What are the two embryological structures that give rise to the kidney?
1. Metanephrogenic blastema
2. Ureteric bud
All humans have approximately 1 million glomeruli. All glomeruli are formed by X months of age. What is this age and what determines the exact number of glomeruli we develop?
6 months of age --> total number is determined by foetal life.
What is a benefit of combining diuretics in patient treatment?
Less dosage of each, therefore decreased chance of side effects.
EXTRA eg. Thiazide diuretics can --> cause hypokalaemia, worsen diabetes by causing hyperglycaemia and increase risk of gout by promoting increased plasma uric acid.
When does a mesoblastic nephroma occur?
First few months of life
What neoplasm presents with hydronephrosis.
Ureteral cancer
What gene mutation is found in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease?
PKHD1 gene (2 copies --> 1 from each parent)
What microscopic change can be observed in minimal change GN?
Diffuse effacement of foot processes
--> of visceral epithelial cells
Which class of diuretics act exclusively on the distal convoluted tubule?
Give an example for 100 bonus points.
Thiazide diuretics.
eg. Hydrochlorothiaide, Indapamide
What carcinoma is multifocal and bilateral in nature and initially presents with no symptoms, soon followed by haematuria, dysuria, flank pain, fatigue and weight loss.
Renal pelvis urothelial carcinoma
Name the two disorders that can result from prolonged grief.
1. Persistent complex bereavement disorder
2. Prolonged grief disorder
Differentiate between simple cysts and polycystic kidney disease.
Simple cycts are abnormal, fluid filled sacs that form on the kidney, however they don't change kidney function. They increase in incidence as people age.
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that leads to the degradation of kidney function.
In Crescentic GN, the glomerulus is pushed aside by cell proliferating.
a. What is the name of these cells?
b. Where does this proliferation occur?
a. Monocytes
b. Bowman's capsule
What are 3 'factors' that regulate renal blood flow? What is each factors effect on blood vessels?
(Excluding the 3 systems and prostaglandins).
1. Bradykinin --> vasodilation
2. Endothelin --> vasoconstriction
3. Nitric Oxide --> vasodilation
What are the 3 most common presentations of renal cell carcinoma?
Bonus 100 points: what percentage of patients present with each symptom?
1. Haematuria --> 40%
2. Flank pain --> 40%
3. A palpable mass in the flank or abdomen --> 25%
Contrast the terms Loss and Mourning.
a. Loss = Experience when something or someone we are emotionally attached to becomes permanently unavailable.
eg. House burning down, losing a person, possessions like a teddy bear, cat or car
b. Mourning = The process by which people adapt to loss
A 32-year-old male complains of back pain. After being diagnosed with X the doctor instructs the man to restrict protein intake in his diet and take medication to control his blood pressure. He also said X disease causes an increased risk of intracerebral haemorrhage.
a. What condition does the 32-year-old have?
b. What tests can be done for a definitive diagnosis?
a. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
b. imaging (eg. ultrasound, MRI, CT scan) and genetic testing
What is the disease labelled as 'collection of end stage GN' and associated with chronic renal changes? Name 3 of these changes.
Chronic GN
1. Pericarditis
2. Hypertension
3. Hyperparathyroidism
What effect would you expect a non-selective beta adrenergic receptor blocker to have on:
a. Plasma renin level?
b. Plasma renin activity?
c. Plasma angiotensin II levels?
a. Decrease renin level
b. No effect
c. Decreased levels
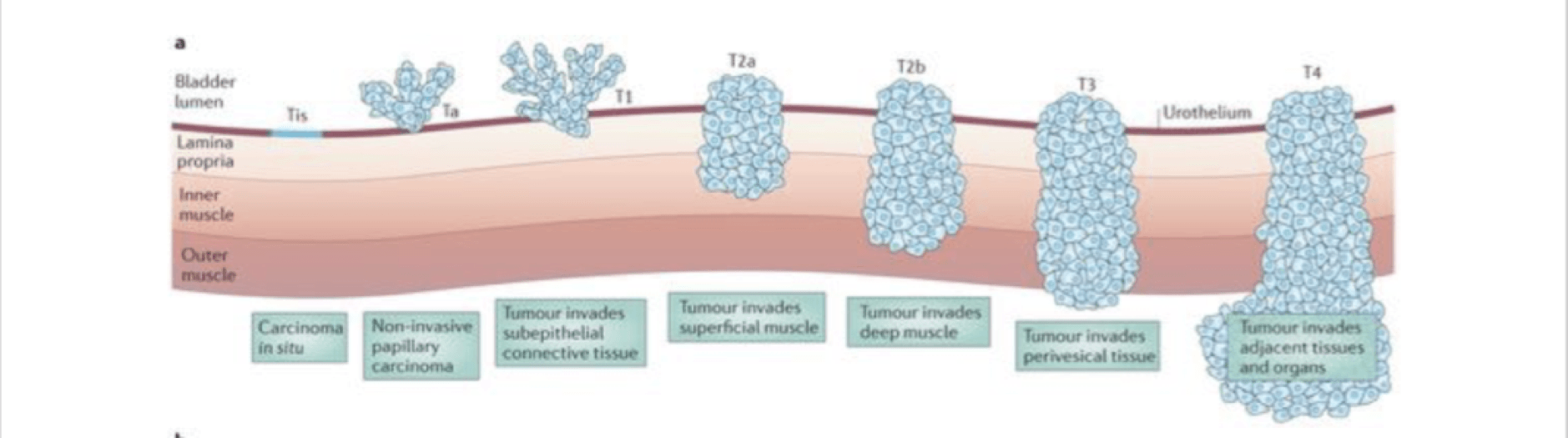
What are the levels of staging of Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and what invasion occurs at each level?
CIS – T1 = invasion of lamina propria
T2 = invasion of superficial muscularis
T3 = invasion through muscularis to subserosal layer
T4 = invasion beyond and to adjacent organs
Contrast complicated, intense prolonged grief and depression.
a. Complicated, intense prolonged grief = persistent yearning and preoccupation with the decreased
b. Depression = pervasive “free-floating” sadness and loss of interest and pleasure
Cystic renal dysplasia is a congenital cystic anomaly.
a. What is this anomaly?
b. When does it occur?
c. Name one macroscopic feature.
d. Name one microscopic feature.
a. Mesonephros and Metanephros not joining properly
b. By week 20 in utero
c. numerous cysts on enlarged kidneys, disorganised parenchyma, between cysts --> immature tubules surrounded by mesenchymal collars
d. congested blood vessels, loose connective tissue
Diffuse proliferative GN occurs post-infection. It presents with both kidneys affected, hyperglomerular cells and lots of inflammatory cells. It has an increased incidence in X populations.
a. What is this population?
b. What infection would you want to know if a patient has recently had?
c. What pathogen causes this infection?
a. Indigenous Populations
b. Throat infection
c. Group A streptococcal (caused by bacteria known as Group A beta-haemolytic Streptococcus)
Antidiuretic hormone is a hormone that targets Vasopressin 2 receptors in the collecting ducts. This increases water reabsorption.
a. What class of drugs can be used to block V2 receptors?
b. Give an example.
c. What is their basic mechanism of action.
d. Give an example of what they are used for.
a. Aquaretics
b. Tolvaptan (selective V2 receptor antagonist)
c. Promote water loss without simultaneous loss of electrolytes
d. Used for management of hyponatraemia in euvolaemic or hypervolaemic conditions --> eg. syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
After hours of tests an intern working with pathology is unable to identify what disease the biopsy contains from a patient with tuberous sclerosis. The consultant then instructs the intern to utilise histochemistry to detect the HMB-45 antibody.
a. What disease does the Pathologist suspect the patient has?
b. Name two microscopic and two macroscopic feature of this disease.
a. Angiomyolipoma
b. MICROSCOPIC = Large thick walled hyalinised blood vessels, adipocytes, surrounding spindle cells
MACROSCOPIC = Yellow in colour, regular edge, expansile growth pattern, small areas of pallor
- A 52-year-old mother suffered a cut to the underside of her jaw which weeks later becomes infected. She begins to realise that maybe this will affect the wedding of her daughter in a few weeks and visits 4 GPs desperately trying to find a way to heal the wound quicker. She starts yelling at her daughter at small inconveniences. Outline each emotional response in the “change curve” model of grief and which response the mother is experiencing.
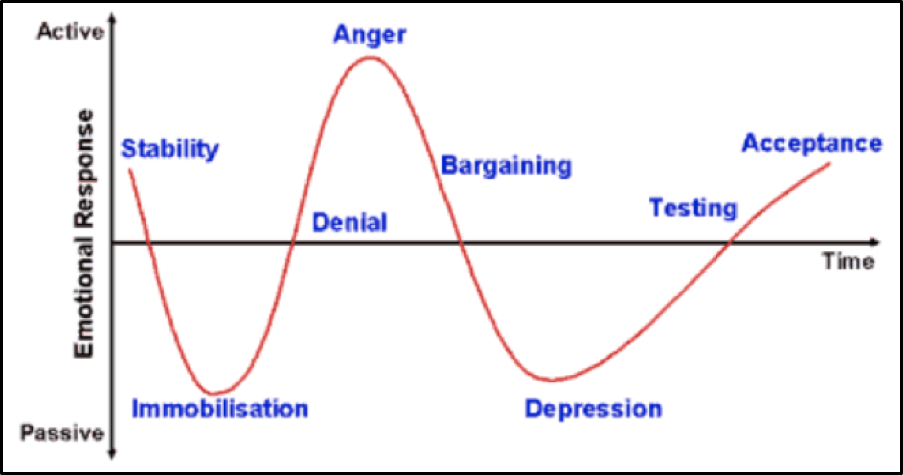
The mother is currently experiencing anger.