The primary muscle of inspiration.
What is the diaphragm?
The process of drawing air into the lungs.
What is inhalation?
Amount of air inhaled/exhaled during quiet breathing.
What is tidal volume (TV)?
These muscles elevate the ribs during inspiration.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/external-intercostal-muscles/otuZGFH3IGVuQsIji9IQ3A_pasted_image_0.png)
What are the external intercostals?
Air pressure below vocal folds.
What is subglottal pressure?
Structures that branch off the trachea.
What are the bronchi?
This type of breathing occurs during exercise, singing, or speech.
What is forced breathing?
The process of contraction and relaxation of muscles in the diaphragm and thorax.
What is pulmonary ventilation?
These muscles push the diaphragm upward.
What are the abdominal muscles?
Ratio of inspiration to expiration in speech breathing.
What is 10:90?
______ skeleton provides the structural framework for respiration.
What is the axial skeleton?

Percentage used for expiration during speech breathing.
What is 90%?
The process of lungs and aveoli's ability to contract.
What is respiratory compliance?
Intercostal muscles that depress the ribs during forced exhalation.
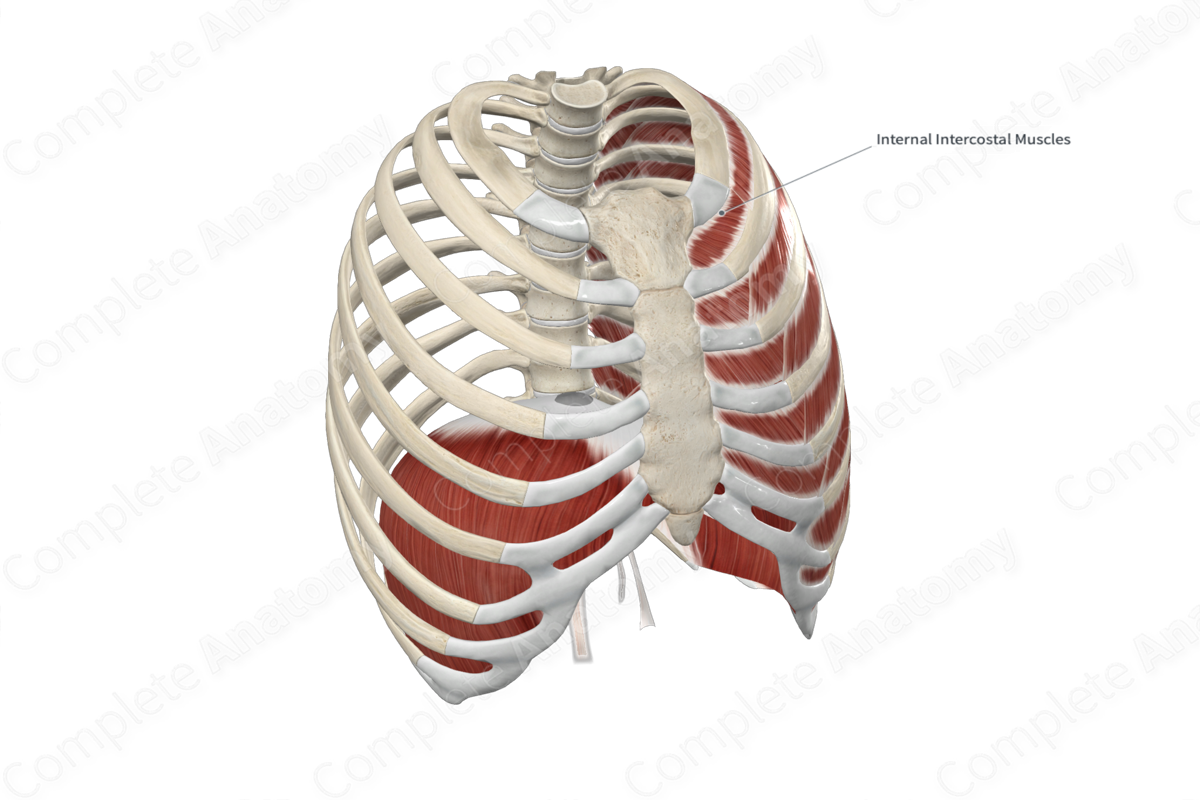
What are the internal intercostals?
Quick inhalation that happens before a long sentence.
What is inspiration for speech breathing?
Main site of gas exchange in respiration.
What are the lungs?
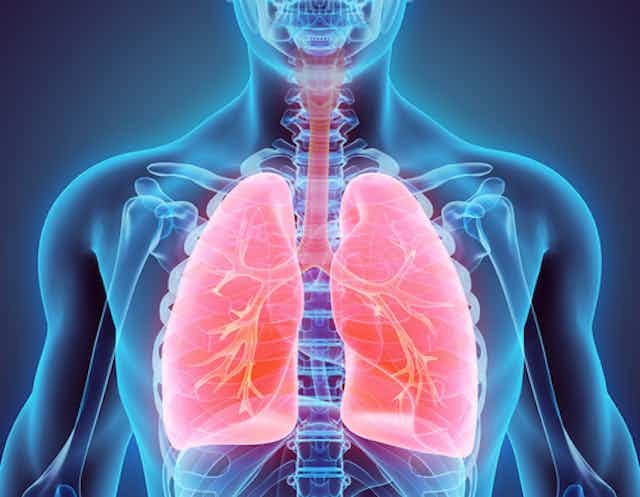
Structure with C shaped cartilage rings.
What is the trachea?
Volume of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation.
What is residual volume?
What is the transversus abdominis?
System that works together with respiration to produce voiced sound.
What is the phonatory system?
Pathways.
What are receptors, bulbs, tracts and cerebral cortex.
Maximum amount of air exhaled after maximum inhalation.
What is Vital Capacity (VC)?
Total amount of air lungs can hold.
What is TLC (total lung capacity)?
Chest muscle that helps elevate the sternum and expands rib cage.
What is the pectoralis major?