The theory that the laws of mechanics are the same in steadily moving reference frames as they are in inertial reference frames. The first person to say that motion is relative to your frame of reference.
What is Galilean Relativity?
Newton built on what this giant did. Einstein and others were trying to get maxwell's equations, which required the speed of light to be the same in every reference frame, to fit in the relativity of Galileo and Isaac Newton.
The theory that there is no preferred reference frame, and therefore, no ether. It does not include considerations for acceleration or gravity, but only inertial systems.
What is special relativity?
This theory states that acceleration and gravity are indistinguishable, and is founded on a set of 10 tensor calculus field equations.
What is the General Theory of Relativity?
The city in which Albert Einstein developed his theory of special relativity as well as 4 other key theories in 1905.
What is Bern, Switzerland? (Just Switzerland will give you 1/2 points.)
The study of objects in one reference frame as seen from another reference frame that is moving with respect to the first.
What is relativity?
This scientist who was born in the year that Galileo died, supported Galileo's theory of relativity.
Who is Isaac Newton?
One of the authors of what is now referred to as the special theory of relativity. The 1st author.
Who is Hendrik Lorentz (1890)? Albert Einstein came up with a more complete analysis a few years later.
A strong gravitational field that is so strong that even light cannot escape, since the "escape velocity" is greater than the speed of light.
What is a black hole?
Einstein's job when he published his theory of relativity.
What is a clerk at a patent office?
This equation shows the relationship between light's energy and its frequency.
What is E=hf or 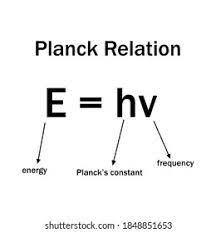
He came up with a heliocentric model of the universe.
Who is Copernicus?
The length of an object as measured by an observer moving with the object - in the same reference frame.
What is proper length or rest length?
 The phenomenon by which massive distant galaxies contain enough matter to deflect the light of even more distant objects that would not be visible from earth otherwise, and cause what appears to be 2 - 4 objects from the one.
The phenomenon by which massive distant galaxies contain enough matter to deflect the light of even more distant objects that would not be visible from earth otherwise, and cause what appears to be 2 - 4 objects from the one.
What is Gravitational Lensing?
This prediction by Einstein's general relativity theory was what verified by Eddington during an eclipse of the sun.

This man sent an assistant to see Einstein in Switzerland in 1907 regarding his theories put forth in 1905.
Who is Max Planck?
"Maxwell Smart"... lose 400 pt.
These unstable subatomic particles (with a very short life), somewhat smaller than protons (about 1/9th the mass), part of the lepton group. They have either a + or - charge with spin of 1/2, and with a mass between that of electrons and protons. Scientists first recognized that general relativity time dilation occurs near large masses, similar to special relativity time dilation based on these particles.
What are muons?
DNA damage is known to be caused by these particles resulting in aging, mutations and disease. Gravitational time dilation was shown to lengthen the life of these particles, further evidence of Einstein's General theory of Relativity.
A reference frame that is not accelerating, but at rest or moving at a constant velocity.
What is an inertial reference frame?
The mass of an object as measured by one who is not moving (at rest) with respect to the object.
What is rest mass? Proper mass OK.
This occurs when light's wavelengths are distorted by gravity as objects move away from us.
What is a gravitational red shift?
It is essentially the doppler effect for light. Hubble used this to convince Einstein that the universe is expanding.
This value is written as c in Einstein's famous theory of relativity E=mc2. 3.0 x 108 m/s
What is the speed of light?
The phenomenon by which a moving clock runs slower.
What is the clock paradox? Time paradox OK for 1/2 points.
This was theorized to be a colorless, odorless, weightless substance that fills space around transparent objects. (disproved) It was required to try to explain how light must vary in its speed between reference frames, just as other objects.
What is the aether? (ether)
Even Einstein supported it for a time.
This equation, E0 = MoC2, is used to find the energy of a mass at rest.
What is the equation for Rest Mass Energy?
Corrections to this planet's orbit was predicted by Einstein's field equations (General relativity) - the first evidence supporting General Relativity. This planet is close to the sun.
What is Mercury?
For his explanation of this, Einstein received his Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
What is the photoelectric effect?
This Dutch physicist won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1902 and created the accepted alternative to Galilean Transformation named after him.
Who is Hendrik Lorentz?