Identify the angular notch.
What is D?
page 454
The patient has a creatine level of 0.9mg/dL, this is how the patient should be handled for a iodinated contrast exam.
What is proceed with the exam?
This patient care concern would prevent the use of an oral, water-soluble contrast.
What is a sensitivity to iodine?
page 542
This term describes the event in which contrast leaks out of the vein and into the surrounding tissue.
What is extravasation or infiltration?
page 540
The following characteristic belong to which iodinated type of contrast:
low osmolality
inability to dissociate into two seperate ions
less chance of reaction
What is nonionic iodinated contrast?
page 538
This is preparation for an adult having an upper GI is to be NPO ____ before the procedure.
What is 8 hours?
page 499
The structure indicated by the red arrow.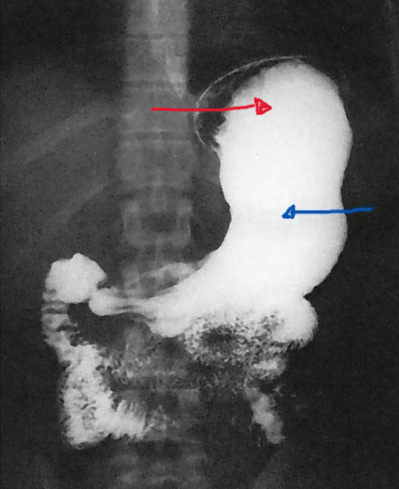
What is the fundus of the stomach?
page 456
Letter that identifies the pylorus.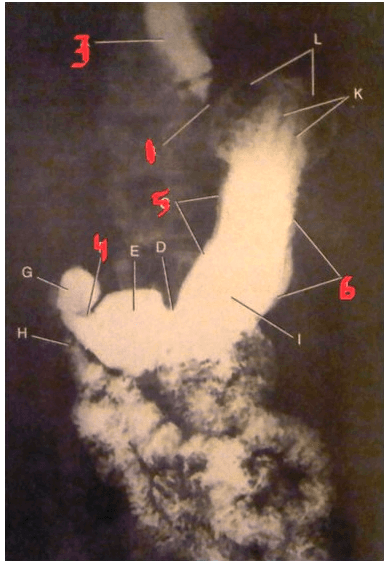
What is E?
page 454
You should reassure the patient and continue the injection of iodinated contrast and imaging sequence, while carefully observing the patient, when the patient experiences these type of side effects.
What or common side effects?
Page 539
This is the clinical indication from the following list that would mandate the use of an oral, water-soluble contrast agent:
esophageal reflux
bezoar
perforated bowel
peptic ulcer
What is a perforated bowel?
page 462
This contrast iodinated contrast contains no positively charged cations.
What is nonionic?
page 538
This is the component in ionic contrast media that increases its solubility.
What is the cation?
page538
This is the specific structure is adjacent to the C-loop od the doudenum.
What is the head of the pancreas?
page 456
The structure indicated by the letter B.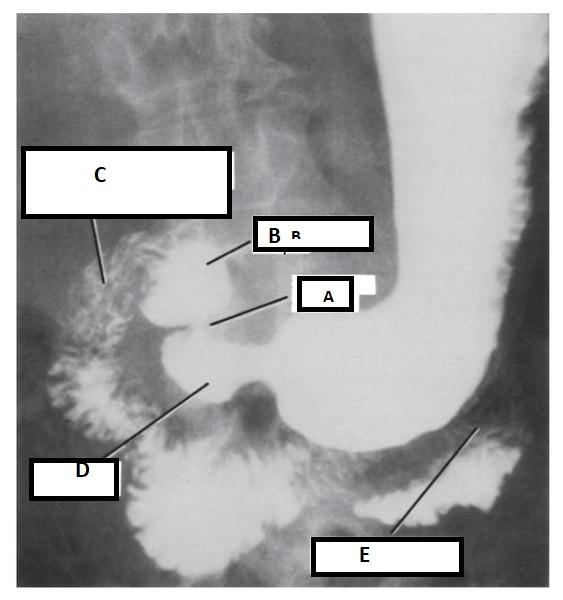
What is the doudenal bulb?
page 456
Letter G indicates the structure.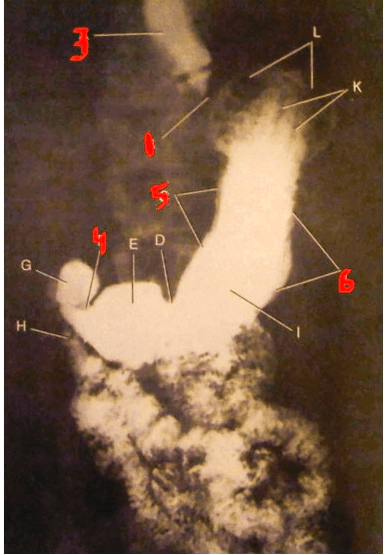
What is the duodenal bulb?
page 454
This type of contrast agent may increase the severity of side effects.
What is ionic iodinated contrast?
page 538.
This the type of reaction call is a true allergic reaction.
What is anaphylactic reaction?
page 542
This substance are not digested chemically.
What is water, vitamins or mineral?
page 457
This is the medical term for subcutaneous swelling that is caused by an allergic reaction to foods or drugs.
What is angioedema?
page 541
This is the structure of the stomach is attached to the duodenum.
What is the pylorus?
page 456
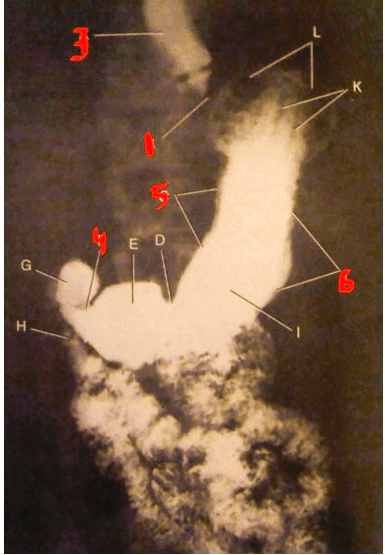
The structure indicated by the number 3.
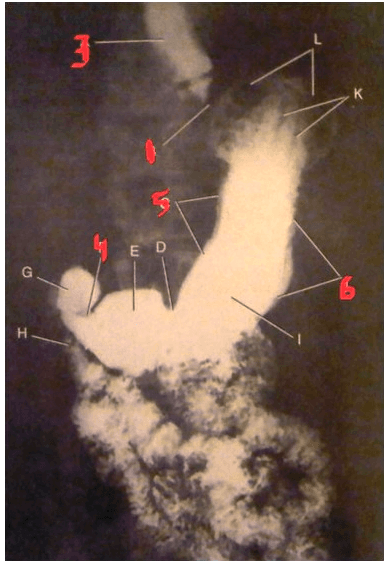
What is the distal esophagus?
page 456
The structure represented by the number 5.
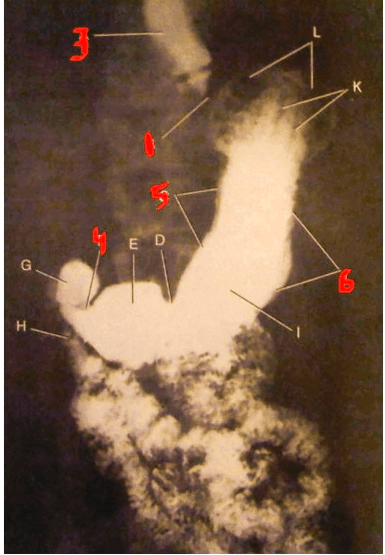
What is the lesser curature of the stomach?
page 454
These common side effects of iodinated contrast do not need medical intervention. Reassuring and comforting patient is all that is required.
What are "hot flashes", copper penny or metalic taste or sensation of "wetting your pants"?
Page 539
Phlebitis is considered to be this type of reaction.
What is a local reaction?
page 540
Blood chemistry ranges for kidney function should be in the ranges of __________mg/dL for creatine and ______________mg/100mL for BUN for a patient to receive iodinated contrast.
What is 0.6 to 1.5 mg/dL for creatine and 8 to 25 mg/100 mL for BUN?
page 539
This is the term used for solution of barium mixed wth water.
What is a clloidal suspension?
page 461
This is the term for the longitudinal folds found within the stomach.
What are the rugae?
page 455
The structure indicated by the number 6.
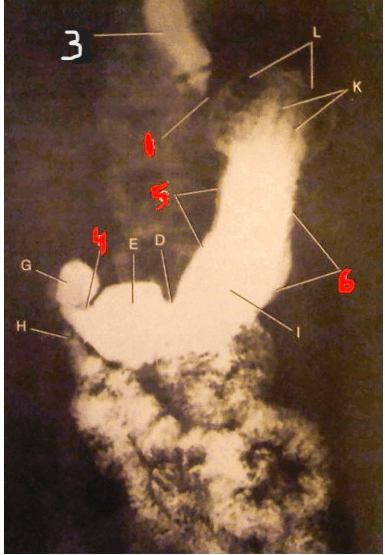
What is the greater curvature of the stomach?
page 456
The structure represented by the number 3.
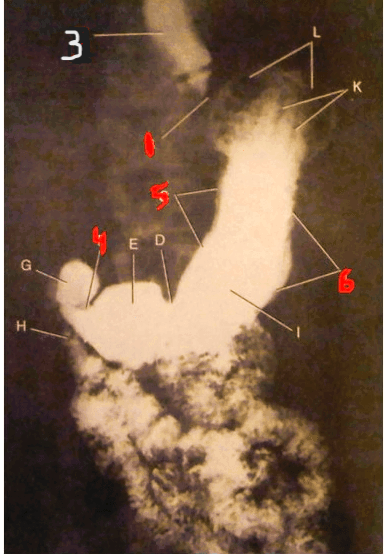
What is the distal esophagus?
page 454
Regardless of severity, all of these must be documented.
What are contrast reactions?
Page 541
This contrast agent uses a parent compound of a carboxyl group (benzoic acid).
What is ionic contrast?
page 538
This is where bile is produced.
What is the liver?
page 446
Barium sulfate is classified as this type of radiologic contrast media.
What is radiopaque?
page 461
This is the term that describes the outer lateral border of the stomach.
What is the greater curvature?
page 454
Structure indicated by blue arrow.
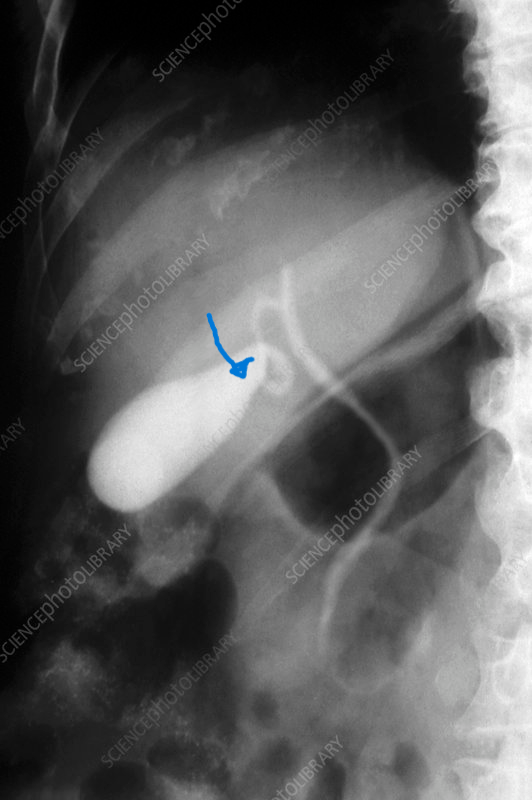
What is the neck of the gallbladder?
page 448
This structure is indicated by the letter C.
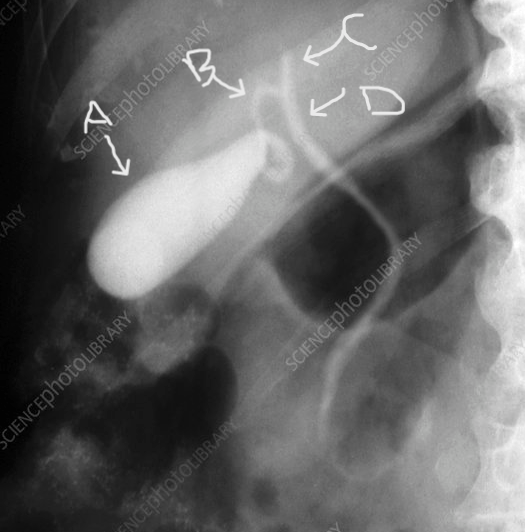
What is the common bile duct?
page 447
Cardiac Arrhythmias are considered this type of reaction.
What is severe?
page 541
This is the action taken if a patient develops severe urticaria during an exam using iodinated contrast.
What is get medical assistance?
page 542
This structure indicates the junction between the duodenum and jejunum.
What is the supensory muscle of the duodenum (ligament of Treitz)?
page 456
These are the two most common forms of negative contrast agents used to create gas.
What are calcium and magnesium citrate?
page 462
These are the main subdivisions of the stomach.
What are the fundus, the body and the pylorus?
page 454
Structure indicated by the orange arrow.
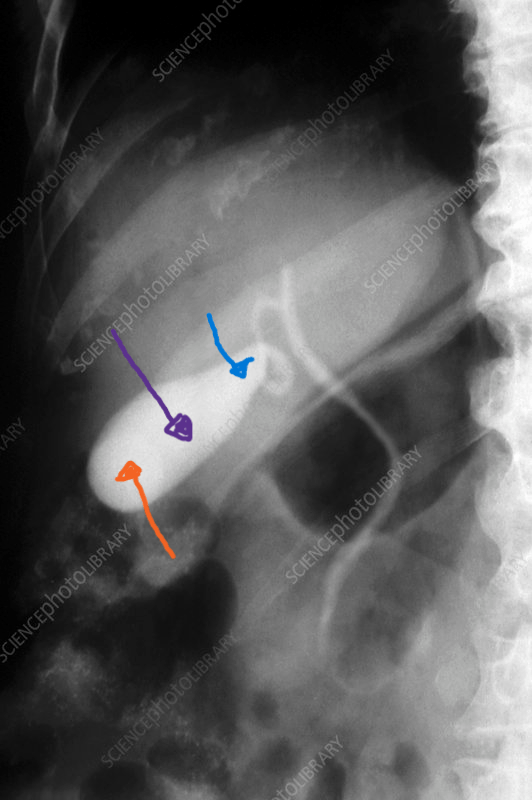
What is the fundus of the gallbladder?
page 448
The letter B represents this structure.
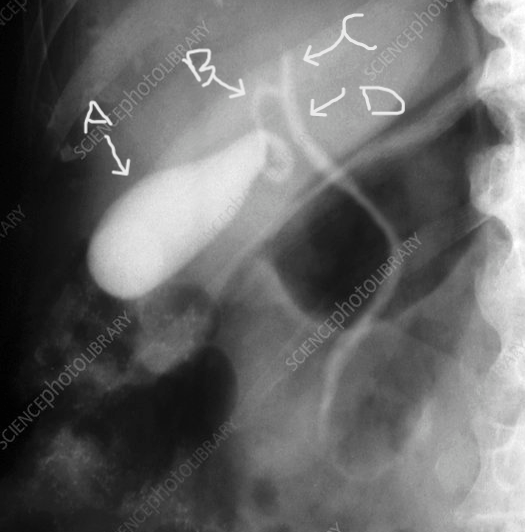
What is the cystic duct?
page 447
When the patient experiences laryngeal swelling after an injection of iodinated contrast is can be considered one of these types of reactions.
What is moderate or severe reaction?
page 541
This is the type of reaction that a medical emergency MUST be declared.
What is a severe reaction?
page 542
This is the classification of body habitus of letter C.
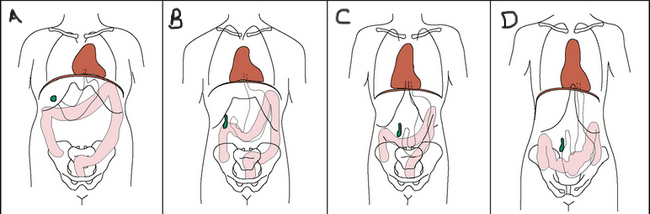
What is hyposthenic?
page 458
This the iodinated contrast that creates a hypertonic condition in the blood plasma.
What is ionic contrast agents?
page 538
This is where lipids (fats) are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, digesting and absorbing them.
What is the stomach and small bowel?
page 457
Structure indicated by the purple arrow.
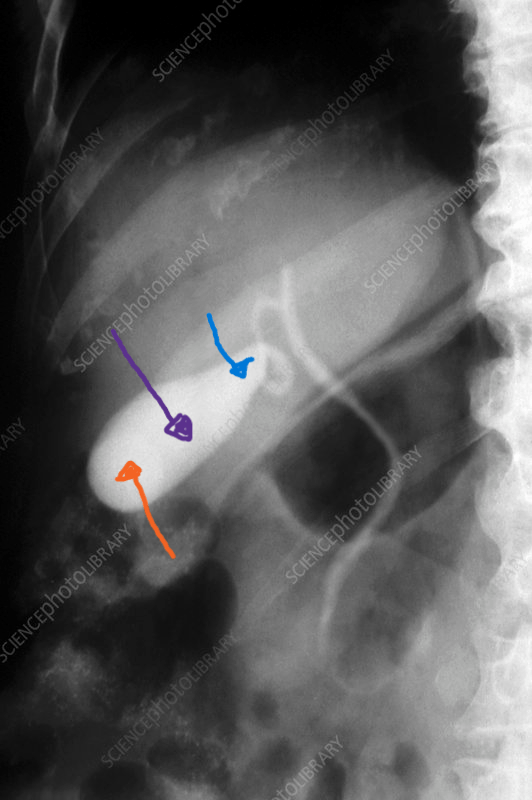
What is the body of the gallbladder?
page 448
Thie number 2 represents this structure.
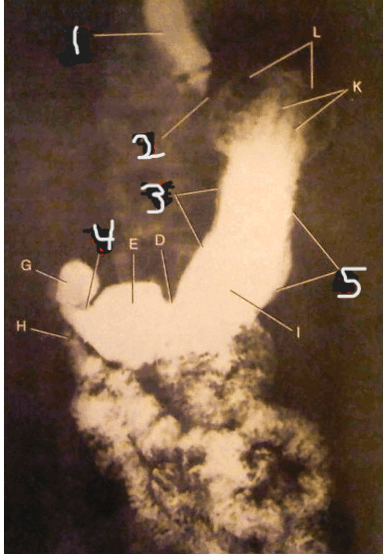
What is the esophagogastric juncture?
page 456
These are the most common drugs given to a patient as a premedication for an iodinated contrast exam.
What are benadryl and prednisone?
page 540
This is the immediate protocol for a patient who experiences extravasation.
What is elevate the arm and apply a cold compress?
page540
The body habitus that a high and transverse stomach wound be found in.
What is hypersthentic?
page 459
Moderate urticaria is considered what level of iodinated contrast reaction.
What is a moderate contrast reaction?
page 541
This the term for swallowing.
What is deglutition?
page 452
Structure indicated by the letter B.
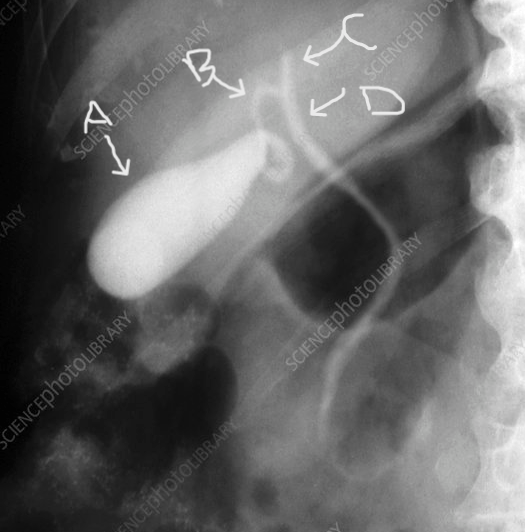
What is the cystic duct?
page 447
The letter C represents what structure.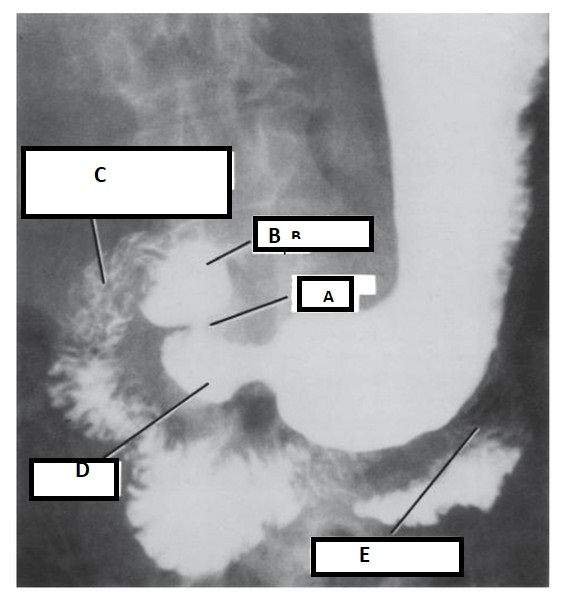
What is the doudenum?
page 456
This is how long metformin or Glucophage, medications for diabetes, should be held after an iodinated contrast injection.
What is 48 hours?
Page 539
This type of reaction can be life threatening.
What is severe or vasovagel?
page 542
This part of the GI tract is mostly responsible for the absorption of digested products, water, mineral and vitamins.
What is the small bowel?
page 458
This compound is a common cation (+) found in ionic cantrast media.
What is sodium or meglumine?
page 538
This is the substance that begins to be broken down by saliva in the mouth.
What are starches?
e 451Ghent
Structure indicated by the arrow.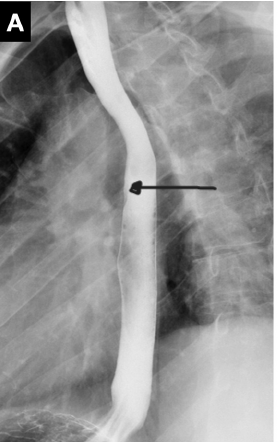
What is the esophagus?
page 453
Anatomical structure that is indicated by arrow.
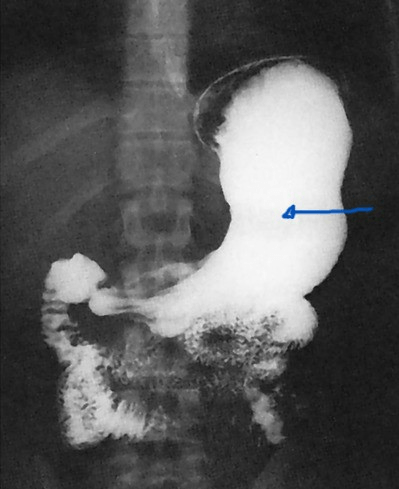
What is the body of the stomach?
page 456
These are common side effects expected when a patient receives an exam involving iodianted contrast.
What are "hot flashes" and a metalic taste in the month?
page 539
Extravasation is considered this type of reaction.
What is a local reaction?
page 540
This is the reaction, from the following list , is considered a moderate level contrast reaction.
hypotension
nausea and vomiting
syncope
diminished urine output
What is hypotension?
page 541
This is the most common contrast used for GI studies.
What is barium?
This is the abdominal quadrant where the liver is located.
What is the RUQ?
page 446
Structure indicated by the letter B.
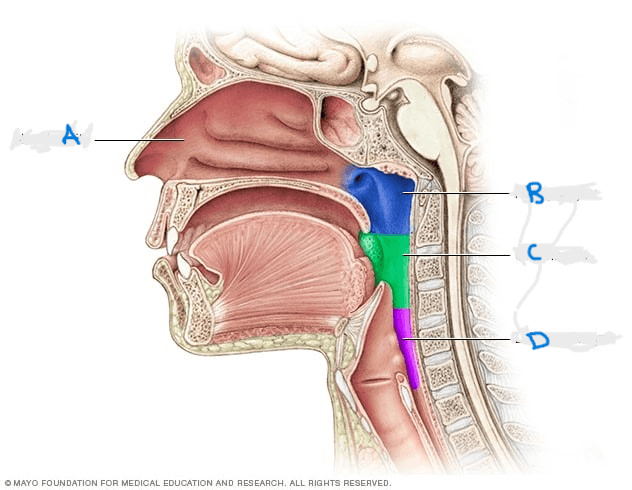
What is the nasopharnyx?
page 452