What vertebral level does the central ray enter for the PA projection of the chest?
T7
What SID is used for abdominal radiography?
40-48"
The humeral epicondyles should be placed _________ to the IR for the AP projection of the humerus.
parallel
The AP Axial projection of the clavicle is performed to demonstrate the clavicle in a more _____________ position.
horizontal / flat
The sesamoid bones of the foot are located at which digit?
First digit
The ______ pelvis is narrow and more heart-shaped.
male
Ribs that attach directly to the sternum are called?
True ribs
What is the minimum number of posterior ribs that must be seen above the diaphragm on a PA chest radiograph?
10 posterior ribs
Where does the central ray enter for the AP Supine Abdomen (KUB)?
MSP, at the level of the iliac crest.
Where does the central ray enter for the PA projection of digits 2-5?
The PIP joint of interest
Where does the central ray enter for the AP projections of the shoulder (internal, external, and neutral rotation)?
1" below the coracoid process
How much and in what direction is the central ray angled for the AP projection of the foot?
10 degrees cephalic (towards the heel)
The hip joint is formed by the _________ of the femur and the __________ of the pelvis.
head of the femur & acetabulum of the pelvis
The articulation between the tubercle of a rib and the transverse process of a vertebra is called a?
costotransverse joint
Why is a left lateral chest x-ray performed instead of a right lateral?
To reduce the magnification of the heart.
The AP erect abdomen must demonstrate what anatomy that is not required on the KUB?
The diaphragm.
Where does the central ray enter for the PA projection of the hand?
3rd MCP joint
The AP projetion of the shoulder with internal rotation demonstrates which tubercle in profile on the medial aspect of the humerus?
lesser tubercle
How much should the knee be flexed for the lateral projection of the patella?
The __________ trochanters should be seen in profile in the AP projection of the pelvis.
greater
Which image performed in a rib series is the most important?
PA Chest
(Rules out pneumothorax / hemothorax)
Angled to be perpendicular to the sternum.
What is the minimum amount of time a patient should be upright before performing the AP erect projection of the abdomen?
5 minutes (15-20 minutes is preferred)
How much obliquity is required for the PA and AP obliques of the wrist?
Take slow breaths (or normal breathing, to blur out ribs).
Which position of the ankle is demonstrated in the image below?
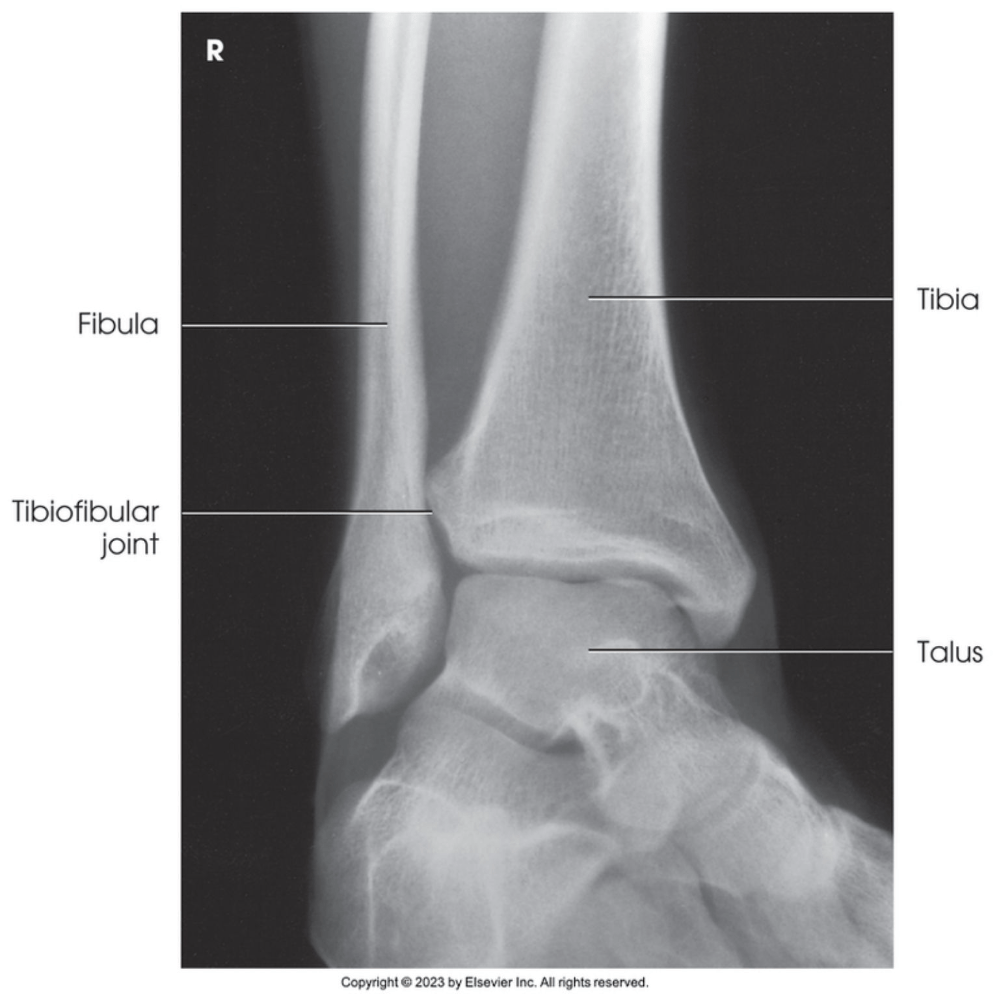
Medial oblique ankle (45 degree oblique)
The lesser trochanter should be in profile on which position of the hip?
Frog-leg lateral
What phase of respiration is used for imaging above the diaphragm ribs?
inspiration
The AP chest should be similar in appearance to a PA chest x-ray with a few exceptions. State one of the exceptions.
- Heart is magnified
- Fluid levels not demonstrated (XR beam isn’t horizontal)
- Limited inspiration when not erect
If the patient cannot stand for the AP erect abdomen, which position should be performed to demonstrate the same view?
Left Lateral Decubitus Abdomen
How should the hand be positioned for the lateral projection of the wrist?
Semisupinated 5 degrees
What is the advantage of shooting the clavicle in the PA position as opposed to the normal AP position?
PA results in less magnification of the clavicle due to reduced OID.
The top of the IR should be placed at what level when performing the proximal AP image of the femur?
Top of IR at the ASIS
Where does the central ray enter for the AP projection of the pelvis?
2" below ASIS OR 2" above pubic symphysis.
When evaluating the AP above the diaphragm rib image, what is the minimum number of posterior ribs that must be seen above the diaphragm?
nine
Which projection of the chest is performed to demonstrate the area behind the clavicles?
AP Lordotic Chest
Which marker should be placed on the IR when performing a left lateral decubitus projection of the abdomen?
Right marker (placed on elevated side)
Why is the forearm performed as an AP projection as opposed to a PA projection?
To avoid radial crossover.
How should the arm be positioned for the lateral projection of the scapula if the acromion and coracoid processes are of interest?
Arm down by side and flexed behind the back.
What error has occurred if the femoral condyles are not superimposed and the fibular head is "popping out" from behind the tibia on a lateral knee?
over-rotation
If the lesser trochanter is seen on the medial aspect of the femur on the AP projection of the hip, what error has occurred?
The foot/leg is not medially rotated.
What SID is used for the RAO projection of the sternum? Why?
30" SID is used to blur the ribs.
If fluid is suspected in the left lung, which decubitus position of the chest should be performed?
LLD (Left Lateral Decubitus)
(Fluid side should always be down)
What positions/projections are included in an Acute Abdominal Series?
- KUB
- AP Erect Abdomen
- PA Chest
A fracture of the fifth metacarpal neck is termed?
Boxer's Fracture
What SID is used for the bilateral projection of the AC joints?
72" SID
A _________ fracture is an avulsion fracture of the fifth metatarsal.
Jones fracture
When centering for the AP projection of the hip, the central ray should enter ____-____ inches medial and ____-_____ inches distal to the ______.
1-2" medial and 3-4" distal to the ASIS
Where does the central ray enter for the AP bilateral projection of the lower ribs (below the diaphragm ribs)?
MSP, midway between xiphoid process and lower rib margin.
When performing posterior obliques of the chest (RPO & LPO) which side is demonstrated?
The dependent (down) side.
What repeatable error is demonstrated in the KUB image below?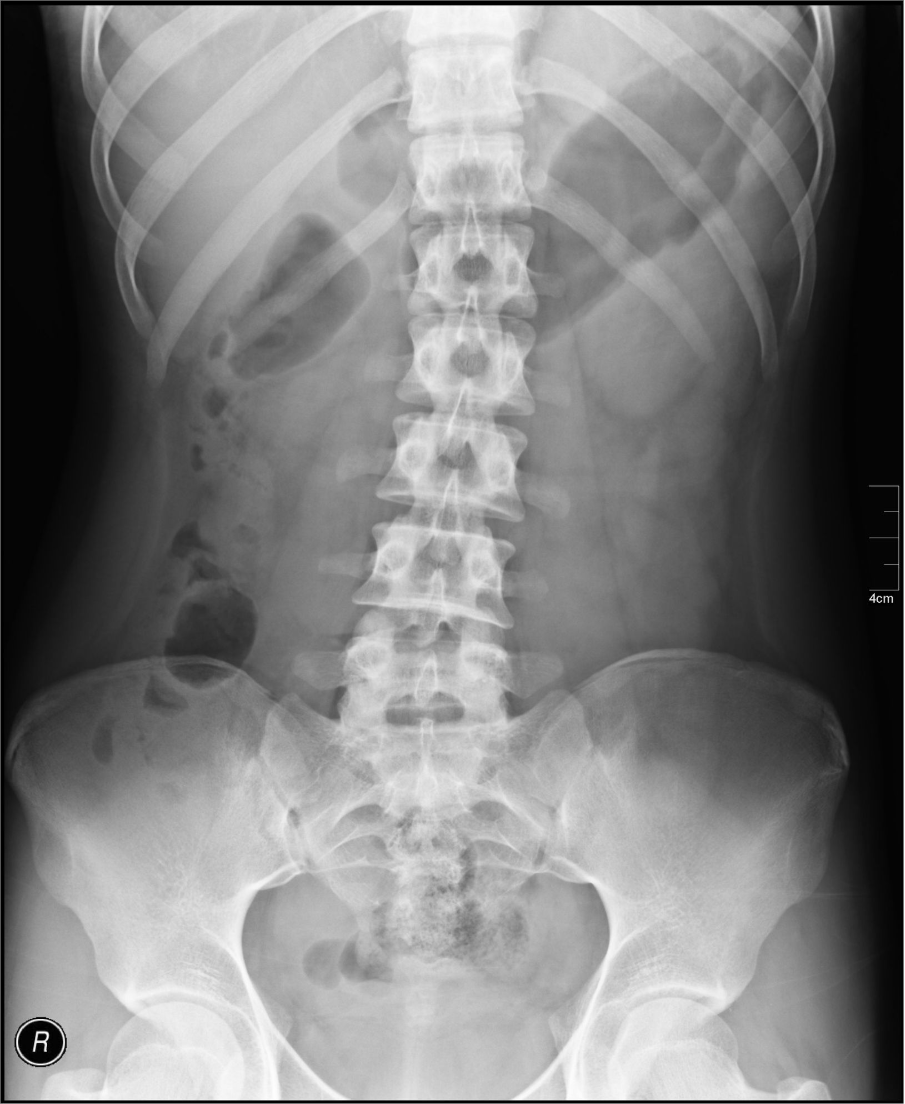
The pubic symphysis is clipped.
Which oblique projection of the wrist is best for demonstrating the lateral carpal bones?
PA oblique
If the head of the humerus is seen under the acromion process on the lateral projection of the scapula, what type of dislocation is seen?
posterior dislocation
How much and in what direction is the central ray angled for the plantodorsal axial projection of the calcaneus?
40 degrees cephalic
What projection/method is useful for diagnosing fractures of the acetabulum?
Judet Method
When performing the RAO position of the sternum, the patient must be rotated _______ degrees into an RAO. This will demonstrate the sternum projected over the _____________.
15-20 degrees.
Sternum projected over the heart shadow.
What range of obliquity is required for the RAO projection of the chest?
45-60 degrees
Rotation is present in the image below. Which side is the patient rotated towards?
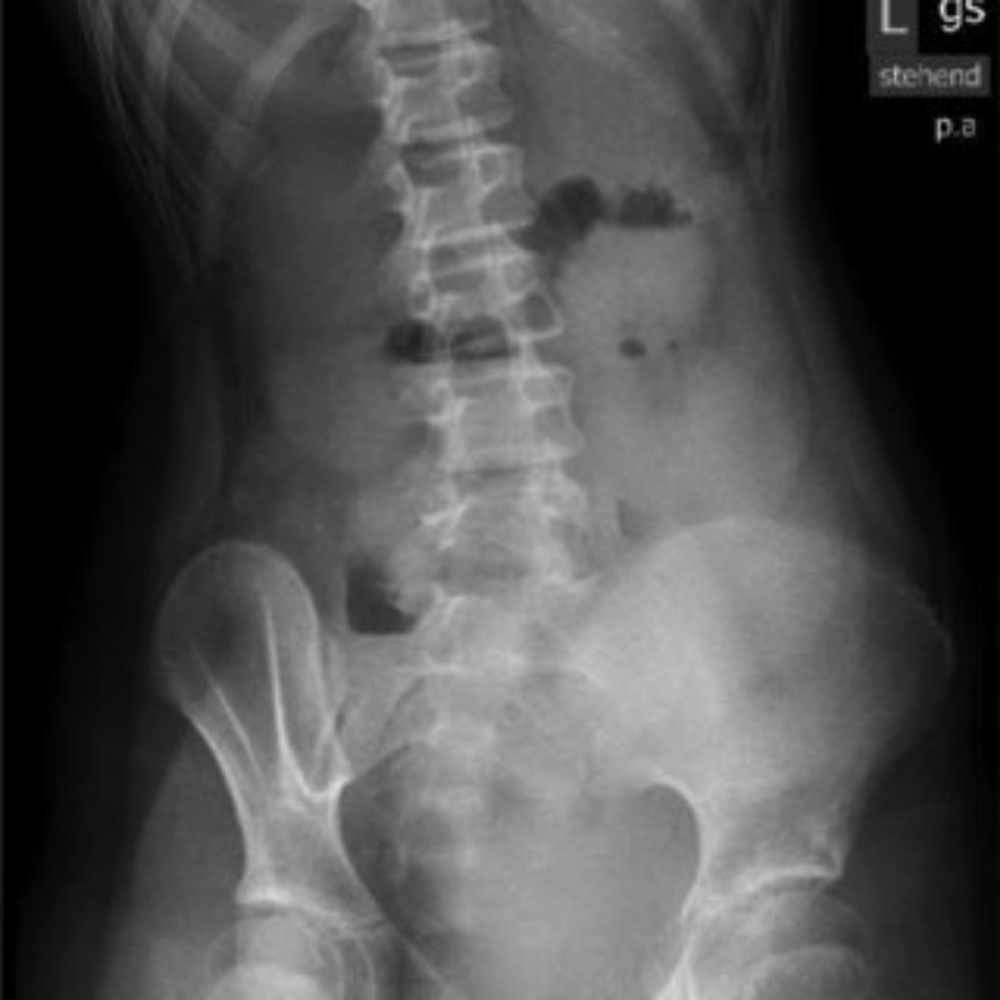
The patient is rotated towards their right side.
Which projection of the elbow demonstrates the coronoid process in profile?
Medial/internal oblique
The Neer Method requires the same positioning as the Scapular Y projection, but the CR must be positioned differently. How is the central ray positioned for the Neer Method?
Which projection/position of the foot demonstrates the structural status of the longitudinal arch?
Lateral Weight-bearing foot
If a patient has a bilateral hip injury, which projection should be performed to demonstrate a lateral view of the hip?
Axiolateral Inferosuperior
(Clements-Nakayama Method)
If a patient has a suspected injury to the left SC joint area, which oblique should be performed?
LAO
(Anterior obliques are performed to minimize OID. The side of interest, or injured side, should be the dependent/down side.)
If the patient is unable to stand for the AP lordotic chest x-ray, how should the central ray be positioned?
Angle the CR 15-20 degrees cephalic.
Which projection of the abdomen is best for demonstrating soft tissue masses, umbilical hernias, and potential aortic aneurysm as well as localization of foreign bodies?
Lateral Abdomen
State the two reasons that the lateral elbow must be performed with 90 degree flexion.
- To place the olecranon process in profile.
- To relax the fat pads.
Which projection of the shoulder demonstrates an open glenohumeral joint space?
AP Oblique Grashey Method
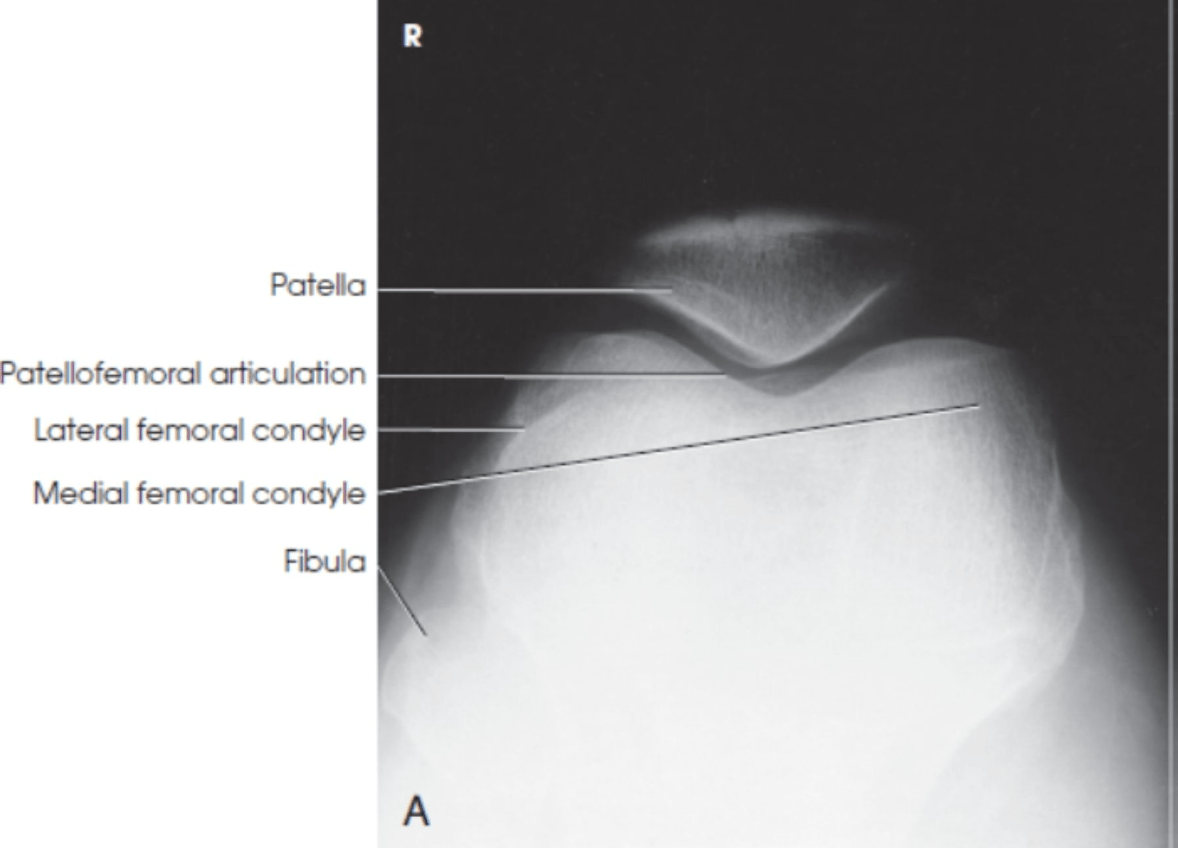
The Settegast tangential patella is performed to demonstrate what joint space?
patellofemoral joint space
How much and in what direction is the central ray angled for the Superoinferior Axial Inlet - Bridgeman Method?
40 degrees caudal
If a patient has right anterior rib pain near the level of the clavicle, which two positions of the ribs should be performed?
PA & LAO
(Remember: LAO and RPO will both demonstrate the RIGHT ribs properly elongated. We do the LAO if there is right anterior pain because this places the anterior aspect closest to the IR and elongates the right ribs.)