What is a sea surface temperature anomaly?
An area of ocean that is either significantly cooler or warmer than the long-term average for that area.
What is a biome?
Biomes are large biological communities shaped by the physical environment, particularly climatic variation.
How does natural selection operate?
Selection occurs based on individuals fitness -- acts on phenotype and whole organism, not on genes!
What kind of species interaction is competition?
Negative Negative
Why is biodiversity important?
Why do we have hadley, ferrel and polar circulation cells instead of just 1 for N/S hemisphere?
Earth's rotation / Coriolis effect
How deep does the photic zone extend?
To where light reaches enough for phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis / 200m
What is genetic drift and why does it especially impact small populations?
Changes in allele frequency due to chance. In smaller pops can randomly eliminate or fix genes.
What are some ways competition can be altered?
environmental conditions, disturbance, species interactions, evolution
What does Jaccard's index measure?
Distinctiveness between sites
What is this? Explain the process behind it.
Rain shadow - area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
What's the difference between lentic and lotic?
lentic – non-flowing water (ponds, lakes, wetlands)
lotic – flowing water (rivers and streams)
What is a geographic cline?
Changes in population along gradient
What do we expect to see in a healthy predator-prey dynamic?
fewer predators than prey, growth of both species cycles, predators lag behind prey in population
What three processes determine species richness?
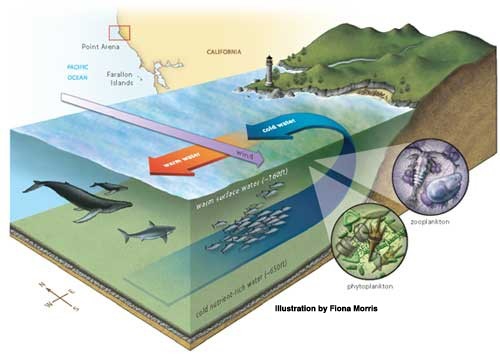
Describe the process of upwelling and why it's important
What is desertification?
Desertification is not the natural expansion of existing deserts but the degradation of land in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas. It is a gradual process of soil productivity loss and the thinning out of the vegetative cover because of human activities and climatic variations such as prolonged droughts and floods.
What are some disadvantages of sexual reproduction?
Only half of genome transmitted
Half of individuals can’t reproduce/have to find mate
Can lead to loss of beneficial combinations
Resources put to finding/selecting/fighting for mate
(intra vs intersexual selection)
What is the difference between an endoparasite and an ectoparasite?
ecto live on body, endo live inside of host
What is the island theory of biogeography?
What are the major soil horizons, and how is soil formation determined?
O =organic layer
A = surface
B = subsoil
C = substratum
Climate, Organic material, Relief, Parent Material, Time
What conditions/factors would help you identify a biome as Boreal Forest (Taiga)
Between 50° and 65° N.
Cold, dry winter and short, cool summer
Evergreen trees are primary vegetation
Cold, wet conditions limit decomposition, so soils have high organic matter.
What is the r-K continuum, and what does r-selected mean?
The r–K continuum is a spectrum of population growth rates, from fast to slow. On the r-selected end: short life spans, rapid development, early maturation, low parental investment, high rates of reproduction.
What is a parasitoid?
Unique parasite that lays eggs in/on another organism, eggs hatch and consume host
What is NPP?
Net Primary Productivity -- GPP (gross primary productivity) - respiration/energy used for growth and reproduction
It is the energy stored in plant tissue available to heterotrophs