What is the Galliverdin phenomenon?
The Galliverdin phenomenon is a physical exam finding in patients with aortic valve stenosis. Auscultation at the cardiac apex reveals a murmur that sounds holosystolic and may mimic the murmur of mitral regurgitation. This is the result of radiation of the murmur of aortic valve stenosis to the apex rather than coexistent mitral regurgitation.
Handgrip exercises or transient arterial occlusion increases afterload and will increase the murmur of mitral regurgitation while not changing that of aortic stenosis
26-year-old male with no PMHx presents with 2 days of headache, malaise, and myalgia. He recently returned from a 2-week camping and hiking trip in eastern Pennsylvania. Temp is 100.4. There is no nuchal rigidity. Next best step in management?
IV Rocpehin
LP and CSF analysis
Western blot test for Lyme disease
Doxycyline PO
ELISA to check for Borrelia burgdorferi
Early localized Lyme disease (within 1-2 weeks of transmision):
Serologic testing is often falsely negative in early infection due to an incompletely developed humoral antibody response. Therefore, pateints are diagnosed clinically and treated empirically with PO doxycycline.
Describe this skin finding!
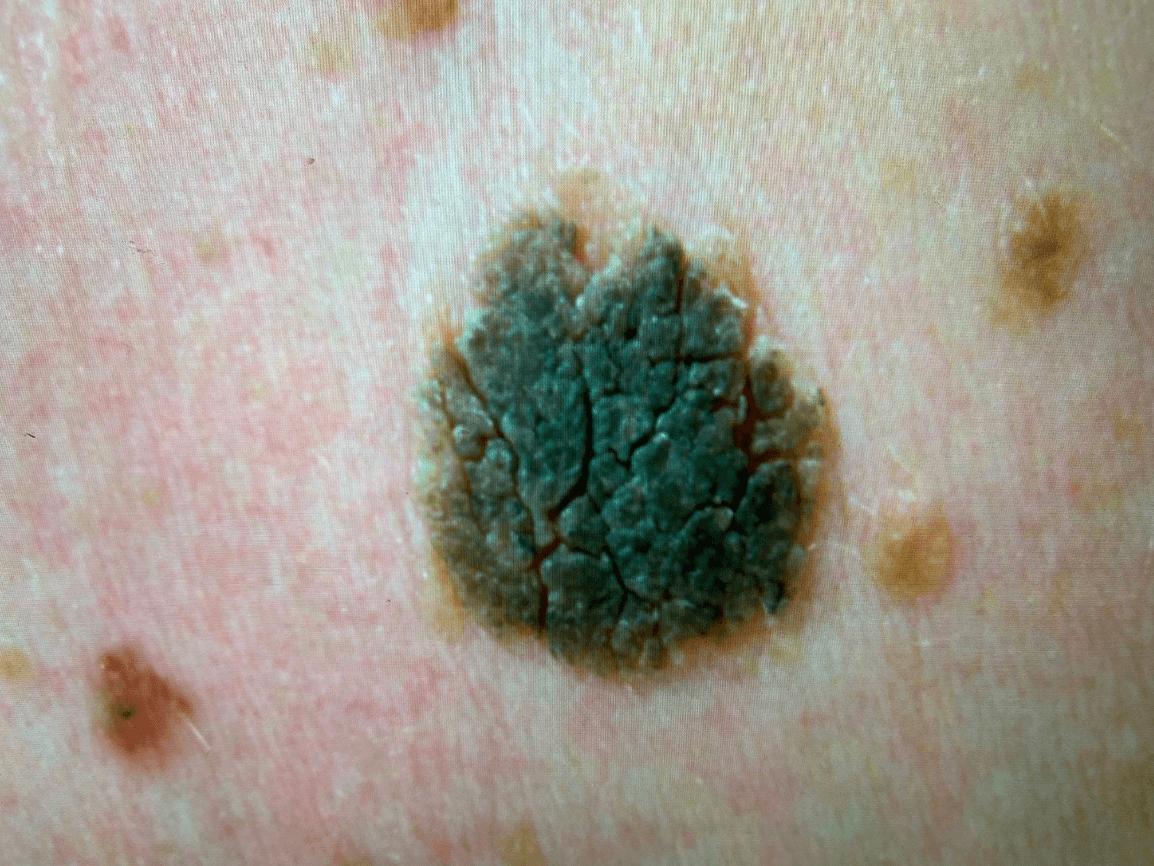
Seborrheic keratosis - benign proliferation of immature keratinocytes. They are usually well-demarcated, round or oval lesions with a typical stuck-on appearance!
___ is characterized by loss of shoulder movement accompanied by pain; examination discloses significant loss of both active and passive range of motion.
Adhesive capsulitis
Adhesive capsulitis may be idiopathic (primary adhesive capsulitis) or secondary to several conditions (secondary adhesive capsulitis). Secondary conditions include diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, prior surgery or trauma, prolonged immobilization, autoimmune disorders, and stroke.
Acetaminophen achieves peak concentrations at what time point after ingestion?
Between 45 minutes to 2 hours after ingestion
Middle aged female presenting with dyspnea. Previous mastectomy for breast carcinoma. What does the ECG show?
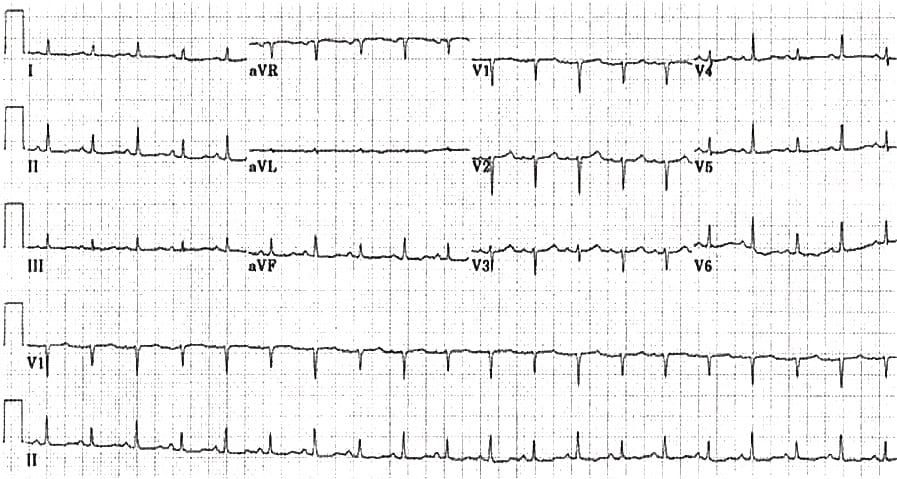
The triad of tachycardia, low QRS voltages and electrical alternans is extremely suspicious for massive pericardial effusion!
Abx for fulminant C.diff? (Hypotension or shock, ileus, or megacolon )
Oral Vancomycin (500 mg four times daily) plus parenteral metronidazole (500 mg every 8 hours)
What is this skin condition? Bonus: what is the treatment?
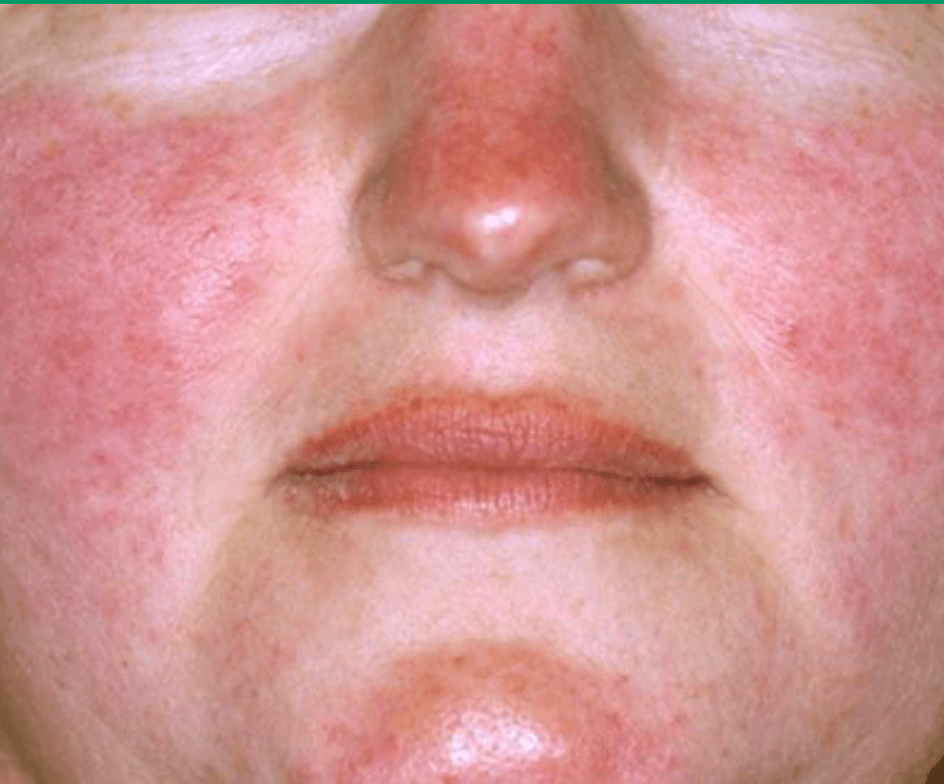
Rosacea - topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, ivermectin
Physical exam test to confirm Achilles tendon rupture?
No plantar flexion w/ calf squeeze (Thompson test)
When do you give patients Naloxone to take home?
Pts receiving ≥50 morphine milligram equivalents daily of prescribed opioids
20-year-old female who presented to the Emergency Department following an episode of chest pain!
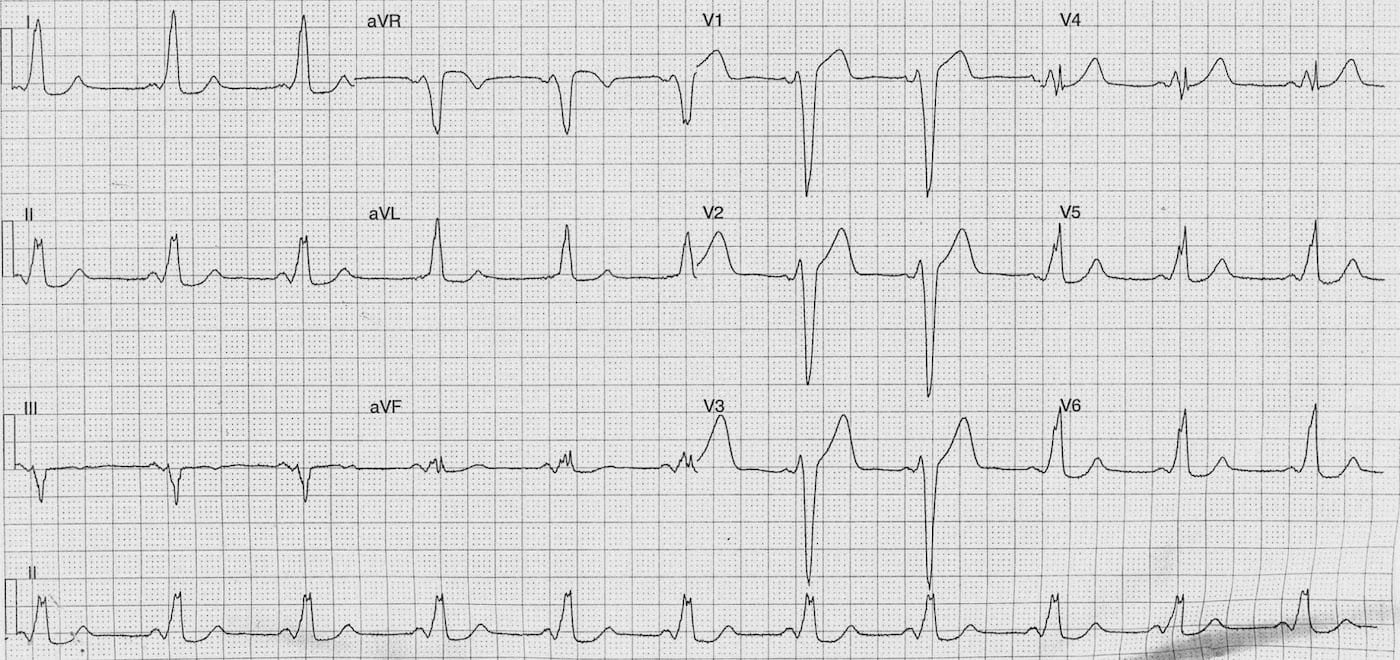
Wolff-Parkinson-White
PR – Short (100ms)
QRS – Prolonged (140-160 ms)
Delta waves best seen in lateral precordial leads
Postmenopausal woman w/ recurrent UTIs (>2 in 6 months or >3 in 1 year) failed cranberry products, d-manose, topical vaginal estrogen cream.. most effective treatment?
Prophylactic ABX -- Bactrim or Macrobid are options
How do you treat this condition and for how long?
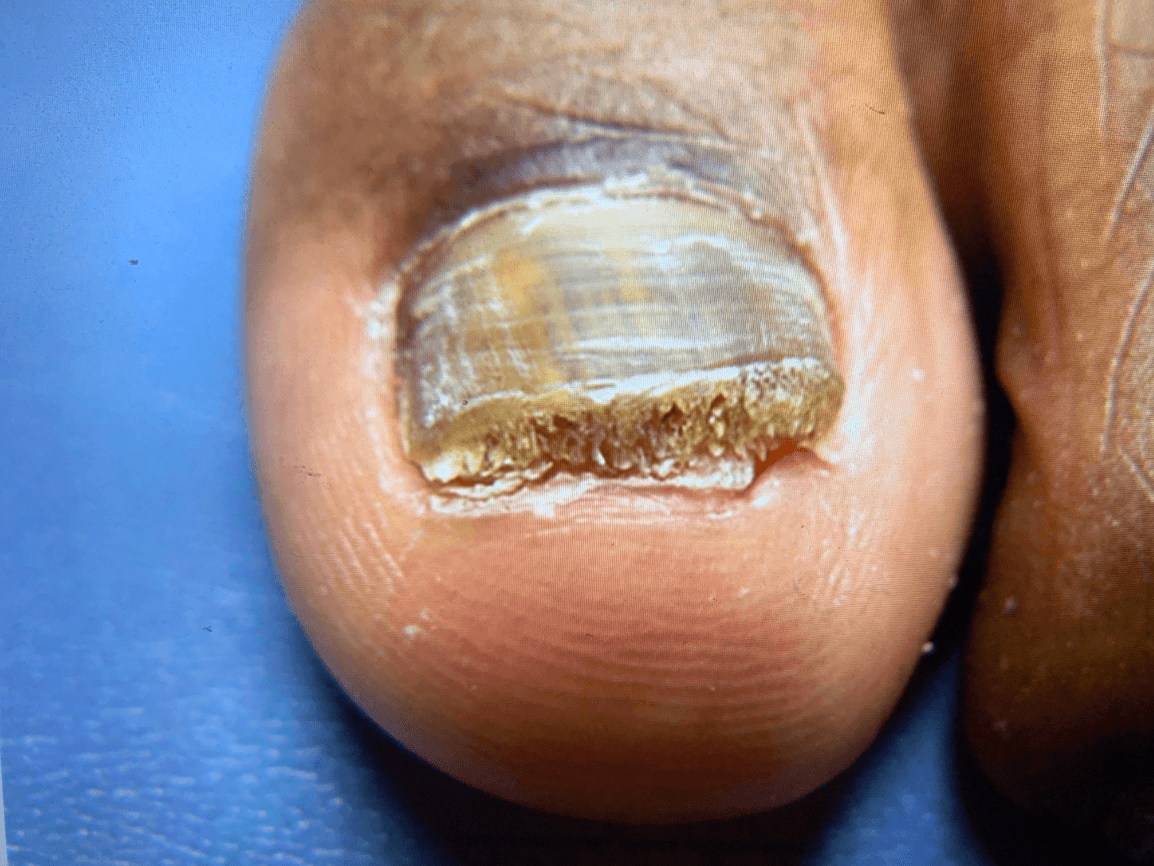
Onychomycosis - Terbinafine 250 mg daily for 12 weeks
28 year y/o male returns from 2 week vacation where he engaged in permiscuous behavior. He recalls having dyuria which he ignored. Now has has progessive back pain and pain in elbow and MCP. What is this called?
Reactive arthritis. (formerly Reiter’s syndrome)
Bugs to consider: Chlamydia trachomatis, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile, and Chlamydia pneumoniae
TX: treat underlying condition + NSAIDs
**Migratory Tenosynovitis is similar w/ gono
For patients undergoing orthopedic surgery without increased bleeding risk, postoperative dual venous thromboembolism prophylaxis with intermittent pneumatic compression and low-molecular-weight heparin is recommended during hospitalization; low-molecular-weight heparin should be continued for up to ___.
35 days.
The ACCP guideline identifies hip arthroplasty, knee arthroplasty, and hip fracture surgery as major orthopedic surgeries.
This 53-year-old male presented to ED following an episode of collapse!
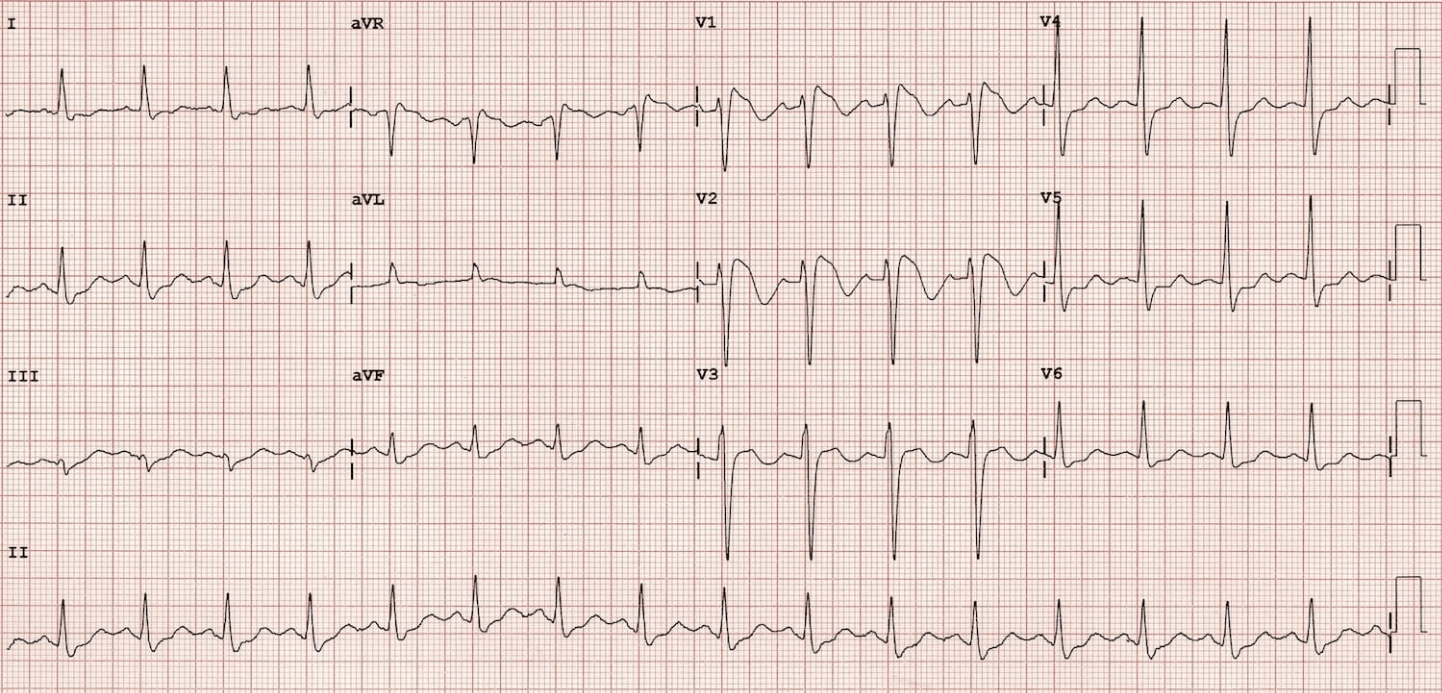
Brugada sign:
Coved ST segment elevation >2mm in >1 of V1-V3 followed by a negative T wave.
This is the only ECG abnormality that is potentially diagnostic.
This ECG abnormality must be associated with one of the following clinical criteria to make the diagnosis:
VF, polymorphic VT, Family history of sudden cardiac death at <45 years old, Syncope, nocturnal agonal respiration.
A 26-year-old immigrant from South America comes to the ED with palpitations and lightheadedness. He is found to have VT, which is terminated by IV amio. Echo shows a dyskinetic and think left ventricular apex consistent with apical aneurysm. Angio shows no coronary artery obstruction. Which is the most likely cause?
Alcohol consumption
Borreliosis
Giant Cell Myocarditis
Protozoan infection
Coxsackie myocarditis
Chagas Disease: caused by Trypanosoma cruzi. Most common in Mexico, Central & South America
Biventricular HF with cardiomegaly
Ventricular apical aneurysm
Mural thrombosis with embolic complications
Fibrosis leading to conduction abnormalities
Progressive dilation of esophagus & colon
A 29-year-old male presents with nodules under his arm. He reports a 6-month history of slowly enlarging nodules in his right axilla associated with mild discomfort. He has a history of chronic obesity but is other wise healthy. What is the best next step?
I&D
Topical nystatin powder
Oral Doxycyclin
Surgical excision
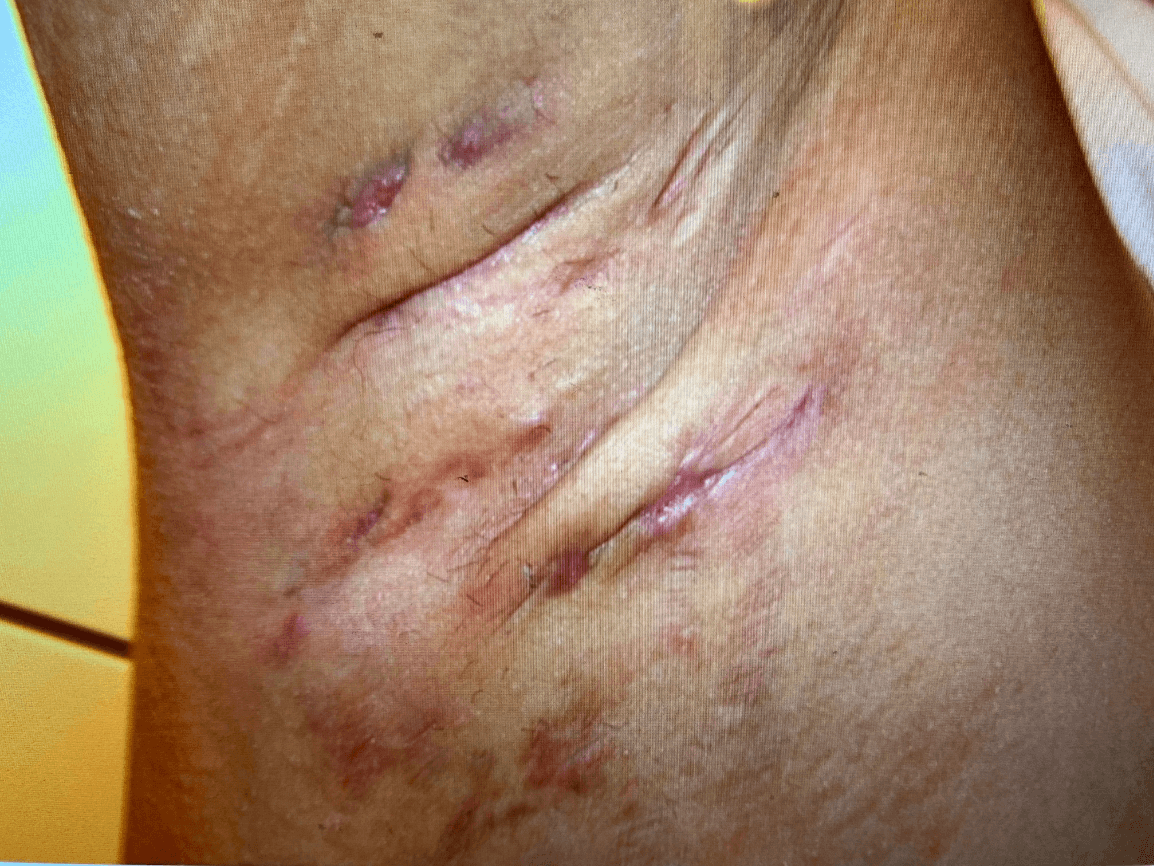
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Chronic inflammatory skin disease manifesting as recurrent inflammatory nodules, abscesses, sinus tracts and scar formation
Treatment: Hurley stage II (moderate disease with nodules, sinus tracts & scarring) - oral tetracyclines
Most frequently observed UA finding in Lupus Nephritis patient?
Proteinuria.
Dr Newmans recent email-- if proteinuria is less than 500 does not warrant kidney biopsy unlikely to have a class of nephritis that warrants immunosuppressive therapy
Up to 10 percent of patients with lupus nephritis develop end-stage renal disease, and patients with lupus nephritis have a higher mortality than SLE patients without lupus nephritis
Pt comes in after mistakenly taking his entire bottle of propanolol -- his fasting glucose is 40 but he feels fine. What is the mechanism for hypoglycemia? Why doesn't he feel symptomatic?
The mechanism responsible for β-blocker–induced hypoglycemia involves inhibition of hepatic glucose production, which is promoted by sympathetic nervous stimulation. In addition, adrenergic counterregulation is diminished, resulting in a reduction in glycogenolysis
B blockage = no tremor and or palpitations
64-year old female presenting with severe chest pain and diaphoresis. Describe the rhythm!
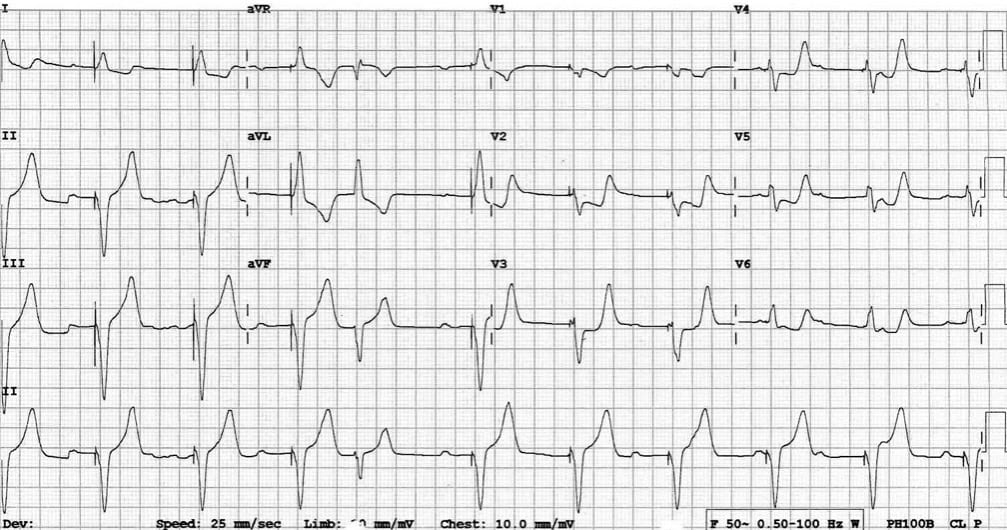
This ECG shows a ventricular paced rhythm with positive Sgarbossa criteria:
There is concordant ST depression in V2-5. This violates the expected pattern of discordance for a V-paced rhythm and is a marker of superimposed myocardial infarction
Pt with TB is newly diagnosed w/ HIV. Pt is started on antiretroviral therapy as well as 4 drug TB treatment. He gets better at first but then 3days after forms fever 103.2 w/ worsening hilar lymphadenopathy and worsened lung opacity. What is going on?
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS) -- paradoxical worsening of infectious symptoms
What is the FDA-approved monoclonal antibody treatment for refractory moderate-severe atopic dermatitis?
Dupilumab (Dupixant) - 300 mg SC q2weeks
Binds to and inhibits IL-4, interfering with IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines, reducing inflammation and altering immune response
Pt on your service falls at bedside and breaks femur and you are assessing for compartment syndrome-- other than your clinical impression what threshold of compartment pressure would confirm your suspicion?
-ACS most often develops soon after significant trauma, particularly involving long bone fractures of the lower leg or forearm.
-The classic findings associated with arterial insufficiency are often described as signs of ACS, but this is inaccurate. Of the five classic signs of arterial insufficiency (five P’s: pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesias, cold skin temperature]), only pain is commonly associated with compartment syndrome, particularly in its early stages. Paresthesias may also occur.
-When interpreting compartment pressure measurements in patients with clinical findings suggestive of ACS, literature suggests using a difference between the diastolic blood pressure and the compartment pressure of 30 mmHg or less as the threshold for an elevated compartment pressure.
Trend the pressures-- down trending might not necessitate fasciotomy
*can also use MAP also want 20-30 delta
Serotonin syndrome and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) and anticholinergic toxicity are often tested together and confused -- what is a physical exam finding that is unique to SS?
Spontenous clonus is much more suggestive of SS. NMS involves sluggish neuromuscular responses (rigidity, bradyreflexia)
NMS develops over days to weeks whereas serotonin syndrome develops over 24 hours