Which of the following breath sounds would you NOT expect to hear in a patient with atelectasis?
a. bronchial
b. diminished
c. fine crackles
d. wheezes
d. wheezes
Pulmonary edema is more likely to occur in a patient due to which of the following scenarios?
a. Being in a minor MVA
b. Traveling to higher altitudes
c. Having abdominal surgery
d. Receiving a pneumonia diagnosis
b. Traveling to higher altitudes
Which disease is characterized by a blockage of the pulmonary vascular system?
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Which CXR finding is consistent with a pneumothorax?
a. Bilateral fluffy consolidation
b. Patchy consolidation
c. Absent lung markings
d. meniscus sign
c. Absent lung markings
Which CXR finding is consistent with a pleural effusion?
a. Meniscus sign
b. Hyperlucency
c. Deep sulcus sign
d. Patchy consolidation
a. Meniscus sign
Which treatment would you recommend to treat an atelectatic patient?
a. CPAP
b. Incentive Spirometry
c. Duoneb
d. Supplemental Oxygen
a. CPAP
What is the most common cause of pulmonary edema?
Left sided heart failure (CHF)
Which of these would indicate the presence of a blood clot?
a. Elevated INR
b. Elevated Fibrinogen
c. A white blood cell count of 16,000 per microliter
d. Elevated troponin
b. Elevated fibrinogen
Which complication may occur secondary to a pneumothorax?
a. pleural effusion
b. subcutaneous emphysema
c. pulmonary edema
d. pulmonary embolism
b. subcutaneous emphysema
A pleural effusion is characterized by the accumulation of ________ in the pleural space.
Fluid
Which CXR finding would you expect from a patient with right-sided atelectasis?
a. Hyperlucency
b. A raised right hemi-diaphragm
c. Tracheal deviation toward the left
d. Deep sulcus sign on the right
b. A raised right hemi-diaphragm
Your patient frequently complains of orthopnea. His breath sounds reveal inspiratory crackles bilaterally. Which treatment would help resolve this issue?
a. Furosemide
b. Metoprolol
c. Duoneb
d. Pulmicort
a. Furosemide
Which of the following treatments is indicated when treating a patient who is suffering from an acute myocardial infarction?
a. Nitric Oxide
b. Epoprostenol
c. Nitroprusside
d. Dornase Alpha
c. Nitroprusside
What intervention should be performed on a patient with tympanic percussion notes on the right side, and tracheal deviation toward the left? The patient's vital signs are rapidly deteriorating.
a. insert a chest tube
b. start NIV (Bipap)
c. needle decompression
d. administer streptokinase
c. needle decompression
What complication should you monitor for when draining a large pleural effusion?
a. spontaneous pneumothorax
b. atelectasis
c. flash pulmonary edema
d. asthma exacerbation
c. flash pulmonary edema
A patient with a recent abdominal surgery has developed atelectasis. Which of the following therapies would NOT help resolve this issue?
a. CPAP
b. Increasing the nasal cannula from 2 to 4 L/min
c. PEP therapy
d. IPPB
b. Increasing the nasal cannula from 2 to 4 L/min
Which of the following CXR findings is NOT consistent with cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
a. Hyperlucency
b. Bilateral fluffy opacities
c. An enlarged heart
d. Kerley lines
a. Hyperlucency
What troponin level indicates myocardial ischemia or infarction?
a. greater than 100 pg/mL
b. greater than 10 pg/mL
c. greater than 0.1 ng/mL
d. greater than 1 ng/mL
c. greater than 0.1 ng/mL
Which of the following is contra-indicated in the presence of an untreated pneumothorax?
a. Thoracentesis
b. Aerosolized albuterol
c. Supplemental oxygen
d. Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation
d. Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation
What type of pleural fluid would you expect to drain from a pleural effusion that was caused by CHF?
Transudative
The CXR on the left is before treatment and the CXR on the right is after treatment. What has changed?
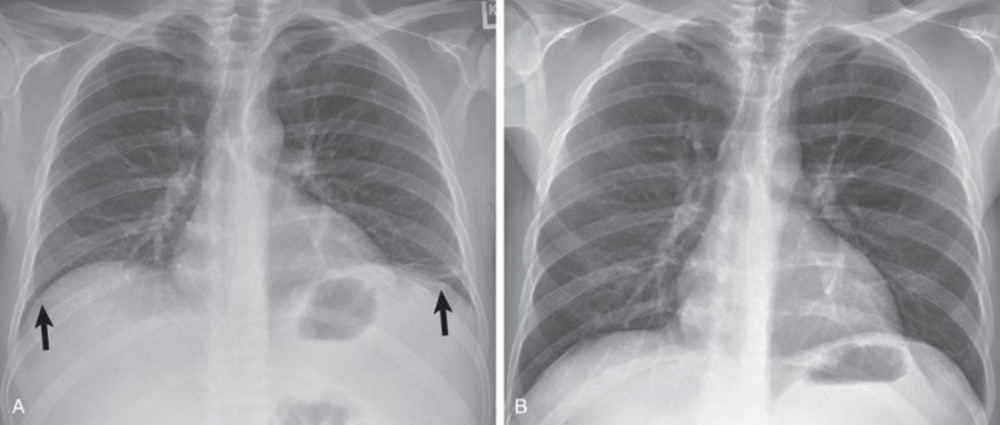
a. pulmonary edema has improved
b. the lungs have been expanded
c. free air in the pleural space has been removed
d. fluid in the pleural space has been drained
b. the lungs have been expanded
Your patient presents in the emergency department and reports mild shortness of breath and production of pink frothy sputum. You note the presence of accessory muscle use, jugular vein distension, and her SPO2 is 85%. Which of the following should the respiratory therapist do first?
a. Order a stat chest X-ray
b. Initiate noninvasive ventilation at 60% FiO2
c. Place the patient on a non-rebreather mask
d. Perform PEP therapy
b. Initiate noninvasive ventilation at 60% FiO2
Which drug can be given to treat a patient with a pulmonary artery pressure of 40/25 mmHg?
a. Epoprostenol (Veletri)
b. Ribavirin
c. Magnesium Sulfate
d. Ventolin
a. Epoprostenol (Veletri)
Which disease is likely present when a portion of a patient's chest cavity moves inward during inspiration?
Flail Chest
An 86-year-old male is admitted for pneumonia. His CXR shows a non-loculated pleural effusion on the right side. What intervention should the RT expect from the care team?
a. CT pulmonary angiogram
b. Bronchoscopy
c. Thoracentesis
d. Bedside PFT
c. Thoracentesis