preserving participant engagement.
Use automated/scripted/standardized instructions/protocol to minimize variability in how participants are treated.
Identify the threat to Validity.
A team of researchers is conducting a 6-week experimental study to evaluate the effects of a phonological awareness app on kindergarteners’ early reading skills. Participants are randomly assigned to either the experimental group (who use the app for 20 minutes daily) or the control group (who receive regular instruction). Halfway through the study, the school introduces a new district-wide literacy initiative that includes daily read-aloud sessions and teacher-led phonics instruction for all students. At post-test, both groups show significant improvement, and the experimental group performs slightly better.
History Threat
Calculate the mean, median, mode, and range for the following data set.
4, 8, 12, 4, 7, 9, 10, 12
Mean: (4 + 8 + 12 + 4 + 7 + 9 + 10 + 12) / 8 = 8.25
Median: Arrange the numbers: 4, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 12 → Middle values: (8 + 9) / 2 = 8.5
Mode: Most frequent = 4 and 12 (bimodal)
Range: 12 - 4 = 8
A researcher is testing whether there is a significant difference in reading comprehension scores between two groups of children: one group that received a specialized reading intervention (Group A) and another group that did not receive the intervention (Group B). The scores from both groups are analyzed.
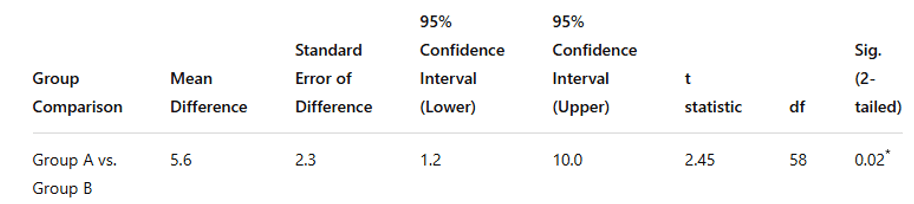
What type of statistical test did they use to analyze the data?
Is there a significant difference in reading comprehension scores between Group A and Group B? How do you know?
A t-test was used
Yes, there a significant difference in reading comprehension scores between Group A and Group B.
We know this because the p value of the t-statistic is below .05.
In a new study, researchers are testing whether a mindfulness intervention can reduce anxiety in teenagers with social anxiety disorder. They are concerned with Type II error because they believe the intervention may have a modest, but clinically significant effect. What can they do when they run the experiment to reduce the risk of Type II error?
Increase the sample size – Larger sample sizes increase the statistical power of the test, making it more likely to detect a true effect if one exists.
Imagine a scenario where the researcher's knowledge of participant conditions affects data collection. Describe a protocol change that could mitigate this effect.
Blinding - Introduce blind assessment procedures so that data collectors remain unaware of group assignments.
Identify two threats to validity in the following scenario and what you would do to mitigate the treats.
Researchers select the lowest-performing students on a phonological awareness test to participate in a new program. Students are pre-tested, complete a 6-week intervention, and are then post-tested using the same assessment. After the program, the group shows significant improvement.
Statistical Regression to the Mean – Because students were selected based on extreme low scores, some improvement may occur naturally due to regression.
Maturation - Students may be demonstrating natural growth in their skills.
Pretesting – Familiarity with the test format could contribute to higher post-test scores, independent of the intervention.
How to mitigate: A control group, random assignment, alternative forms testing
You are a clinician evaluating children's scores on a language proficiency test. The cutoff for qualifying children is 1.5 standard deviations below the mean. You know that the standard deviation for this test is 8 points, and the national average score is 90. You observe the following scores for the children:
Max – 72
Lucy – 78
Omar – 84
Sara – 94
Tom – 102
Based on your criteria of 1.5 standard deviations below the mean, which children qualify (2 points - select all that apply)?
Only Max Qualifies.
Determine the cutoff score for qualifying:
The mean score is 90, and the cutoff is 1.5 standard deviations below the mean.
1.5 standard deviations below the mean = 90 - (1.5 * 8) = 90 - 12 = 78.
Compare each child's score to the cutoff of 78:
Max – 72 → Qualifies (score is below 78)
Lucy – 78 → Does not qualify (score is exactly 78, not below)
Omar – 84 → Does not qualify (score is above 78)
Sara – 94 → Does not qualify (score is above 78)
Tom – 102 → Does not qualify (score is above 78)
Jasmine conducts a study to find out whether vocabulary learning in children with language delays is affected by the way words are introduced (through direct instruction or casual storybook reading), the number of children in a session (working alone or in a small group), and the amount of background noise during the session (quiet, moderate noise, or loud noise). After the session, she measures how many new words each child can correctly define and use in a sentence.
Identify the IV(s), the level of the IV(s), and describe the factorial design.
Independent Variable 1: Type of instruction (2 levels: explicit instruction, incidental exposure)
Independent Variable 2: Group size (2 levels: individual, small group)
Independent Variable 3: Background noise level (3 levels: quiet, moderate classroom noise, loud background noise)
DV: Vocabulary learning outcomes (e.g., number of correctly defined and used new words)
It’s a 2 × 2 × 3 factorial design
Lowering the alpha level to 0.01 rather than 0.05 is a strategy to reduce the chance of which type of error?
Type I error
What type of experimenter bias is present in the following scenario.
Researchers are studying whether a new social skills program improves peer interactions in children with autism. Observers, who know which children received the intervention, rate behaviors like eye contact and sharing.
When children in the treatment group make brief eye contact, observers give high scores. But when children in the control group show the same behavior, it's often ignored or scored lower. This subtle scoring difference supports the researchers' expectations.
Recording/Scoring Bias
will also accept expectation bias
A university wants to evaluate the impact of a financial literacy course on students’ budgeting skills. They offer the course as an elective and compare students who enroll in the course to those who do not. At the end of the semester, students in the course demonstrate significantly better budgeting skills, leading the researchers to conclude that the course was effective.
- Which kind of bias is present in the above scenario?
- What could the experimenter do to minimize this bias
Differential Subject Selection
Students who voluntarily enrolled in the financial literacy course may have already been more motivated or financially responsible than those who did not enroll. This self-selection bias makes it difficult to determine whether the course itself caused improvements.
Randomly assigning students to take the financial literacy course or a different elective would help control for pre-existing differences between groups. If randomization is not possible, researchers could match students from both groups on factors like prior financial knowledge and motivation to ensure comparability.
A researcher is studying how background noise and session format affect children’s word retention. She runs her analysis and gets the following results.
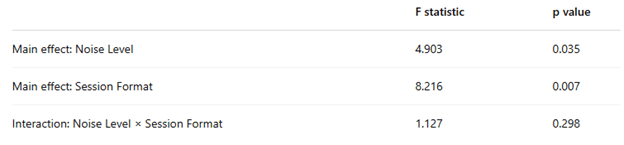
a. What type of statistical analysis did she run?
b. Was there a significant main effect of Noise Level on word retention?
c. Was there a significant main effect of Session Format on word retention?
d. Was there a significant interaction effect on word retention?
a) Factorial ANOVA
b) Yes (since p = 0.035, which is less than 0.05)
c) Yes (since p = 0.007, which is less than 0.05)
d) No (since p = 0.298, which is greater than 0.05)
A researcher wants to evaluate the effects of a new phonological awareness program implemented in one school district. She compares the performance of two groups of students on a blending task:
Group A consists of 1st graders from School X, who completed the new program.
Group B consists of 2nd graders from a nearby district who did not receive the program.
The researcher finds that Group B scores significantly higher and concludes that the program was not effective.
Describe the design of the study (This is a two part answer)
Describe at the main threat to validity.
Quasi-experimental, between-subjects design
(Participants were not randomly assigned; they come from different naturally existing groups.)
Differential Subject Selection
A researcher runs a study with a large sample and finds a statistically significant effect (p < .01), and the effect size is d = 0.10. What does this tell us about the meaningfulness of the result?
The result is statistically significant but may not be practically meaningful due to the small effect size.