A 6-year-old boy develops periorbital edema and heavy proteinuria. Creatinine is normal. Light microscopy and immunofluorescence are normal. Electron microscopy shows diffuse podocyte foot process effacement. He responds rapidly to steroids.
Minimal change disease
A 70-year-old woman is started on hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension. Two weeks later, she presents with confusion. Labs show: Na⁺: 119 mEq/L, K⁺: 3.3 mEq/L
Which diuretic is most likely responsible for her these lab findings?
Thiazide diuretic acts in the distal convoluted tubule, causes Na⁺ loss while water can still be reabsorbed
Not potassium sparing
A 60-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, and jaundice for the past 24 hours. She reports nausea but no vomiting. On examination, she is febrile (38.9°C), hypotensive (BP 88/56 mmHg), and tachycardic (HR 115 bpm). Murphy’s sign is negative. Labs reveal: WBC: 18,000/mm³, AST: 120 U/L, ALT: 135 U/L, ALP: 420 U/L, Total bilirubin: 5.2 mg/dL.
Ultrasound shows a mildly dilated common bile duct (10 mm) without gallstones visualized in the gallbladder.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Ascending cholangitis
Charcot's triad!
A newborn infant has not passed meconium in 2 days. Distended abdomen is appreciated on exam. During digital rectal examination, gas and stool is expulsed. What is the diagnosis?
Hirschsprung disease
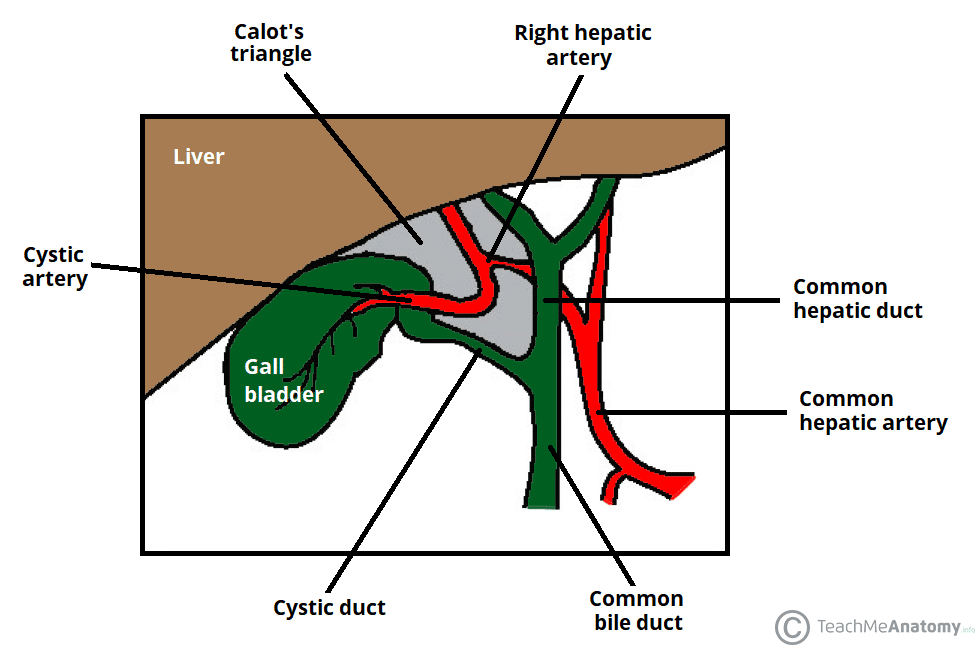
A 45-year-old woman presents with right upper quadrant abdominal pain, fever, and nausea. She is scheduled for a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. What important anatomical landmark should be identified to find the cystic artery, and what are its borders?
Triangle of Calot
A 42-year-old man with chronic back pain has been taking high-dose ibuprofen daily for several months. He presents with new-onset peripheral edema and frothy urine. Urinalysis shows heavy proteinuria. Renal biopsy demonstrates podocyte injury associated with a hypersensitivity reaction.
What is the most likely mechanism of his kidney injury?
NSAID-induced nephrotic syndrome due to a hypersensitivity reaction.
Mechanism: Hypersensitivity/allergic reaction
This is NOT prostaglandin-mediated
A 67-year-old man with heart failure is started on a new diuretic in addition to his loop diuretic. Two weeks later, labs show: K⁺: 5.8 mEq/L, Na⁺: mildly decreased
Creatinine: stable
Which class of diuretic was most likely added?
Potassium-sparing diuretic
ex: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs)
A 35-year-old patient is anticipating dinner after seeing a cooking show. Vagal stimulation activates parietal cells in the stomach. Which phase of gastric secretion is primarily responsible for this increase, and which mediator directly stimulates the parietal cells?
Cephalic phase, acetylcholine
A 4-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents due to painless rectal bleeding that began 6 hours ago. The parents report that he has passed three maroon-colored stools. He has no history of abdominal pain, fever, or recent trauma. He has been otherwise healthy with normal growth and development. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 110/min, respirations 22/min, and blood pressure 95/60 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a well-appearing child with mild conjunctival pallor. The abdomen is soft and nontender without masses or organomegaly. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin of 9.8 g/dL (normal: 11-13.5 g/dL). What scan do you want to order?
A technetium-99m pertechnetate scan will diagnose Meckel diverticuum
What organ is this?

Colon.
Normal colonic mucosa has crypts containing abundant goblet cells that secrete mucin. There is an underlying submucosa. Small nodules of gut-associated lymphoid tissue.
A 45-year-old woman with chronic knee pain has been taking high-dose NSAIDs for several weeks. She presents with acute kidney injury.
She reports low-grade fever and malaise. Laboratory studies show rising creatinine. Urinalysis reveals sterile pyuria.
What is the most likely diagnosis? Why?
Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
Caused by a hypersensitivity reaction
Common trigger: NSAIDs
Immune-mediated injury of the renal interstitium
A 24-year-old man is brought to the ED with confusion and rapid breathing. He has been vomiting for two days. Labs show:
Na⁺: 140 mEq/L, Cl⁻: 100 mEq/L, HCO₃⁻: 10 mEq/L
Calculate the anion gap.
Does this patient have an anion gap metabolic acidosis?
List common causes of this acid–base disturbance.
Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
A 10 year old girl presents to the emergency department with severe epigastric pain radiating to the back, nausea, and vomiting that began 6 hours ago. She reports two similar episodes over the past year. Vital signs are temperature 37.8°C (100°F), pulse 102/min, and blood pressure 128/84 mm Hg. Physical examination shows epigastric tenderness without guarding or rebound. Laboratory studies suggest pancreatitis. Abdominal ultrasound shows no gallstones or biliary dilation. MRCP demonstrates a pancreatic duct draining through the minor papilla with a small ventral duct entering the major papilla. The pancreatic parenchyma appears normal without any encircling tissue around the duodenum. What is the anatomical variant called?
Pancreatic divisum, characterized by failure of fusion between the dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts during embryologic development.
A 58-year-old woman with a 15-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the clinic with a 6-month history of early satiety, postprandial fullness, nausea, and intermittent vomiting. She reports that symptoms worsen after eating solid foods and improve when she consumes liquids. Her hemoglobin A1c is 8.2%. Physical examination shows mild epigastric tenderness without distension or masses. Upper endoscopy reveals no mechanical obstruction or mucosal abnormalities. Gastric emptying scintigraphy demonstrates 65% retention of a solid meal at 4 hours (normal <10%). What is the first-line medication and MOA?
Metaclopramide - enhances acetylcholine release in the gut to increase motility
A 35-year-old woman presents with 1 year of intermittent diarrhea, bloating, and fatigue. What part of the GI tract is this biopsy taken from and what is the disease?
Duodenum, celiac disease
A 46-year-old woman presents with persistent hypertension despite two antihypertensive medications. She reports muscle weakness and intermittent paresthesias. Laboratory studies reveal: Na⁺: High-normal, K⁺: 2.9 mEq/L, HCO₃⁻: Elevated, Plasma aldosterone: Elevated.
Two different patients with this biochemical profile undergo further evaluation:
Patient A: Plasma renin activity is suppressed, CT scan shows unilateral adrenal mass
Patient B: Plasma renin activity is elevated, imaging shows significant unilateral renal artery narrowing
For each patient:
Identify the type of hyperaldosteronism
Explain the renin–aldosterone relationship
Patient A
Diagnosis:
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Patient B
Diagnosis:
Secondary hyperaldosteronism
A 72-year-old woman is started on hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension. Two weeks later, she presents with confusion and mild nausea. She drinks large amounts of water daily because she believes it is “good for her kidneys.”
Vital signs are normal. Physical exam shows no edema, no orthostasis, and moist mucous membranes.
Laboratory studies: Na: 118 mEq/L, Serum osmolality: low, Urine osmolality: high, Urine sodium: elevated
BE SPECIFIC: What is the mechanism / what channel was impacted to lead to this?
Sodium reabsorption blockade in the distal convoluted tubule.
Thiazides block the Na⁺/Cl⁻ cotransporter in the DCT.
A 42-year-old woman presents to the clinic for routine follow-up 18 months after undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. She reports progressive numbness and tingling in her feet over the past 3 months. She has been taking a daily multivitamin but admits inconsistent adherence. On examination, she has decreased sensation to light touch and vibration in both feet in a stocking distribution, with preserved deep tendon reflexes. Gait is mildly ataxic. What is the pathophysiology of her symptoms?
Gastric bypass (specifically Roux-en-Y) causes vitamin B12 deficiency due to decreased gastric acid and intrinsic factor (IF) production in the excluded stomach.
A 52-year-old man presents with fatigue and pruritus for several months. He denies alcohol use. Physical exam shows mild jaundice and excoriations on the arms. Labs show: AST: 82 U/L, ALT: 95 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase: 620 U/L, Total bilirubin: mildly elevated. Ultrasound shows no biliary obstruction. What disease is this and antibodies would be positive?
AMA (anti-mitochondrial antibody) for PBC (primary biliary cholangitis)
(US rules out PSC because no extrahepatic cause)
A 2-week-old male infant presents with bilious vomiting and abdominal distension. He was born full-term via vaginal delivery and had no complications at birth. On physical examination, the abdomen is mildly distended, and bowel sounds are present. An upper GI series shows the duodenojejunal junction located to the right of the midline and a “corkscrew” appearance of the proximal small bowel.
BE SPECIFIC: How many degrees and around what axis is normal midgut rotation?
270 degrees CCW around SMA
A 64-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes presents with confusion and lethargy. Labs show: Na: 126 mEq/L, Glucose: 820 mg/dL, K: 5.2 mEq/L, Serum osmolality: elevated.
What is the most appropriate initial treatment? (with calculation)
Give insulin. This is translocational hyponatremia from hyperglycemia.
Corrected Na = Measured Na + 0.016 × (Glucose – 100)
126 + 0.016 × 720
≈ 126 + 11.5
≈ 137.5 (normal)
Treatment = fix glucose → give insulin.
A 50-year-old man with a history of poorly controlled diabetes mellitus presents with confusion and lethargy. Vital signs: BP 110/70 mmHg, HR 105 bpm. Laboratory studies reveal: Na⁺: 162 mEq/L, K⁺: 4.2 mEq/L, Glucose: 120 mg/dL, BUN: 35 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.2 mg/dL.
He weighs 70 kg. He appears dry, with decreased skin turgor and dry mucous membranes.
What is the diagnosis (BE SPECIFIC: use calculation) and what side effect must be avoided with treatment?
This patient has an estimated free water deficit of 6.6 L, which should be corrected gradually (no more than ~10–12 mEq/L Na⁺ per 24 hours) to avoid cerebral edema.
Free Water Deficit = TBW x [(Current Plasma [Na+] / Target) – 1] = (70 x 0.6) x [(162/140) - 1] = 6.6
A 10-year-old boy presents with recurrent episodes of epigastric pain and nausea. Laboratory studies during an episode show elevated serum amylase and lipase. His father and paternal grandfather both had chronic pancreatitis beginning in childhood. Genetic testing identifies a mutation that increases autoactivation of trypsinogen within the pancreas. What is the gene?
PRSS1 mutations cause hereditary pancreatitis by increasing trypsinogen autoactivation → premature pancreatic autodigestion.
A 55-year-old man with a history of chronic hepatitis C presents with increasing abdominal distension and lower extremity edema over the past 2 weeks. He denies fever, abdominal pain, or gastrointestinal bleeding. On examination, he has a distended abdomen with a fluid wave and shifting dullness.
Paracentesis is performed, and the following results are obtained: Ascitic fluid albumin: 1.2 g/dL, Serum albumin: 2.8 g/dL, Ascitic fluid total protein: 1.0 g/dL,
PMN count: 120 cells/mm³
What is the most likely etiology of his ascites?
Portal hypertension–related ascites (most commonly cirrhosis, heart failure, or Budd-Chiari).
SAAG < 1.1 g/dL would suggest non-portal hypertension causes (peritoneal carcinomatosis, TB, nephrotic syndrome).
PMN < 250 cells/mm³ rules out spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
A 62-year-old man with long-standing hyperglycemia undergoes renal biopsy for progressive proteinuria.
Identify the diagnosis AND list all 4 characteristic histopathologic findings responsible for this patient’s renal disease.
Diabetic nephropathy
Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickening, best seen on electron microscopy
Mesangial expansion, increased mesangial matrix
Nodular glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel–Wilson nodules, PAS-positive, acellular mesangial nodules)
Hyalinosis of both afferent AND efferent arterioles (critical distinguishing feature)