Identify two anatomical landmarks visible on this radiograph: Maxillary Right Pre-molar PA, Mandibular Anterior PA.
Inverted Y
Genial tubercles
Identify any possible carious lesions present.
#5D, 31M
What is the stage and grade of the patient?
Stage II Localized III
Grade B
Identify restorative dental materials visible in this radiograph.
Composite, Porcelain fused to metal crown, Endo gutta percha, Endo posts (metal and fiber reinforced),
Are there any anomalies or variations from normal anatomy present in this case?
Pulpal stones (#18, 21 & 28)
Fused roots (#2, 15)
List pathological findings in the CIS
Internal resorption on #6
External resorption #19
Peiapical abscess #19 & 30
What type of bony wall defect is present in the CIS?
one-wall defect
two-wall defect
2, 3, 6, 30, 31
Is there evidence of previous endodontic treatment?
Yes.
#4, 29 & 30.
How might the anomalies impact the patient’s dental health?
Pulp stones: no symptoms
Fused roots: less periodontal attachment
What clinical findings would you expect to be associated with tooth #19 or #30?
Any of the following: Supuration, Fistula, Abscess, Mobility, Edematous, Bleeding, supra eruption.
What would be the first phase of treatment planning?
Treating the Endo Abscess
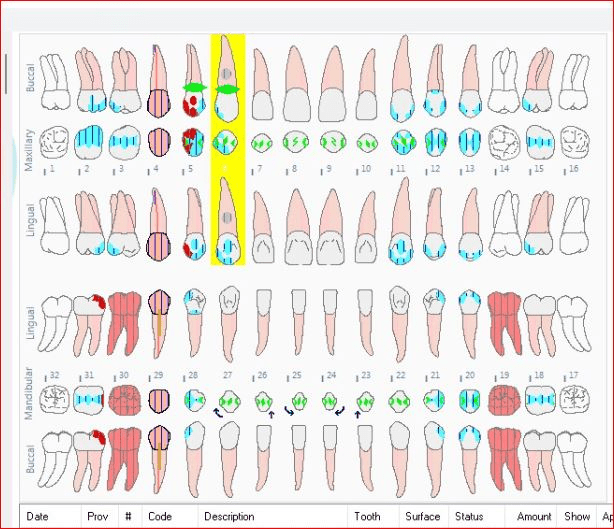
Dentition charting of Quad 1 and 4
Which condition could have caused the radiolucency on tooth #19?
Caries.
what are the radiographic indicators of a successful or failed endodontic treatment?
Successful: Root canal filling has no visible voids or gaps and is within 0.5 to 2mm of the radiographic apex
Failed: Vsible gaps or voids in the filling, Periapical radiolucencies