The question has alcoholic / intense alc consumption, what should you be thinking?
ASPIRATION
Anaerobes (Fusobacterium, Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus, Prevotella etc)
Abscesses
Big Bugs (Klebsiella and Staph)
Kleb -
- Challenging to grow on culture medium
- Lactose fermenter
- Facultative anaerobe
- Urease
- Capsular
- Treat with Cef, carbapenems, aminoglycosides
Staph -
- Beta-hemolysis
- Mannitol fermenter
- Coag, Cat positive
- Toxins (heat stable enterotoxin (Superantigen))
- Protein A avoid phaco
- Capsular
- Treat with Naf or Vanco if MRSA
JVD and Facial reddness / Swelling
Lung Cancer
Pancoast Tumor: Carcinoma at the apex involve the superior sulcus groove formed by subclavian vessels: ARM EDEMA on the affected side → there is shoulder pain and arm parentheses and weakness → can compress sympathetic chain → Horner's syndrome miosis, ptosis, anhidrosis
Increased Anterior Posterior Diameter or any lateral XR
Emphysema
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency think lung and WHAT OTHER ORGAN?
Complicating measure be careful and think LIVER!!!!!
Lung: Panacinar emphysema, imbalance of neutrophil elastase to destroy elastin and lower lung damage
Liver: Abnormal alpha1 builds up in liver → cirrhosis (due to accumulation in the hepatocytes) (SHOULD NEVER SMOKE)
Glass, Sand, Foundry, Eggshell calcifications, hilar lymphadenopathy
WHAT CAN THIS LEAD TO?
Silicosis --> TB
Pneumonia with Hyponatremia
LEGIONELLA
Frequently accompanied by Diarrhea & GI Issues
Doesn't take up gram stain great even tho gram neg INSTEAD USE SILVER STAIN
Grown on buffered charcoal yeast extract
- Oxidase positive
- Water issues!
Macrolides and Fluoroquinolones (maybe better a less side affects)
Someone is having surgery. Think of what main two things? (Vascular and Lung)
DVT/PE, Atelectisis (Decreased ratio of ventilated alveoli, A right-to-left pulmonary shunt or a V/Q mismatch increases the A-a gradient)
BNP is normal and sepsis
ARDS (increased alveolar capillary permeability and fluid in lungs)
Bleomycin, Busulfan, Methotrexate (esp Bleomycin)
Pulmonary Fibrosis
WHAT ANTIARRYTHMIC ALSO CAUSES THIS?
Aerospace and manufacturing industries
Granulomatous (noncaseating) C on histology and therefore occasionally responsive to glucocorticoids. Increased risk of cancer and cor pulmonale. Affects upper lobes.
The patient is sleepy or somnolent or excessively tired
SLEEP APNEA
OSA leads to inc Erythropoietin which leads to facial redness and swelling
Legit, sometimes the question has a lot of random and confusing stuff. If the question ever says excessive somnolence (not necessarily fatigue), sleep apnea should be #1
Question about a baby and hear Ground Glass Opacities
NRDS Instantly
- Little or no reduction of alveolar surface tension → increased alveolar collapse → atelectasis → decreased lung compliance and functional residual capacity → hypoxemia and hypercapnia
- Hypoxemia and hypercapnia → vasoconstriction of the pulmonary vessels (hypoxic vasoconstriction) and respiratory acidosis → intrapulmonary right-to-left shunt → increased permeability due to alveolar epithelial damage → fibrinous exudation within the alveoli → development of hyaline membranes in the lungs (hyaline membrane disease)
Military Camp or College Dorm think what bug?
What is another super defining feature about this bug in relation to blood?
MYCOPLASMA
NO CELL WALL (CANNOT APPER ON NGRAM STAIN, and instead have STEROLS (cholestrol) to stbalie nad give it flexibility
Associated with the formation of cold agglutinins (IgM) and subclinical hemolytic anemia. → suggests Raynaud phenomenon. In combination with anemia, this should raise concern for a cold agglutinin disease.
Patchy infiltrates or reticulonodular (looks worse)
EATONS-AGAR (Eatin' MY Plasma)
- Treatment: No cell wall, use instead use macrolides like azithromycin
Bell's palsy, Hypercalcemia, Red Eyeballs, Skin changes with lung issues
SARCOIDOSIS
- immune-mediated, widespread noncaseating granulomas A
- elevated serum ACE levels
- elevated CD4/CD8 ratio in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.
- Treatment: glucocorticoids (if symptomatic)
Associated with shipbuilding, roofing, plumbing, Construction. “Ivory white,” calcified, supradiaphragmatic and pleural A plaques are pathognomonic
ASBESTOSIS (NOT ALWAYS MESO. I WANT YOUR BRAIN TO TRAIN TO GO ASBESTOSIS --> BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA & MESOTHELEOMA AND THEN CHOOSE)
NOTE: Risk of bronchogenic carcinoma > risk of mesothelioma.
Inc risk of Caplan syndrome (rheumatoid arthritis and pneumoconioses with intrapulmonary nodules).
Affects lower lobes. Asbestos (ferruginous) bodies are golden-brown fusiform rods resembling dumbbells, found in alveolar sputum sample, visualized using Prussian blue stain B , often obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage. BIG INC risk of pleural effusions
Cough super hard or cough so hard vomit
bortadella pertussis / whooping cough
Very contagious & attaches to respiratory epith thru pilli (Filamentous hemagglutinin / fimbriae / pilli)
Inhibits Gi protein and increases cAMP
Lymphsytosis: overabundances of white cells in lymphocytosis
Macrolides (grows)
Vaccine: dtAP vaccine for acellular pertussis
USE Bordet-Gengou agar

Someone is having a PE (Pleurtic Chest pain, Dyspnea). What does there ABG Almost Always show?
Respiratory Alkalosis
Young Adult with Sudden Dyspnea, Chest Pain, Tall and Thin we think
Think Spontaneous Pneumothorax.
Primary: Rupture of subpleural bleb (a small, air-filled cyst or blister that forms in the tissue that lines the lung, called the visceral pleura) and common in tall, thin young males
Secondary: Older patient with pulmonary disease (more common)
Treat with Chest Tube (2nd intercostal)
Encapsulated Gram Neg, Green Blue agar sweet grapes
PSUEDOMONAS
Oxidase & Catalase positive (chronic granulomatous disease) →
ENCAPSULATED AEROBE!
- Gram Neg Nomosocial Pne & Pulm inf in CF pts
- Treatment: Piperacillin and Taxobactam
Tram Track Lines
BRONCHEACTASIS
Sx: recurrent Inf, cof with excessive sputum (foul), hemoptysis,s cor pulmonale, amyloidosis
Causes: Tumor Obstruction (mucus backs up and inc risk for inf), SMOKING, CF, Kartagener's syndrome

Severe Trauma (eg car crash) and petechiae
ALWAYS FAT EMBOLISM. IF YOU SEE SERIOUS TRAUMA AND PETECHIAE FIRST THOUGHT SHOULD BE FAT EMBOLISM.
After long bone fracture and can lead to small artery infarction. Affects --> Pulm, neuro and skin
- ARDS, Confusion / focal deficits, petechiae
Pleuroperitoneal issue in baby
CHD (Congenital Diaphragmatic hernia).
ORGANS IN THORAX!!!
Pulmonary Hypoplasia results due to impaired growth and inflation of the newborn’s lungs as a result of compression from herniated bowel. There's dyspnea and cyanosis and may result in death unless it can be repaired surgically.
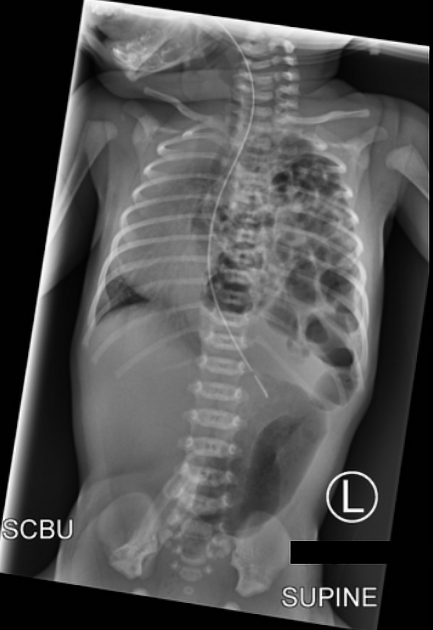
5 days ago Jimmy Dashimme developed rhinorrhea, muscle aches, fv, ha and NOW THYE HAVE INTENSE PNE WHAT IS THE BUG?
Staph Auerus
Night Sweats, Weight loss, Recent Immigration, Healthcare, Prisons, Homeless, IV Drug use
TB, we all know it.
Tell me the treatment, MOA of each drug, and 1 big side affect for each
KEY POINTS
Mycolic Acid cell walls → Acid fast
Infects macrophages Intracellular)
Delayed hypersensitivity reaction
Hilar lymph and ghon omelx
Reactivation upper lobes immunosuppressed
Latent infection diagnosed with ppd
Treat latent disease with INH
Treat active disease with multidrug regimen.
Giemsa Stain
Chlamydia
Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies (reticulate bodies) visible on Giemsa stain
2nd leading cause of atypical pneumonia. Lacks peptidoglycans in its cell wall and is therefore resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g., cefuroxime), which act by inhibiting peptidoglycan crosslinking.
First line is macrolide antibiotic, which inhibits bacterial protein synthesis (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin).