In order for a reaction to occur, reactant molecules must collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation.
1. A change that is both observable and quantifiable
2. Time taken for reaction to proceed
Which step of the reaction mechanism determines the reaction rate?
The slowest step
How many steps are there in this multi-step reaction? Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
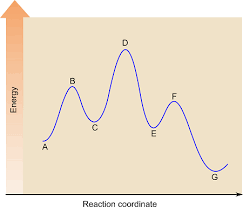
3 steps, exothermic.
How does caffeine wake us up?
It acts as an inhibitor. The molecular structure of caffeine is very similar to that of adenosine, the buildup of which induces sleepiness.
As the caffeine binds strongly to the adenosine receptors, our brains do not experience the adenosine molecules.
1. Increase the number of collisions per time
2. Increase the success rate per collision
In general, the rate of a reaction decreases as it progresses. Why?
As reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants will decrease.
According to collision theory, as the concentration of reactants decreases, there will be less collisions of reactants, which decreases the rate.
In a reaction mechanism, which chemical species initially acts as a reactant, and then regenerated at the end as a product?
Catalyst
How many activated complexes are in this reaction mechanism? Where are they located?
A reaction changes colour as it progresses. What is the instrument that is required in order to measure the reaction rate of such a reaction?
Spectrophotometer.
Since the change in colour is too difficult to quantify by eye, you must use a spectrophotometer in order to quantify the exact change in concentration of coloured species as the reaction progresses.
The concentration of the coloured species in solution can be calculated from the intensity/absorption of light by using the Beer-Lambert law.
The following Boltzmann distribution represents the reactant molecules of a reaction. The temperature of the reaction was lowered, and a catalyst was added. How do these two things affect this diagram?
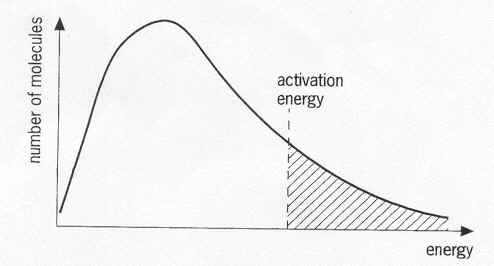
1. Lowering the temperature shifts the curve towards the left. The "peak" (or average kinetic energy / temperature) shifts towards the left.
2. The line that indicates the activation energy will move towards the left (catalyst decreases activation energy).
This data table represents the concentrations of AB over the time of reaction.
Is AB a product or a reactant?
What is the average reaction rate? Give correct units.
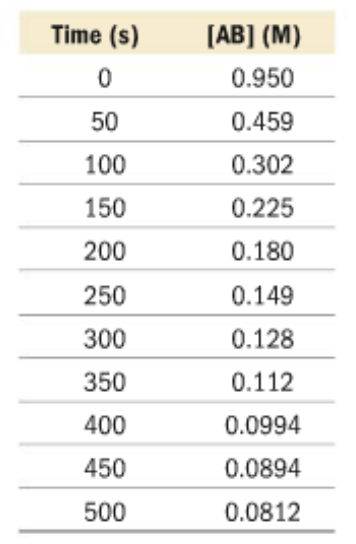
AB is a reactant because it decreases over the course of the reaction.
Rate = (0.0812M - 0.950M) / 500s = -0.00174 M/s
In a reaction mechanism, which chemical species is produced as a product in an initial step, but is then used as a reactant in a later step?
Reaction intermediate (NOT activated complex / transition state)
Subtracting point D from point G gives you the

Activation energy of the reverse reaction
What is a radical?
A radical is a chemical species with a single, lone electron. Radicals are extremely reactive as they will try to find an electron from a different compound in order to pair up and become more stable.
Such reactions in the body can cause cancer, and antioxidants are what we take in order to prevent damage from "free-radicals".
What are the five possible nature of a chemical reaction that can influence the rate of reaction?
You must name at least 4.
1. Number of bonds broken and formed
2. Geometry (simple or complex)
3. Number of molecules colliding
4. States of reactants (aq > g > s)
5. Charged (oppositely charged ions will attract)
What would you need to do in order to calculate the instantaneous rate of reaction at t = 100s?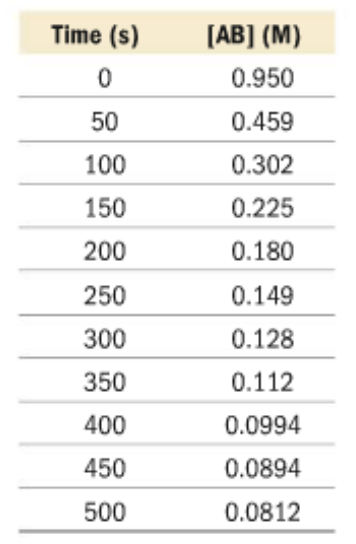
Graph the following data, find the tangent line at t = 100s, then find the slope of the line.
The activated complex is formed, old bonds are broken and new bonds are made.
If this reaction was catalyzed, what would you expect will change in this diagram?
Peak D will be lowered
OR
A new, different reaction mechanism could take place (one with a lower activation energy than this one)
Between these two steps in a reaction mechanism, which do you expect to be the slower step and why?
Overall reaction: 2NO2 + Cl2 --> 2NO2Cl
1. NO2 + Cl22 --> NO2Cl + Cl
2. NO2 + Cl --> NO2Cl
The first step.
1. The second step does not require breaking the bond between the two chlorine atoms.
2. The single chlorine atom has a simple geometry, which makes all collisions effective as opposed to the dichlorine molecule
3. (Not required) Cl is a radical, which is a highly reactive species that will react faster with NO2 compared to Cl2
3H2(g) + N2(g) --> 2NH3(g)
In order to increase the rate of this reaction, the pressure of the container was increased by adding argon gas. However, the rate of the reaction did not increase. Why?
The addition of argon gas does not increase the partial pressures (concentrations) of the reactants.
According to collision theory, the Ar gas can both help and hinder the collisions between hydrogen and nitrogen gas, and therefore has a net effect of 0 on the rate.
How would you predict the [AB] and t = 75 s?
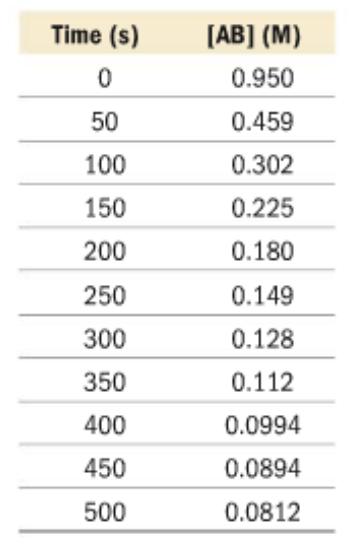
Graph the following data to find the trendline. Using the equation of the trendline, plug in the x(time) as 75 seconds, to calculate for y([AB]).
Reaction 1, is a single step reaction.
Reaction 2, is a multi-step reaction with 6 elementary processes.
Which reaction is faster?
Not enough information. The reaction with the lower activation energy would be faster.
Which reaction, the forward or the reverse reaction, is faster?

The forward reaction is faster, because the activation energy for the forward reaction is lower.