A classification for a molecule that has an unequal distribution of charges in it.
List 3 ways to determine if a molecule meets this classification?
What is polarity?
1. Symmetry
2. Electronegativity difference
3. Lone pairs.
What type of IMF force is most relevant in acetone? Why?????????
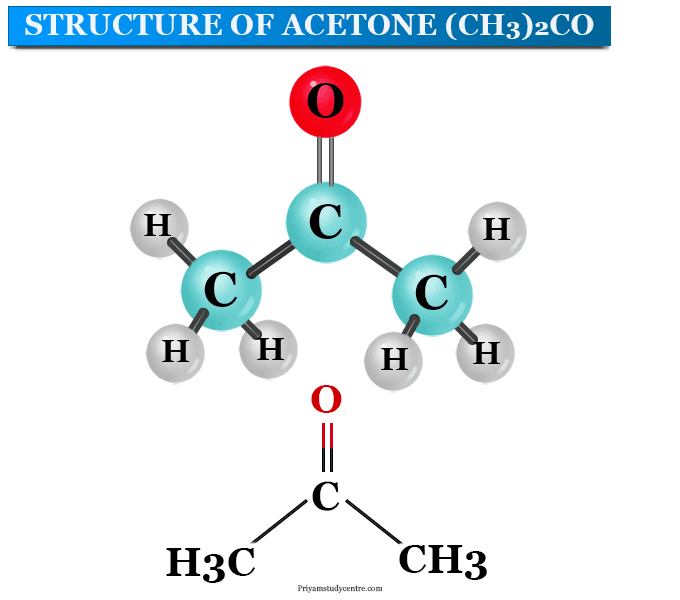
Dipole - dipole, it is polar but there are no hydrogen bonds, so it must be dipole dipole
CO2 has which name?
Which type of binary compound is this?
Covalent
Carbon monoxide
A compound that contains multiple atoms but is an ion.
Is this compound electrically neutral?? Why or why not?
What is a polyatomic ion?
Elements from this part of the periodic table will lose electrons when forming ionic bonds.
Why do they do this?
What are metals?
What are cations?
Both are True.
What is an ionic bond?
How many total hydrogen bonds are on this molecule of Urea?

What are 4 hydrogen bonds.
Is this ionic or covalent?
How about Magnesium Chloride?
Both are Ionic
Magnesium Oxide
MgO
Magnesium Chloride
MgCl2
True or false - Transition metals can have more than one possible oxidation number.
True,
Transition metals are special because they can lose multiple numbers of electrons.
Consider the two questions and ID which atom is more electronegative? Explain why WITHOUT USING TRENDS. Talk about shells and NUCLEAR charge
1. Nitrogen or Oxygen?
2. What about Fluorine or Bromine?
Consider the two questions and ID which atom is more electronegative? Explain why WITHOUT USING TRENDS.
1. Nitrogen or Oxygen?
Oxygen, it has a greater number of protons in the nucleus pulling in the electrons closer.
2. What about Fluorine or Bromine?
Fluorine, it has less shells than Bromine making the electrons closer to the nucleus and more attracted to the nucleus.
This is a general term to describe the forces that keep molecules together in liquids and solids and can explain properties like evaporation rates and surface tension on a penny?
What are the main three of these forces we studied in lab in order of increasing strength?
What are intermolecular forces?
London Dispersion Forces,
Dipole dipole attractions
Hydrogen - bonding.
Compounds with hydrogen bonding like water will have _________ rates of evaporation than dipole-dipole binding compounds and dispersion force bonding compounds.
Explain your answer?
"Slower"
Explanation: this is because the EN difference within these molecules and the Hydrogen bonding between these molecules is strongest causing them to bind more and evaporate slowly compared to other IMF compounds.
C2O2 has which name?
Is this compound, ionic or molecular?
Dicarbon Dioxide
this is molecular, which means we must use prefixes
This is the difference between Sulfate and Sulfite.
Sulfate would have more oxygens than Sulfite
SO32- "Sulfite"
SO42- "Sulfate"
What is the oxidation number of the following elements? Explain how you know.
Sodium
Iron (II)
Chloride
Oxygen
What is the oxidation number of the following elements? Explain how you know.
Sodium
+1 for elements in group one after losing 1 electron to achieve an octet in its lower shell
Iron (II)
+2 for group this state of iron ion being a transition metal, it can have different number of oxidation states given by roman numerals.
Chloride
-1 since it would add an electron to get an oxtet being in group 17 (one electron away from a noble gas configuration)
Oxygen
-2 since it would add two electrons to get an oxtet being in group 16 (two electron away from a noble gas configuration)
What type of intramolecular bond would form between Hydrogen and Bromine? Why?
A. Ionic,
B. Polar covalent
C. Nonpolar covalent
D. London dispersion Force
B. Polar covalent
The difference in electronegativities here is significant creating a polarity but it is not negligible creating polarity (An unequal sharing of electrons)
True or false: There are more than 1 hydrogens capable of hydrogen bonding on both of these molecules. Explain your answer

False, there is not one hydrogen in either of these atoms that can form a hydrogen bond.
None of the hydrogens are attached to an N, O, or F that has lone pairs.
These molecules would stick via weaker dipole - dipole and LDF because it is polar and also all molecules have LDF's
How would you name the following compound? Why did you choose the particular naming scheme you used?
Al2O3
Answer: aluminum oxide.
For ionic compounds, you just say the metal ion followed by the nonmetal ion with an "-ide" at the end. There are no prefixes to indicate number of ions. This is handled by the oxidation number for ions.
If there were a polyatomic ion, you would just say the name of each without any changes.
Al2(SO4)3 is just aluminum sulphate.
Sodium Sulfate would have which formula?
Explain.
Na2(SO4)
Ions with oxidation number charge.
Na+1. (SO4)2-
Using the cross over method gives the final formula
Na2(SO4)
* What types of inter- and intramolecular forces have we studied so far this year (at least name the 5 main ones)
Inter - between molecules
1. Dipole-dipole
2. Hydrogen bonding
3. London Dispersion Forces
Bonus: Ion-Dipole Attraction
Intra - means within molecules
1. Covalent Bonding
2. Ionic Bonding
Bonus: Metallic bonding.
Properly classify which molecules are polar and why?
H-Cl
H2O
N2
CO2
NH3
CH4

H-Cl (Polar - big EN difference between atoms)
H2O (Polar - big EN difference and oxygen has 2 lone pairs)
N2 (NOT - perfectly symmetrical , EN difference = 0, equal lone pairs )
CO2 (NOT - perfectly symmetrical , dipoles cancel, no net dipole, equal lone pairs on Oxygen)
NH3 (Polar - big EN difference and Nitrogen has one lone pairs)
CH4 (NOT - perfectly symmetrical in electrons and protons , dipoles cancel, no net dipole, low EN difference in -C-H)
Determine which intermolecular force (IMF) is the predominant IMF or which is the only IMF. Please explain why?
H-Cl
H2O
N2
CO2
NH3
CH4

H-Cl (DIP DIP - Polar - big EN difference between atoms)
H2O (H-bonding - Polar - big EN difference with H and oxygen has 2 lone pairs)
N2 (LDF - NOT polar- perfectly symmetrical , EN difference = 0, equal lone pairs )
CO2 (LDF - NOT polar - perfectly symmetrical , dipoles cancel, no net dipole, equal lone pairs on Oxygen)
NH3 (H-bonding - Polar - big EN difference of H and Nitrogen has one lone pairs)
CH4 (LDF - NOT polar - perfectly symmetrical in electrons and protons , dipoles cancel, no net dipole, low EN difference in -C-H
Dinitrogen pentoxide
Has which formula? Is this molecular or ionic?
Bonus (300 pts) Draw this molecule correctly with all lone pairs and octets on every atom.
N2O5
Type of compound: molecular.
What is the correct name for the following formula?
Mg(SO3)
Magnesium sulfite
You just say the name of the first ion and then the second ion without any "-ide" suffix when the second ion is a polyatomic ion.
The atom with the most number of valence electrons but the least number of shells?
YOU MUST EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER.
What is Neon?
