What am I looking at? Name these segments
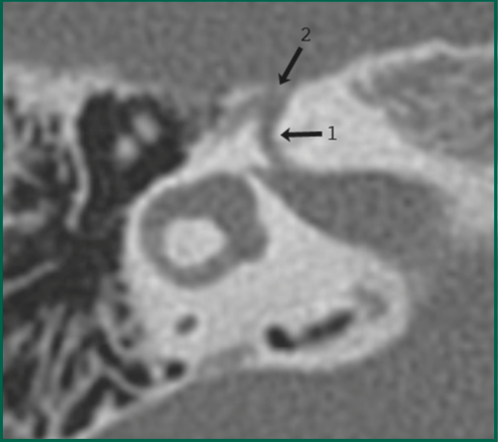
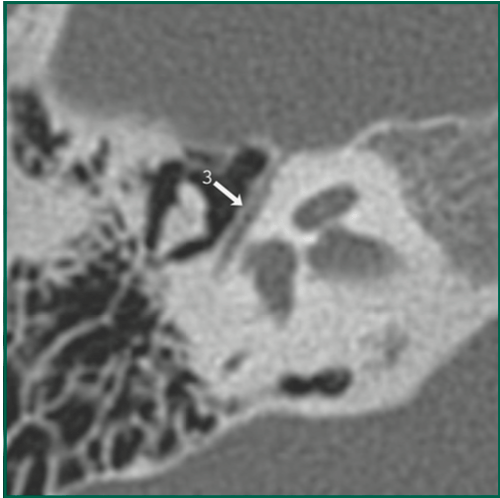
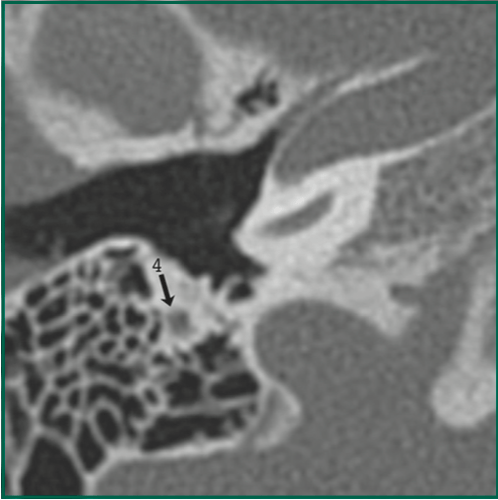
Facial nerve
(1) labyrinthine segment
(2) geniculate ganglion
(3) tympanic segment
(4) mastoid segment
60yM with hx of prior sinus surgery c/o clear, watery discharge from right nostril. What does his CT show?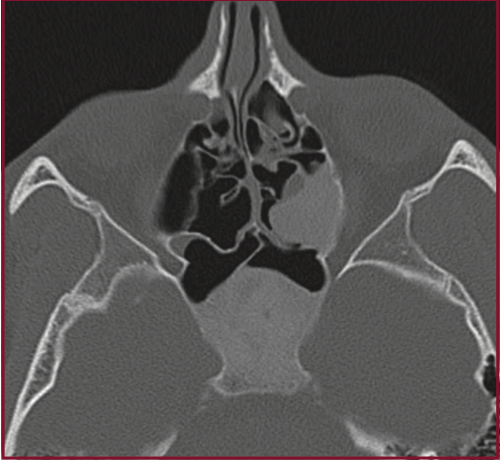
Coronal CT demonstrate absence of ethmoid roof and a large mass that extends from this bony defect into the ethmoid bed, possibly a meningoencephalocele of iatrogenic etiology
What has this mass eroded through? What T stage does that make this tumor?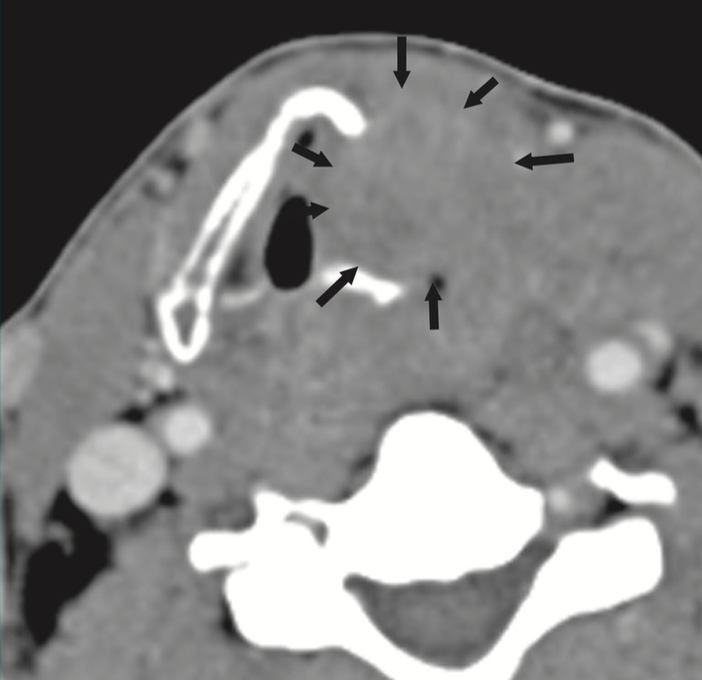
Eroded through the thyroid cartilage, both inner and outer cortex. T4a tumor. (Only inner cortex means T3)
Patient with difficulty swallowing and regurgitation undergoes a barium swallow. What do we see?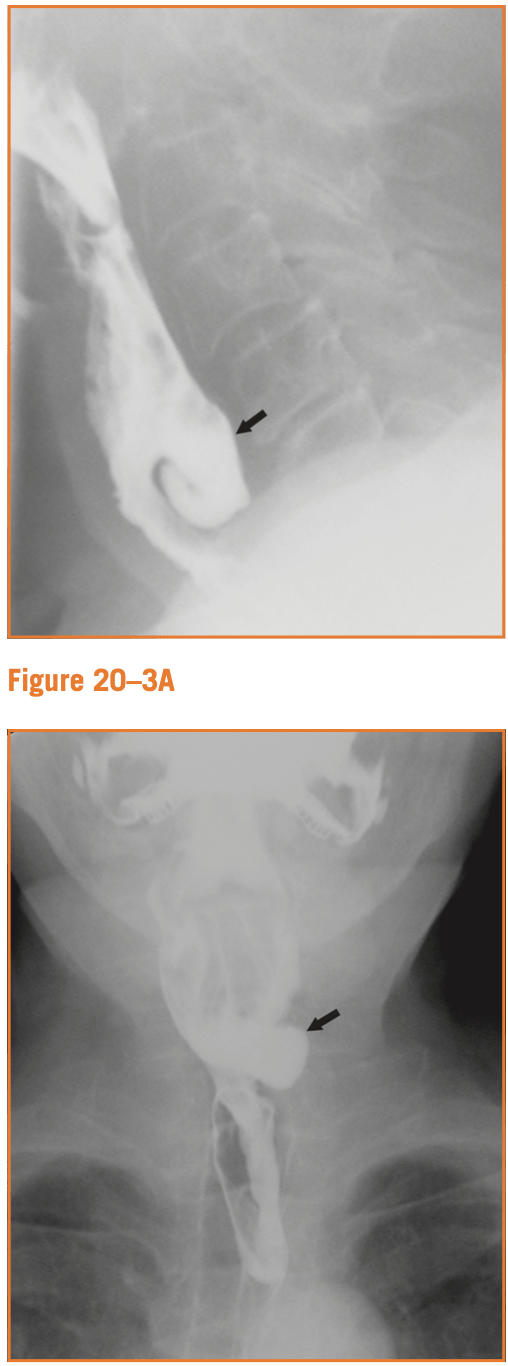
Lateral and AP projections demonstrate an outpouching extending from the left posterior aspect of the cervical esophagus at the level of C5-C6. Typical appearance of a Zenker's diverticulum
11yM presents to the ED with fever, tender neck mass. What are the structures identified in this CT, what is the likely diagnosis? BONUS POINTS - name two other entities on the differential diagnosis.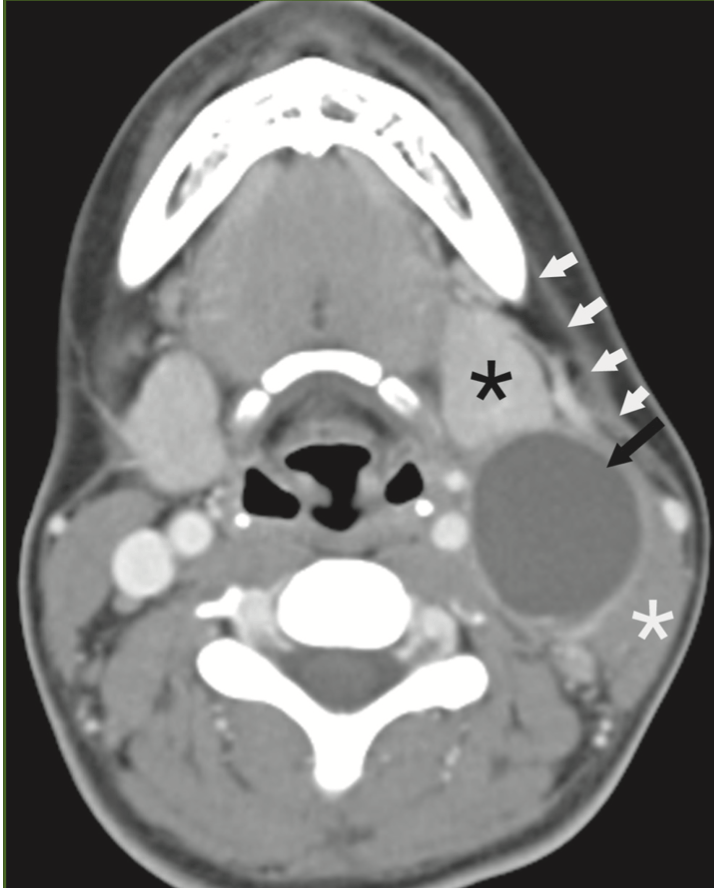
Cystic, rim enhancing lesion that lies posterior to the left submandibular gland, anterior to SCM, some soft tissue stranding. Likely type 2 branchial cleft cyst, could also be a cystic metastatic lymph node, low-flow vascular malformation

48yF with pulsatile tinnitus, PE shows a vascular mass in the middle ear. What does this image show and to what are the black arrows pointing?
Glomus tympanicum - separate from jugular bulb
Black arrows- carotid canal, jugular bulb
20yM in a car accident, abnormality incidentally noted on CT. Describe these scans-
bonus points for naming the diagnosis!
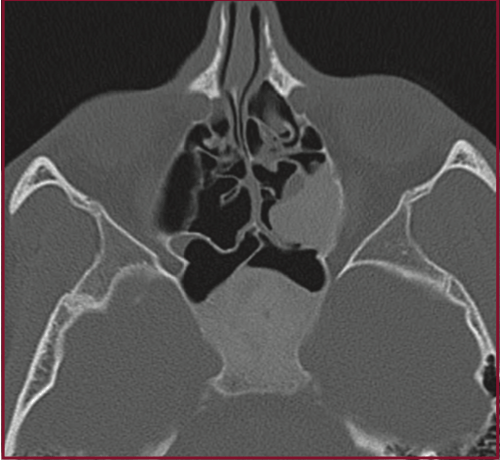
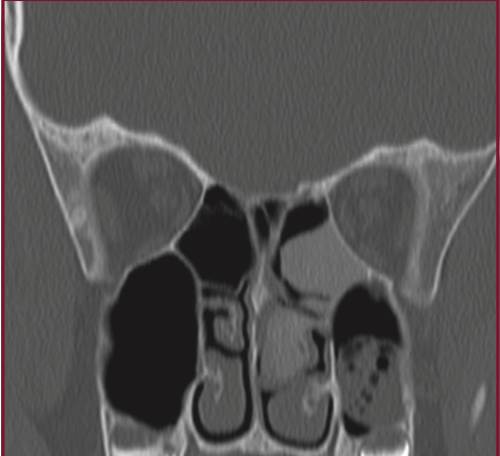
Bone windows, demonstrate expansion of the sphenoid bone, left ethmoid bone, middle turbinate. Ground glass opacity in bone. Consistent with fibrous dysplasia.
1-month-old infant p/w noisy breathing. Normal pregnancy and delivery, but stridor since birth. MRI w/ contrast is ordered. What is the abnormality and likely diagnosis? BONUS POINTS- what external physical exam finding would prompt DLB? BONUS BONUS POINTS - what syndrome would you think about with this diagnosis?
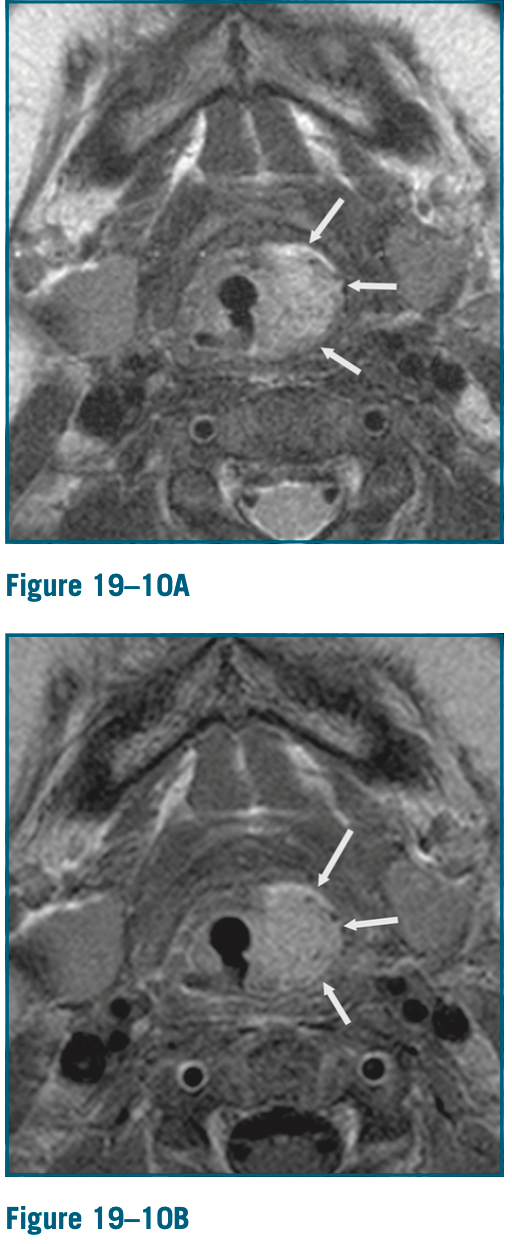
T2 hyperintense, enhancing lesion in left AE fold, c/w hemangioma.
Beard distribution facial hemangiomas
PHACE(S) syndrome -
24-52% of kids with PHACE(S) syndrome have subglottic hemangioma.
P- posterior fossa/structural brain abnormalities, H- large hemangiomas of the face, neck, and/or scalp, anatomical anomalies of the cerebral of cervical (A)rteries, C- cardiac abnormalities/coarctation of the aorta, E-eye abnormalities, S- sternal abnormalities
57yF with difficulty swallowing, complains of a lump in her throat. What do we see on barium swallow?
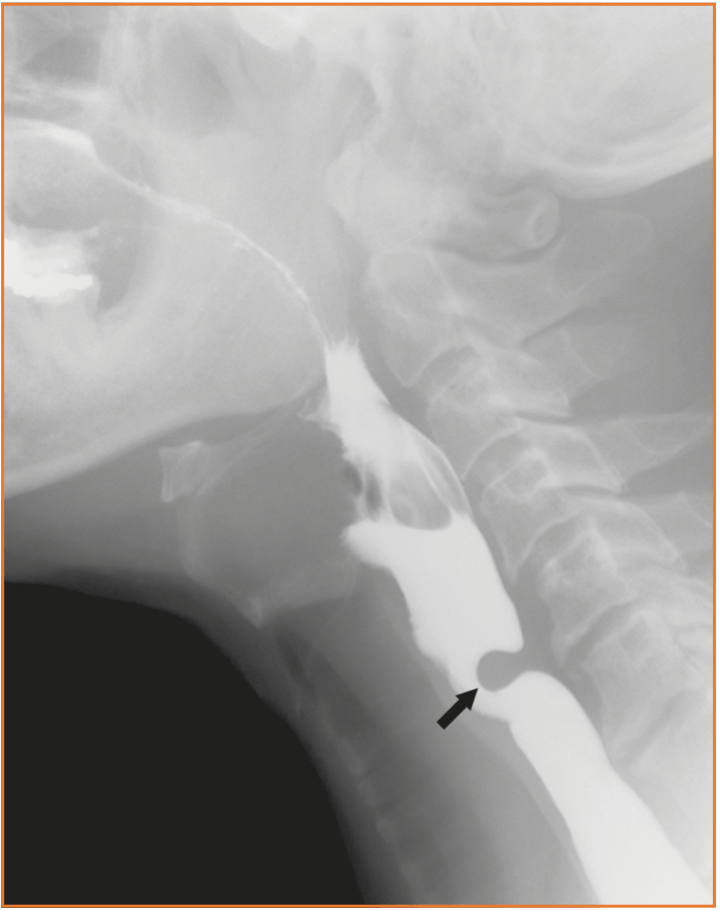
Smooth surfaced filing defect in the barium column arising from the posterior pharyngeal wall at approximately the level of C5. Typical appearance of a cricopharyngeal bar.
18yF presents with 1 month of painless right cervical lymphadenopathy that did not respond to abx. What do we see on CT and what is on the differential dx? BONUS POINTS for listing three alternate dx.
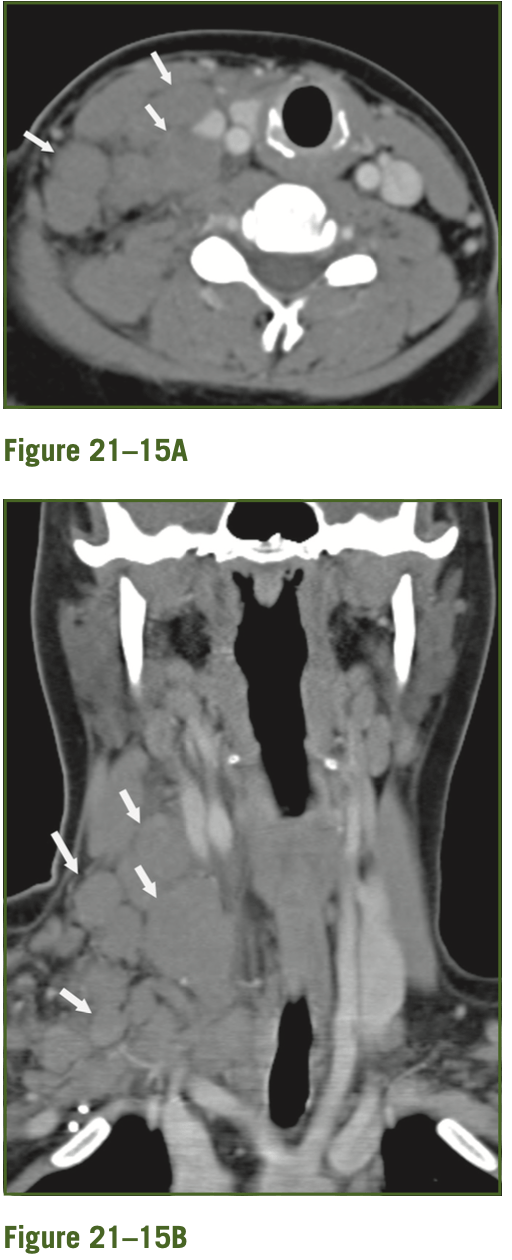
Multiple enlarged LNs in the right neck without central necrosis or cystic change, no infiltration of abnormal soft tissue into the surrounding fat, although there is some fat stranding.
Differential -
reactive lymphadenopathy
lymphoma
Kimura's disease
Rosai-Dorfman
Less likely, but possible - SCC, papillary thyroid ca.
What are the CT findings?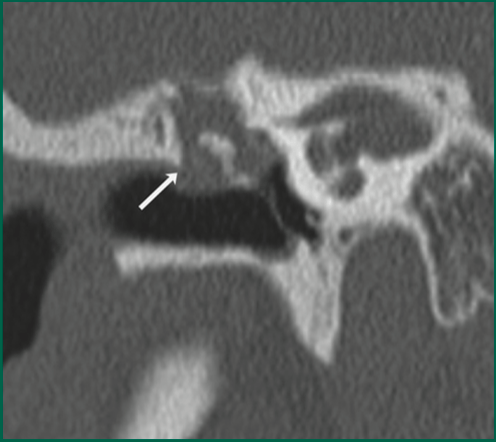
6yM with rhinorrhea, cough, fever, left eyelid swelling, limited EOM. What does this image show? BONUS POINTS - what is the Chandler classification and what stage does this represent?
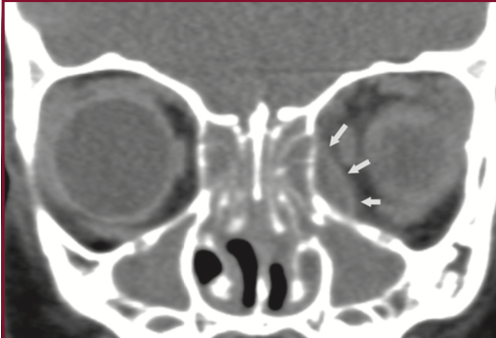
Rim enhancing fluid collection along the inferior medial orbital wall, c/w subperiosteal abscess
Chandler:
(I) preseptal cellulitis
(II) orbital cellulitis
(III) subperiosteal abscess
(IV) orbital abscess
(V) cavernous sinus thrombosis
What do we see on this scan, and what structure is identified by the white arrows? BONUS POINTS - name 4 things that are important to note on a laryngeal CT scan when concerned about a mass
Right false cord is bulging with abnormal soft tissue. Normal paraglottic fat is seen on the left, ID'd by the white arrows.
Look for:
- involvement of paraglottic fat
- laryngeal cartilage involvement
- subglottic spread
- presence of LN mets
An infant presents with a hx of stridor since birth and poor feeding. CXR and barium swallow were performed. What is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
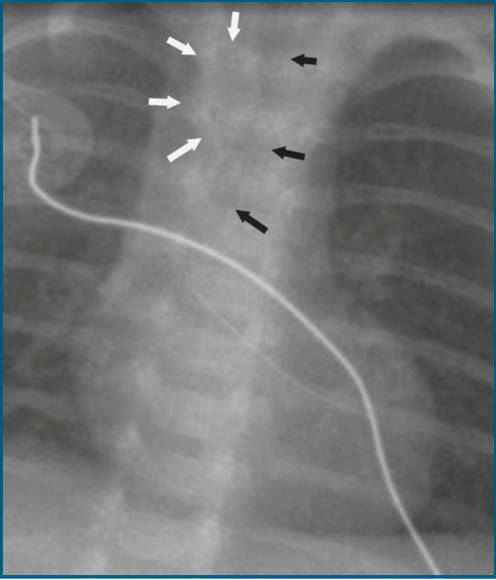

CXR shows an indented trachea rounded by a soft tissue shadow - in this case, the aortic arch.
Barium swallow shows a fixed region of narrowing in the esophagus that is demonstrated on both the lateral and PA view.
The finding of a right aortic arch on CXR and fixed narrowing on barium swallow indicates the presence of a vascular ring encircling trachea and esophagus. Right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery
17yF with a right thyroid mass and a suspected enlarged LN present to the clinic. What do we see on these US images? Is this reassuring or concerning?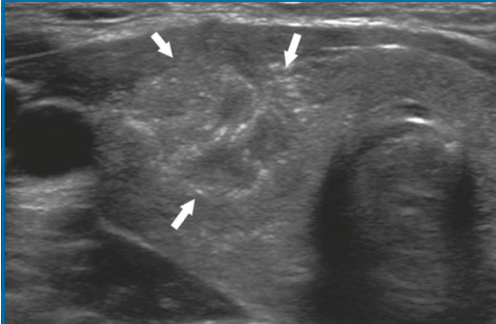
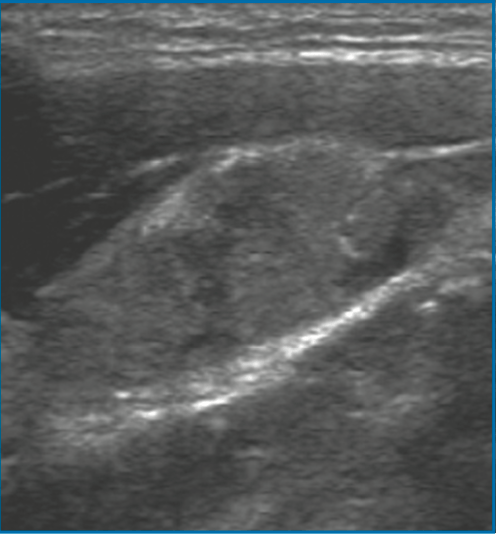
First image- thyroid nodule ill-defined, taller than wide, numerous micro-calcifications.
Second image - enlarged LN, hyper echoic, lost fatty hilum, micro-calcifications
Patient with congenital SNHL. What does this CT show?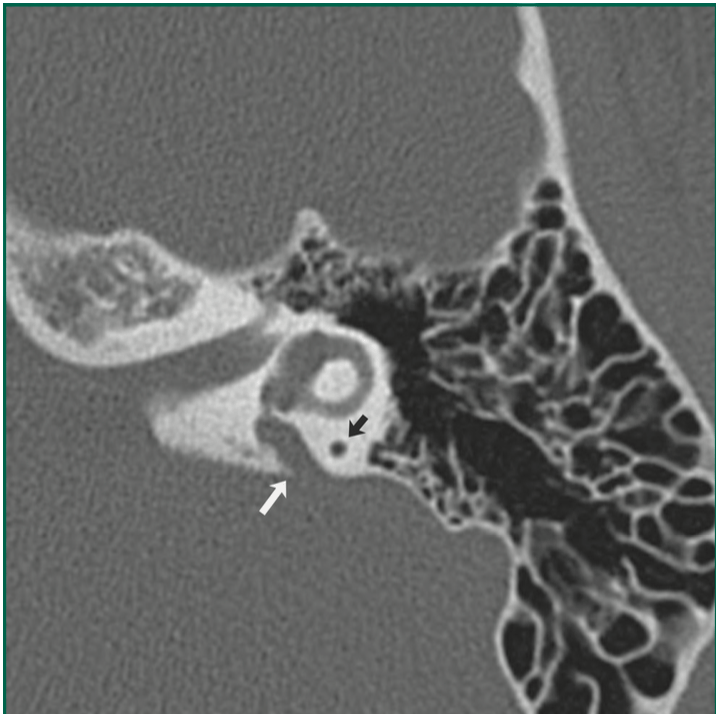
Enlarged vestibular aqueduct; should not be larger than adjacent posterior SCC (black arrow)
14yM with nasal congestion, epistaxis. What do we see on these scans? What area is expanded and what foramen is widened?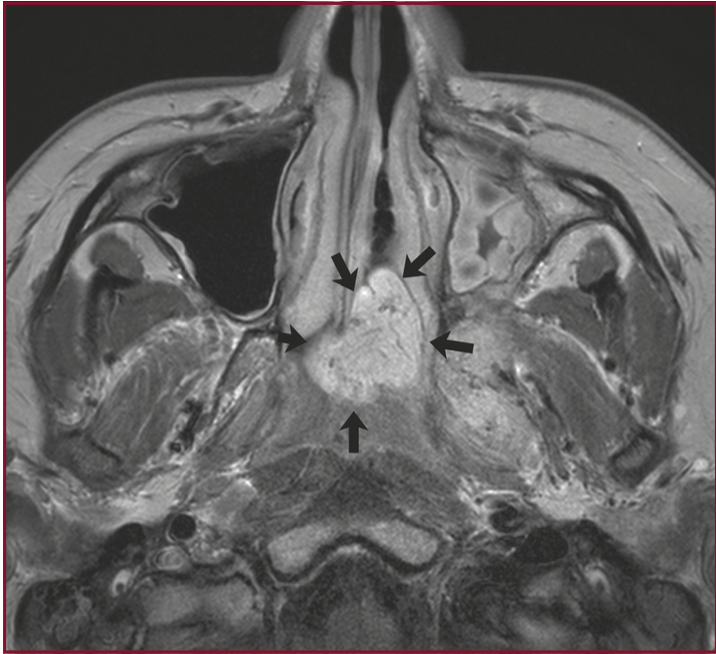
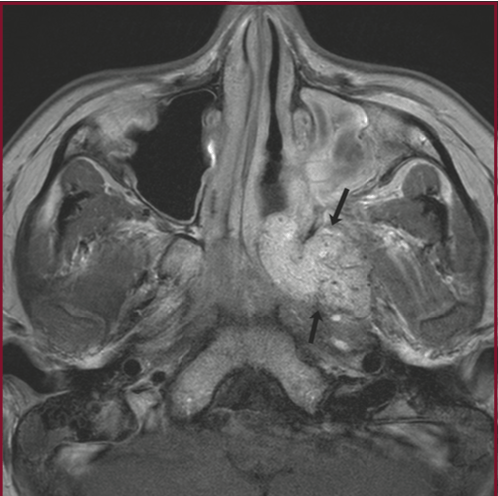
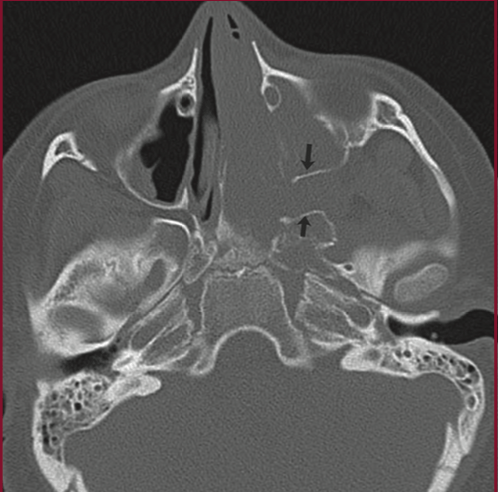
JNA
Expanded into the pterygopalatine fossa with significant widening, widened sphenopalatine foramen
Note: the dots/serpiginous lines within mass on MRI are flow voids representative of fast blood flow, evidence of highly vascular tumor
75yM with chronic hx of SOB. Larynx appears normal on FOE, but tracheal airway is not well visualized. What is seen on CT and what is the differential diagnosis? BONUS POINTS - what is the grading scale and what grade is this?
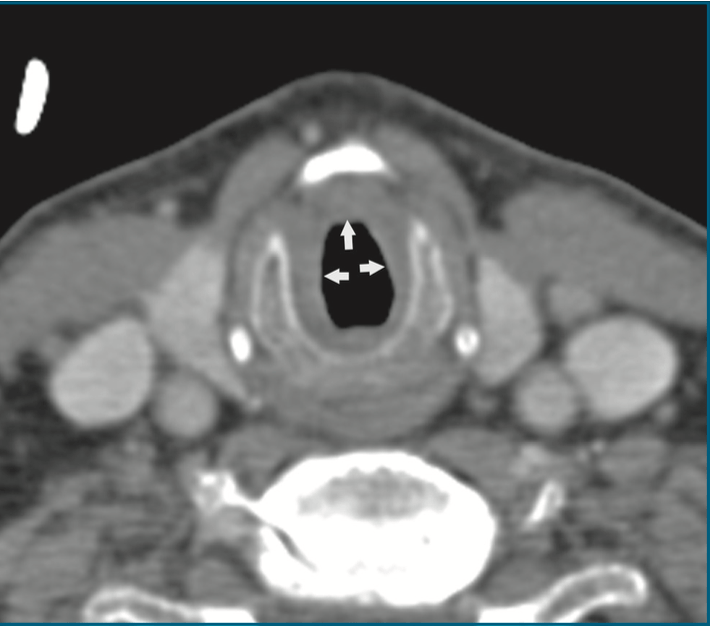
CT shows soft tissue narrowing in the sub glottis. Differential includes Wegeners, amyloidosis, relapsing polychondritis, sarcoid, tracheopathia osteochondroplastica, idiopathic narrowing.
Cotton-Meyer grading scale
Grade 1 - 0-50%
Grade 2- 51-70%
Grade 3- 71-99%
Grade 4- no discernible lumen
Woman with a hx of chemotherapy and radiation for cancer tx develops difficulty swallowing. Barium swallow is performed; what is the abnormality and what is the most likely cause?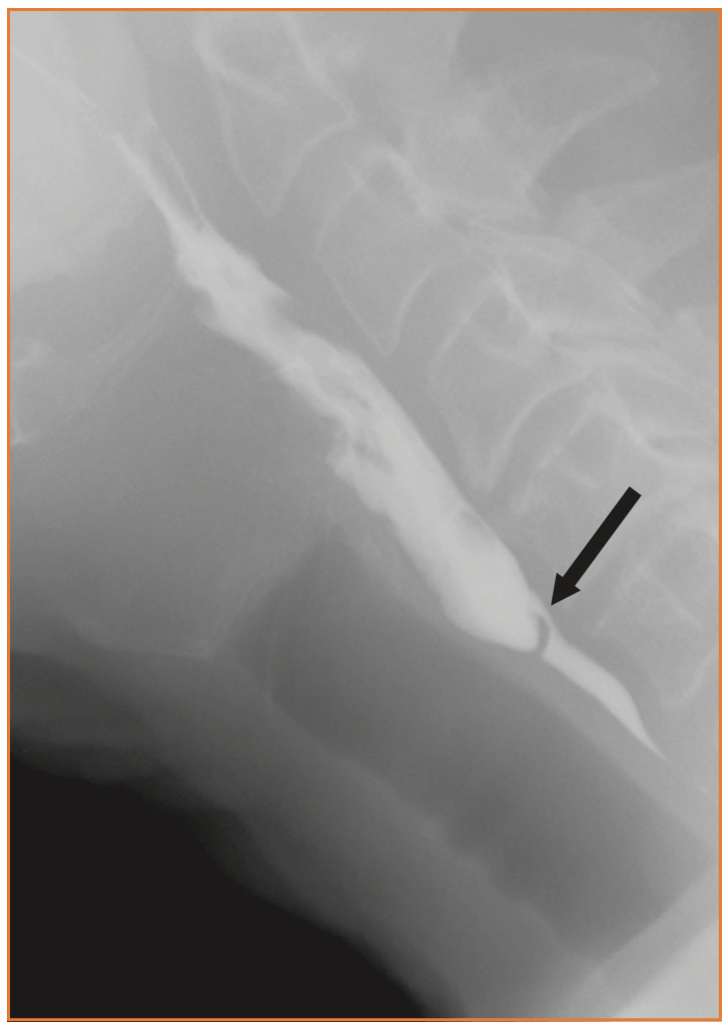
Barium swallow, lateral projection, shows a severe narrowing of the cervical esophagus over a very short segment, likely a cervical esophageal web 2/2 radiation
36yF with chronic dry mouth and dry eyes. What do we see on this MRI? What is a possible diagnosis?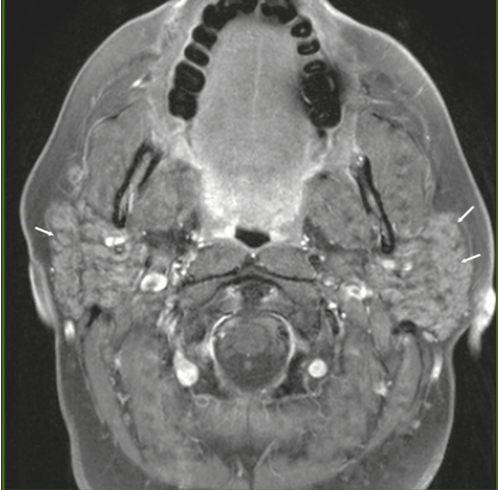
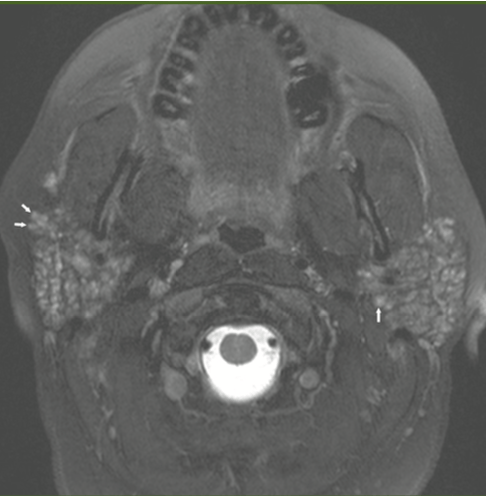
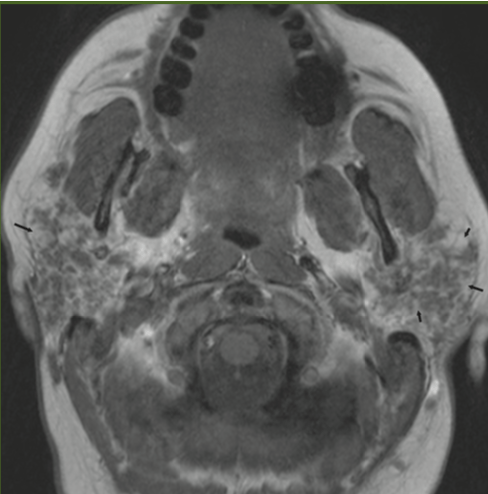
Image 1 ,2- small nodules that diffusely replaced normal parotid parenchyma
Image 3- significant fatty change in the parotid glands
Most commonly seen in Sjogrens disease and sarcoidosis
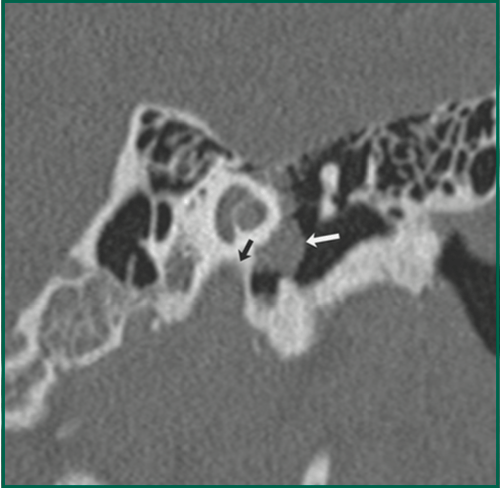
40yF presents with CHL. What does this CT show?What area is this arrow pointing to?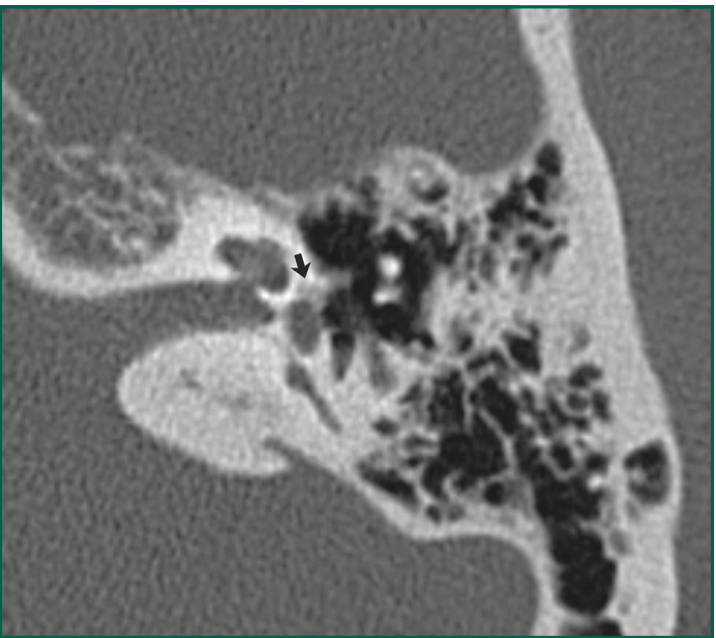
Focus of lucency immediately anterior to the oval window, in the fissula ante fenestram. Consistent with otosclerosis
50yF with long hx of sinus congestion and pulmonary complaints. No hx of substance abuse. What do we see on this scan and what is in the differential diagnosis?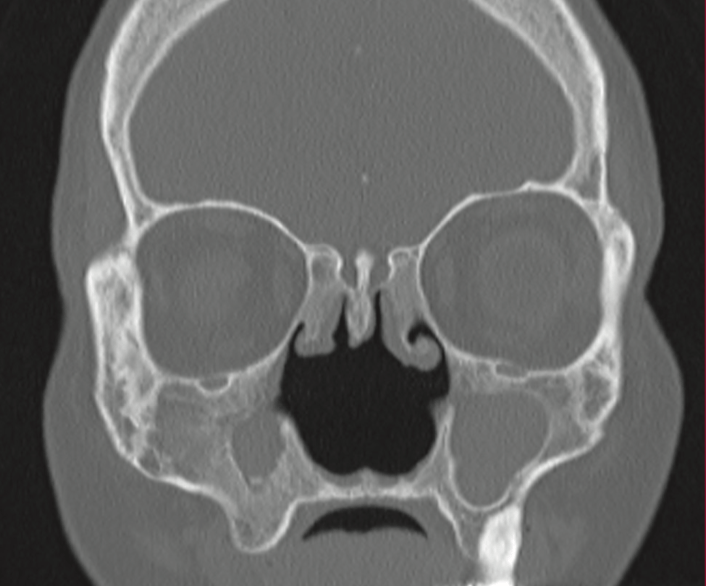
Chronic bony thickening of the maxillary sinuses bilaterally, large nasal septal perforation, erosion of the turbinates and uncinate process. Suggestive of chronic destructive inflammatory process in sinuses, ie Wegeners or sarcoid
What abnormality do we see on CT? What might this represent?
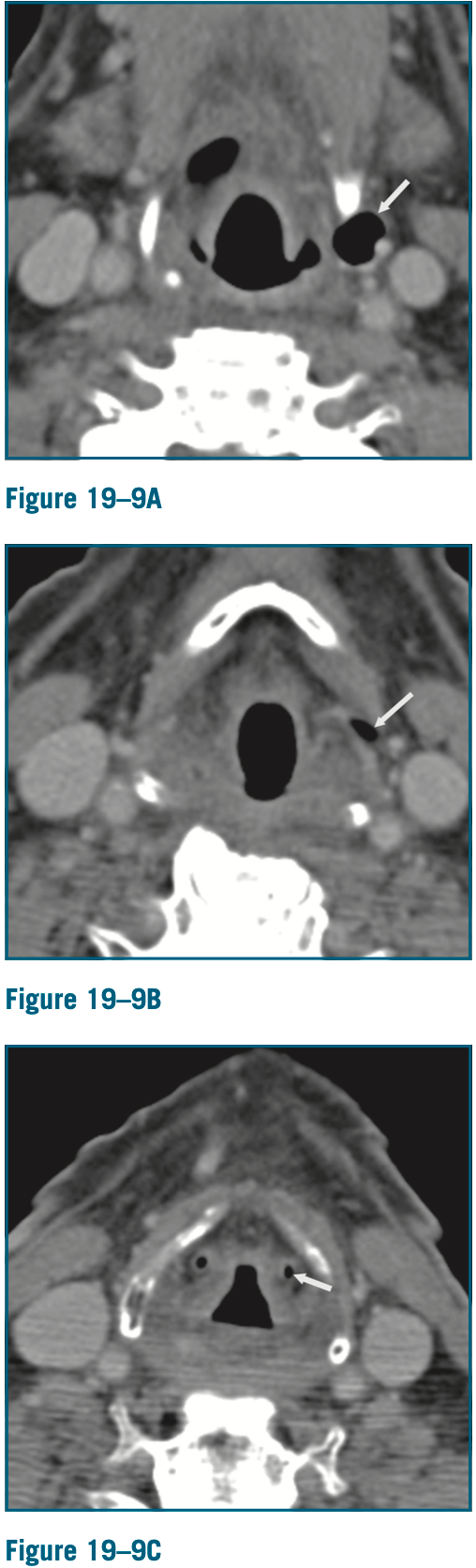
Air collection extending external to the larynx, following inferiorly the air collection communicates with the ventricular appendix, c/w external laryngocele
63yM with sore throat and pain with swallowing. He undergoes a barium swallow and neck CT. What abnormalities do we see?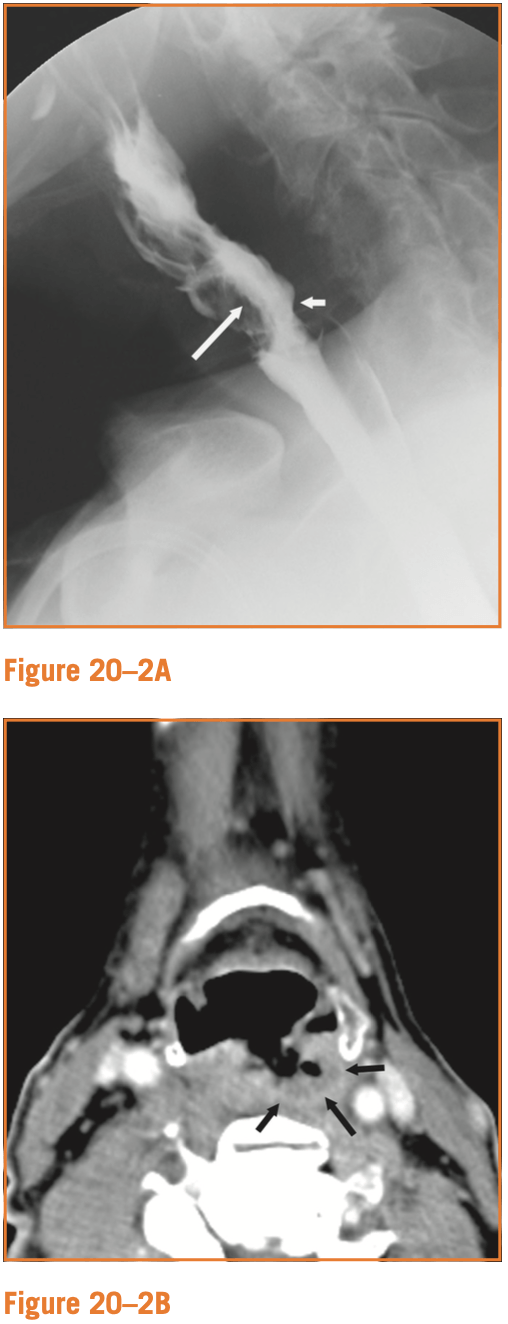
Barium swallow shows irregular, nodular narrowing of the hypopharynx (white arrows). CT shows an ulcerated mass along the posterior hypo pharyngeal wall.
3 month old girl presents with left facial swelling, not present at birth. What is the likely diagnosis and what else is on the differential diagnosis? What space is invaded?
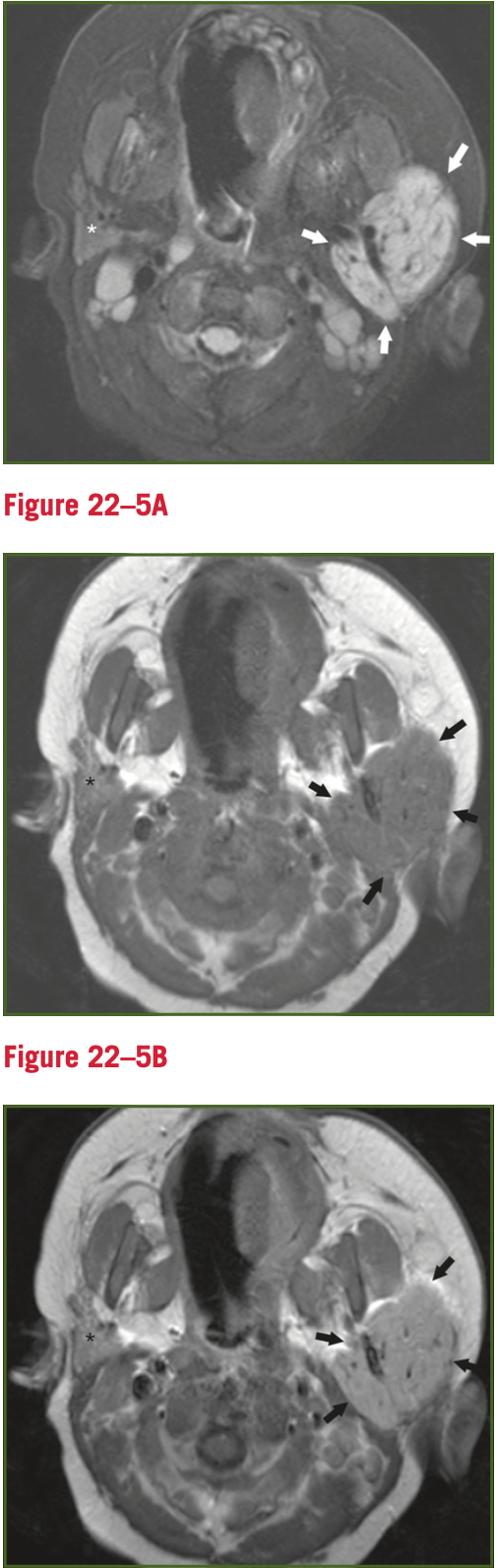
A- axial fat sat T2 weighted MRI
B- axial precontrast T2 weighted MRI
C- axial gad-enhanced T1 weighted MRI
T2 hyperintense, avidly enhancing, well-circumscribed soft tissue mass completely replacing the left parotid gland and extending into the parapharyngeal space.
Differential- primary epithelial tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma and associated sarcomas, neuroblastoma, hemangioma. Hemangioma is the most common and most likely with these images.