What is the accuracy range of pulse ox's? Include units.
+/- 4%
What is the normal EtCO2 value? Include units.
35-45 mmHg
Which of the following will display an inaccurate SO2 measurement when there is a shift in the oxyhemoglobin curve?
A: Pulse oximeters
B: Co-oximeters
C: POCT
D: A & C
C: POCT
What is one advantage of the resuscitation bag shown here?

It can provide free-flowing oxygen to an apneic patient
You can feel the stiffness of the patient's lungs during ventilation
How often should a transcutaneous monitor's electrode be moved to prevent tissue damage?
Every 8 hours
Patients with increased metHb levels will have a pulse ox reading that is
around 85%
State an indication for a non-intubated patient to be placed on EtCO2 monitoring.
Conscious sedation
Continuous pain pump
ABGs that are collected in plastic syringes should be analyzed within ______________ of collection.
15 minutes
What adjunct airway is shown here?

Combitube
At what temperature should ISTAT cartridges be stored? Includes units.
35-45 F
List 3 non-invasive ways to assess oxygenation.
Pulse ox
Transcutaneous monitors
Physical assessment
During CPR, your capnography reveals the following. What could cause this capnography tracing?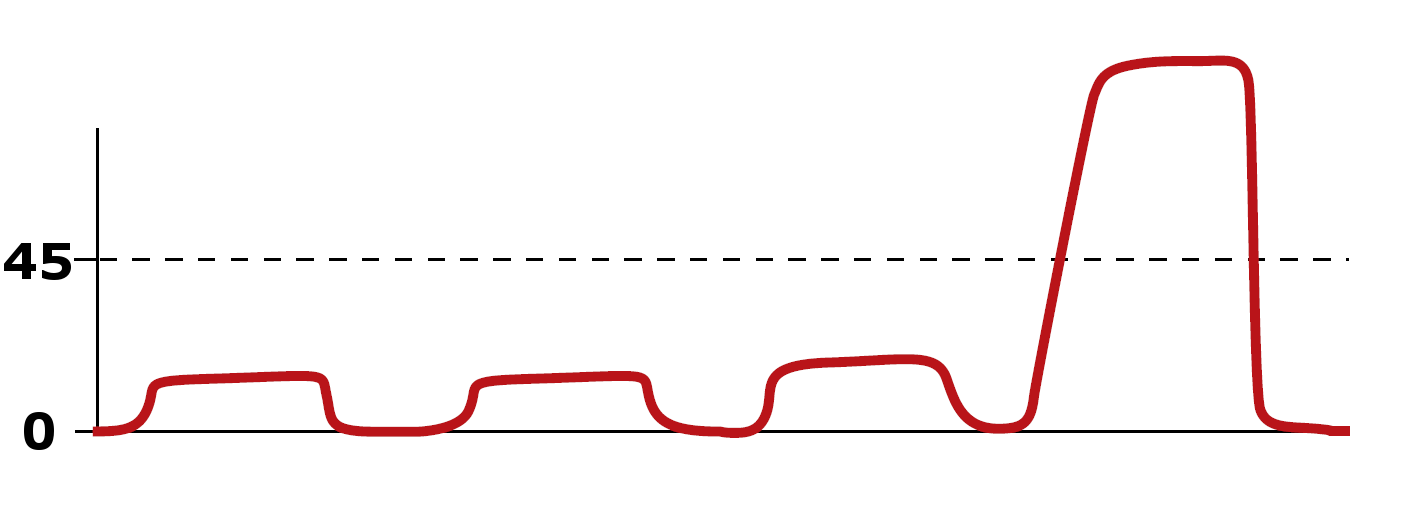
ROSC
How will an air bubble affect ABG results?
PO2 increases toward RA composition and PCO2 decreases toward RA composition
Which adjunct AW can be used in an awake patient?
NPA
What equipment is typically used during sleep studies to measure a patient's RR?
Nasal airflow thermistor
Your patient's vitals are shown here.
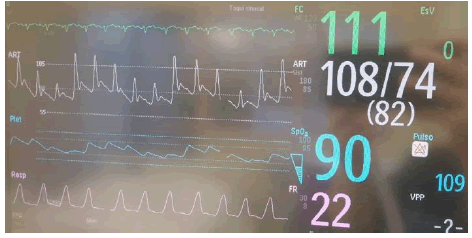
What phenomenon is present in the pulse ox pleth?
What treatment do you recommend?
pulsus paradoxus
SABAs
Your patient's EtCO2 is 32 mmHg and their PaCO2 is 78 mmHg. The equipment is working correctly.
Calculate the patient's VD/VT.
List a cause of the increased deadspace.
58.97% or 59%
Pulmonary embolism
State an indication for a peripheral VBG.
assess tissue oxygenation of a specific body part
When ventilating a non-intubated patient, you should limit pressure to:
What complication does this avoid?
Gastric insufflation
Draw a capnography of a patient who is rebreathing CO2
Label the x and y axis
List 3 causes of a left shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve.
Increased pH (decreased CO2)
Hypothermia
Decreased 2,3 dpg levels
Your patient's EtCO2 has been reading 40-42 mmHg consistently since setup. In the last 20 minutes, the reading has increased to 50-52 mmHg.
List 3 specific causes of an increased EtCO2 reading that you should assess your patient for.
Fever, sepsis, seizure
Sedation, hypoventilation, COPD exac
Rebreathing CO2
CLIA guidelines state that blood gas analyzers must perform QC checks how often?
Every 8 hours
How is an OPA sized?
From the incisors/lips to angle of mandible
List the phases of the capnogram, and describe what occurs in each phase.
State where EtCO2 is measured.
Phase 1: dumping of anatomical deadspace – little to no CO2 present
Phase 2: mixing of anatomical deadpsace with air from alveoli causes CO2 to rapidly rise
Phase 3 (alveolar plateau): air is coming from the alveoli and rises very gradually as little Co2 is added via capillary bloodflow
EtCO2 measured at the very end of exhalation