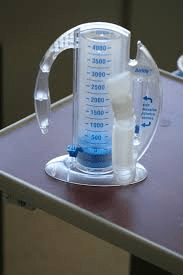
 What is this?
What is this?
What is its purpose?
Incentive spirometer
IS helps to pop open the alveoli sacs and get air moving.
What is one example of a decongestant and what does it do?
Decongestants are medications used to relieve nasal congestion, which is often caused by colds, allergies, or sinus infections. They work by narrowing the blood vessels in the nasal passages, which reduces swelling and allows mucus to drain, clearing up the blocked airways and making it easier to breathe through your nose.
- Temporary relief: They provide temporary relief, so they don’t cure the underlying issue (like a cold) but help manage symptoms.
Examples of Decongestants:
- Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed): A common oral decongestant often found in cold and flu medications.
- Phenylephrine: Found in both oral and nasal spray forms, it's another common decongestant.
- Oxymetazoline (Afrin): A nasal spray that provides relief within minutes.
Caution:
- Nasal sprays: Overuse can lead to "rebound congestion," where your symptoms get worse after stopping the medication.
- Oral decongestants: They can increase blood pressure and may cause side effects like jitteriness or insomnia.
I am chocking on a piece of steak and can't seem to cough it up? What do I have and what is the priority in saving my life?
Airway obstruction due to foreign body
Priority is to promptly identify condition and then open the airway and restore patency
Heimlich maneuver or emergency tracheostomy to remove the obstruction
I produce watery eyes and clear nasal discharge, what am I?
Acute rhinitis
What are varicose veins and how can they be prevented?
Varicose veins are darkened, tortuous raised blood vessels that are more pronounced in prolonged standing. The legs may feel heavy. Patients can have fatigue, pain, and muscle cramps. Legs are edematous and ulcers can be seen.
Prevention:
Elevate legs 10-15 mins at least every 2-3 hrs
Wear elastic stockings
Avoid standing for prolonged periods
Avoid tight fitting clothes
Reduce weight if obese
What symptoms do you expect to see in a person with sinusitis? List 3
Severe headache
Pain and tenderness in affected region
Purulent exudate
Malaise
Fever
Redness and inflammation
What is the most common form of laryngeal cancer? How can you treat it?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Radiation, surgery such as a partial or total laryngectomy, or radical neck dissection
Which medication can cause elevated blood pressure in those with allergic rhinitis?
Medications containing decongestants, like pseudoephedrine (found in Sudafed, Actifed), can cause elevated blood pressure in people with allergic rhinitis, as they constrict blood vessels throughout the body, not just in the nose, forcing the heart to work harder to pump blood.
How can the nurse communicate with patients who are unable to communicate due to tracheostomies? List 2
- Facial Expressions: Encourage patients to use facial expressions to communicate their emotions or needs. Smiling, frowning, or shaking the head can convey messages.
- Eye Movement: Some patients may be able to use eye movement (blinking or looking toward specific items or areas) to indicate choices or needs.
- Gestures: Simple hand gestures or pointing can help patients convey messages. For example, a patient can point to objects or areas of concern to signal their needs.
- Writing: If the patient is able to use their hands, providing a pen and paper or a dry-erase board for writing can allow them to communicate more clearly.
- Speaking Valves: Some patients with tracheostomies can use a speaking valve (e.g., Passy-Muir valve). This device fits over the tracheostomy tube and allows the patient to speak by directing air through the vocal cords. It can be an effective way for patients to communicate verbally when they are able.
- Use a communication board or picture board that includes common phrases, yes/no indicators, or images that the patient can point to. This is especially useful if the patient is unable to write or speak clearly but can still use their hands or eyes to select symbols or words.
- Speech-Generating Devices: For patients who cannot speak, specialized augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices or electronic communication aids can be used. These devices allow patients to type or select words and phrases, which the device then vocalizes.
- Smartphones/Tablets: Some patients may be able to use smartphones or tablets with apps designed for communication. These devices can be programmed with commonly used phrases or can allow patients to type out messages.
- Monitoring Body Language: Pay attention to the patient’s physical movements, body posture, or other signs that may indicate discomfort, pain, or a desire to communicate something. For example, agitation, restlessness, or attempting to point at a particular item might indicate a need or issue.
- Allowing Extra Time: Communicating with patients who have a tracheostomy may take longer, and it’s important to allow extra time for patients to express themselves, especially when using non-verbal or alternative communication methods.
- Active Listening: Ensure that the patient feels heard by giving them your full attention, acknowledging their efforts, and providing reassurance that you're trying to understand their needs.
- Visual Aids: In addition to communication boards, visual aids like pictures, letters, or large print materials can help the patient express themselves
Which lung sound producing a snoring sound and which lung sound produced a seal bark sound?
Rhonchi- produces a snoring sound due to obstruction or narrowing of the larger airways.
Stridor- produced a seal's bark. It requires immediate care due to disturbed airflow in the larynx and trachea.
Explain primary and secondary hypertension? What is the risk 5 factors?
Primary- No identifiable cause
Secondary-Caused by another disorder
Risk factors:
Overweight/obese
Sedentary
Poor diet
High sodium diet
African Americans
Increased alcohol intake
Smoking
Low vitamin K and vitamin D levels
Advanced age
Increased cholesterol
Too much caffeine
Sleep apnea
Family history
A patient newly diagnosed with laryngeal cancer asks you how he could have prevented the diagnosis, what is your response?
"Laryngeal cancer is a serious condition, and it’s natural to wonder if there was something that could have been done to prevent it. While not all cases of laryngeal cancer can be prevented, there are certain risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing it, and some of these can be controlled."
"The main risk factors for laryngeal cancer include smoking and heavy alcohol consumption. Smoking is the single biggest risk factor. The chemicals in tobacco can damage the cells in the larynx, leading to cancer. If you smoke, quitting can lower your risk of developing cancers of the throat, larynx, and other parts of the body. Heavy alcohol consumption also increases the risk, especially when combined with smoking."
"Other risk factors include exposure to certain chemicals or substances, such as asbestos or industrial chemicals, as well as a history of chronic acid reflux (GERD) or persistent hoarseness."
"While we cannot always prevent cancer, there are things you can do moving forward to lower the risk of future cancers, such as avoiding tobacco and alcohol, protecting your throat from excessive irritation, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying on top of follow-up care and screenings."
"I understand this diagnosis may be overwhelming, but we will work together to manage the condition. It's important to focus on treatment options now and take the steps you can to support your recovery and long-term health."
How is tuberculosis confirmed?
What the risk factors for TB?
TB is confirmed by a acid fast bacilli smear x 3 times. This test is usually done first thing in the morning.
Risk factors for TB include: Those exposed to TB, history of infections, alcohol and drug use, gastrectomy, HIV, living in crowded areas, working in healthcare, homeless.
How is a deviated septum managed?
Sinus X-rays can show shadowy sinuses when nasal polyps are present
Surgical intervention with a nasoseptoplasty is the operation where the septum is reconstructed
Nasa packing to control bleeding
Nasal mucosa hydration with nasal saline or nasal irrigation
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Antihistamines to allergy symptoms
Antibiotics to prevent infection
Analgesics for headache that comnonly co-occurs
How is rhinitis treated? List at least 3
Relieve symptoms and prevent infections
Antihistamines
Intranasal corticosteroids
Leukotriene receptor agonists
Decongestants
Analgesics
Antitussives
Expectorants
Mucolytics
Ph 7.55
PaCO2 49
HCO3 27
What is the ABG interpretation? Any compensation?
Respiratory alkalosis, uncompensated
pH is elevated above 7.45 indicating alkalosis
PaCO2 is greater than 45 indicating respiratory alkalosis
HCO3 is within normal range
Uncompensated due to only PaCO2 being abnormal and not both PaCO2 and HCO3
What is Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and what are its symptoms? How is it diagnosed?
PAD is a disease that has narrowed arteries due to atherosclerosis which prevents oxygenated blood from getting to the distal extremities such as the hands and feet.
Manifestations include:
Sharp pain that gets worse at nigh
Weak or nearly absent pulses
Cool temperature to extremities due to no blood getting to extremities
Pale, hairless, dry, scaly, thin skin due to lack of nutrients
Red sores with a regular shape
Tissue death caused by lack of blood supply
Intervention- Dangle arteries, perform daily skin moisturizers, avoid smoking, avoid tight clothing, avoid heating pads. Vasodilators and antiplatelets.
PAD is diagnosed by a doppler ultrasound or ankle brachial index (ABI)
I have a bright red substance leaking from my nose, what am i dealing with? What can you do to help me? List 3
Epistaxis
Nasal packing
Cautery
A ballon tampon
Place patient in sitting position leaning forward or in a reclining position with head and shoulders elevated
Be alert to possible vomiting so have a basin ready
Advise not to pick or scratch the nose
Don't blow the nose vigorously
Encourage use of a vaporizer or nasal lubricants
Avoid NSAIDs
Sneeze with mouth open
As nurse is caring for a patient who just had a laryngectomy, what is your priority?
Maintain a proper airway preventing mucous buildup and secretions
Watch for signs of skin breakdown and infection
Monitor the patient's oral intake
make sure they are able to communicate
Reassure them as their anxiety is usually high
Educate your asthmatic patient on the use beta adrenergic blockers as well as what they should report to their health care provider if they experience?
Beta adrenergic blockers are part of the maintenance therapy that prevents and minimizes symptoms of asthma. They work quickly to relax muscles around the airway.
These are long term medications such as salmeterol and formoterol these are taken regularly
Prophylactic medications such as inhaled corticosteroids like fluticasone, cromolyn and theophylline are taken as needed
Report to the HCP when rescue treatments are no longer effective, when the number of asthma attacks increase, identify triggers and avoid them
How can Raynaud's disease exacerbation be prevented? List 5
Avoid extreme temperatures
Stop all tobacco use
Stress management
Avoid caffeine and other vasoconstrictive drugs like cocaine and amphetamines
Eliminate alcohol
Increase exercise to improve blood flow
Dress in layers
What is peripheral venous disease and what are its symptoms? How is it diagnosed?
PVD is a peripheral vascular disease that is characterized by deoxygenated blood not being able to get back to the heart. In return, oxygenated blood pools in the extremities.
Symptoms:
Dull, constant achy pain
Pulse may not be palpable due to edema
Edema due to blood pooling in the leg
Warm temperature due to blood pooling
Brown, yellowish skin color
Venous stasis ulcers shallow and irregular
No gangrene do to blood supply being present
Treatment: elevate veins, Give aspirin or plavix, statins. Surgical interventions include angioplasty, edarectomy
What are the nursing interventions for a patient with acute tonsilitis? List 5
Give antibiotics
Elective tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy can be done if reoccurance is an issue
Analgesics
Antipyretics
Provide meticulous oral care to combat infection
Observe frequent swallowing which can indicated bleeding
Warm gargles can be helpful
Maintain IV fluids until nausea subsides
Ice cold, clear liquids then advancement to custard and ice cream and then normal diet
Avoid hot and spicy food
Ice collar for comfort and to reduce vasoconstriction
Monitor vital signs for hemorrhage, fever, or other complications
Avoid attempting to clear the throat immediately post op
Avoid coughing, sneezing, or vigorous nose blowing
Avoid ASA due to tendency to bleed
A patient presents with atelectasis. How can you confirm the diagnosis?
How is it treated?
Serial chest radiographs are done to compare changes. A chest CT can reveal compression in the airways.
Treatment includes:
Incentive spirometry
Change position every 1-2 hours
Effective coughing
Analgesics
Early ambulation
What is the etiology of emphysema? What are common findings in someone with emphysema?
In emphysema the alveoli are damaged and enlarged which causes loss of lung elasticity. This results in loss of lung tissue recoil and air trapping.
Weight loss they are thin and emaciated
Barrel chest- hyperinflated lungs
Dyspnea on exertion
Breathe with pursed lips
Scanty sputum production
Clubbing of fingers
Explain sympathomimetics?
Sympathomimetics are drugs that mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls our "fight or flight" response. These drugs help relax muscles, open up airways, and improve breathing.
Sympathomimetics mainly work on beta-2 receptors found in the lungs. When these receptors are stimulated, it causes the bronchioles (airways in the lungs) to dilate (open up). This makes it easier to breathe, which is especially helpful for patients with conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Common Respiratory Sympathomimetic Drugs:
- Albuterol: This is the most common beta-2 agonist. It’s used to relax the airways, making breathing easier during an asthma attack or flare-up of COPD.
- Epinephrine: This drug is used in emergency situations (like anaphylaxis) to open the airways and improve breathing. It works on both alpha and beta receptors.
When a patient takes a sympathomimetic, it causes:
- Bronchodilation: Airway opening.
- Increased airflow: Easier breathing.
- Improved oxygenation: Helps oxygen reach the lungs and body tissues.
Side Effects of Sympathomimetics in Respiratory Care:
- Tremors: Patients may feel shaky, especially with inhalers like albuterol.
- Tachycardia: A fast heart rate, because these drugs can stimulate the heart as well.
- Nervousness or restlessness: Especially if the dose is too high.
- Dry mouth: Can happen with inhaled medications.
Nursing Considerations:
- Monitor the heart rate: If it's too fast, the drug may need to be adjusted.
- Teach patients to use inhalers properly: This helps get the right amount of medication into their lungs.
- Encourage patients to report side effects: If tremors or anxiety are bothersome, inform the healthcare provider.
- Caution with overuse: Overusing medications like albuterol can lead to unwanted side effects and should be avoided.
Sympathomimetics are important for treating respiratory issues like asthma and COPD. They open up the airways, making it easier to breathe. As nurses, we need to monitor side effects like increased heart rate and tremors, and ensure patients are using these medications correctly.
What is pneumonia? How is it managed?
Pneumonia is inflammation of the alveoli and bronchioles caused by an infection. It can also be caused by oversedation, inadequate ventilation, or aspiration.
Treatment included:
Oxygen
Possible chest tube placement
Chest physiotherapy
antibiotics
Analgesics
Antipyretics
Expectorants
Bronchodilators
Humidifiers
Vaccines
What are the risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea?
What are the symptoms of sleep apnea?
Common risk factors are:
Male gender- twice as likely as women
Older age- Incidence increases in those over 60, but can occur in younger patients as well
Obesity- Pharynx may be infiltrated with fat and tongue and soft palate may be enlarged
Nasal conditions- Nasal allergies, polyps, septal deviation
Receding chin- May not have enough room in the pharynx for the tongue
Pharyngeal structural abnormalities- A person with sleep apnea may have enlarged tonsils, elongated uvula, or long tongue
Symptoms include:
Morning headache from hypercapnia
Personality changes
Irritability
Systemic hypertension
Cardiac dysrhythmias
right sided heart failure
Pulmonary Hypertension
Stroke
Impotence
Severe depression
How can peripheral circulation be improved in someone with poor circulation? List 3
- Walking: Gentle aerobic exercise, such as walking, helps stimulate blood flow to the lower limbs and can improve overall circulation. Encourage patients to start with short walks and gradually increase duration and intensity.
- Leg exercises: Simple exercises, such as ankle pumps (flexing and pointing the feet), leg lifts, and toe-tapping, can improve blood flow in the legs and feet, especially for individuals who are sedentary or bedridden.
- Strengthening exercises: Incorporating strength training for the legs can help tone muscles, which can then help push blood back toward the heart more efficiently.
- Elevation: Elevating the legs above the level of the heart for 15-30 minutes several times a day can encourage blood to flow back toward the upper body. This can be especially helpful for individuals who have swelling in the feet or lower legs.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing: Encourage people to take breaks from sitting or standing for long periods. If they must sit, they should elevate their feet when possible to reduce pressure and improve circulation.
- Compression stockings or garments: These can help improve venous return by applying pressure to the legs and supporting blood flow back to the heart. This is particularly helpful for people with conditions like chronic venous insufficiency or varicose veins.
- Pneumatic compression devices: These devices inflate and deflate around the legs to help move blood and fluid through the veins, which can be helpful for those at risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Gentle leg or foot massage: Massaging the limbs in upward strokes can encourage blood to flow toward the heart, helping to improve circulation and reduce swelling. It can also promote relaxation and reduce muscle tension.
- Drink enough water: Staying well-hydrated helps the blood flow more easily and prevents the blood from becoming too thick, which can impede circulation.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine: Both alcohol and caffeine can contribute to dehydration, which can negatively affect circulation.
- Healthy fats: Include healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon, which can help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Foods high in antioxidants, like berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, help improve blood vessel health and circulation.
- Limit salt intake: Excess salt can contribute to fluid retention and high blood pressure, both of which can worsen circulation problems.
- Increase fiber: High-fiber foods can help manage cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis), which can impair blood flow.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and can lead to narrowed arteries (atherosclerosis), reducing blood flow to the extremities. Quitting smoking is essential for improving circulation.
- Warmth: Keep the extremities warm, as cold can cause blood vessels to constrict and reduce circulation. Encourage the use of warm socks, gloves, or heated pads to help improve blood flow.
- Avoid hot showers: Extremely hot showers or baths can also cause blood vessels to dilate, but they can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure in some individuals. It's best to keep showers warm but not too hot.
- Manage Underlying Health Conditions Control diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels over time, leading to poor circulation. Proper management of blood glucose levels can help prevent circulation problems.
- Control blood pressure: High blood pressure can contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels and poor circulation. It’s important to take medications as prescribed and maintain a healthy lifestyle to keep blood pressure in check.
- Cholesterol management
- Manage obesity
How is pleurisy managed?
Nerve block
antibiotics
Antipyretics
Position patient on affected side to splint the chest
Apply heat to the area
Cough effectively every 2 hours
What test is done to assess lung capacity?
Pulmonary function testing
to assess the presence and severity of disease in the large and small airways. PFTs include various procedures to obtain information on lung volume, ventilation, pulmonary spirometry, and gas exchange. Lung volume tests refer to the volume of air that can be completely and slowly exhaled after a maximum inhalation (vital capacity). Inspiratory capacity is the largest amount of air that can be inhaled in one breath from the resting expiratory level. Total lung capacity is calculated to determine the volume of air in the lung after a maximal inhalation. Ventilation tests evaluate the volume of air inhaled or exhaled in each respiratory cycle. Pulmonary spirometry tests evaluate the amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after maximum inhalation. These tests require the use of a spirometer.
Explain why caution should be taken in someone who has hypertension and is using decongestants?
Decongestants, like pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine, are often used to relieve stuffy noses. They work by narrowing blood vessels in the nose to reduce swelling, but they can also narrow blood vessels all over the body.
Why This Is a Problem for People with Hypertension:
- People with hypertension (high blood pressure) already have narrow or stiff blood vessels.
- When they take decongestants, the narrowing effect can raise their blood pressure even more, which is dangerous.
What Can Happen:
- Increased blood pressure: Decongestants can make blood pressure go higher, which is risky for those with hypertension.
- Heart problems: It can also increase the risk of heart complications, like heart attacks or strokes.
What Should You Do?:
- Monitor blood pressure: Always check a patient's blood pressure before and after giving a decongestant.
- Educate patients: Let patients with high blood pressure know they should be cautious with decongestants and talk to their doctor before using them.
- Suggest alternatives: Recommend safer options, like saline nasal sprays or humidifiers, which don't affect blood pressure.
Explain COPD etiology? What are its presenting symptoms?
COPD is a progressive pulmonary disease the causes chronic airflow obstruction. It includes both emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
A FEV1/FVC ratio of less than 70% indicated COPD
FEV1=FORCED EXPIRATORY VOLUME
FVC= FORCED VITAL CAPACITY
What are 5 nursing inventions that nurses should do for ALL postsurgical patients?
- Monitor vital signs to detect signs of complications like infection, bleeding, or shock.
- Watch for abnormal readings: For instance, hypotension, tachycardia, or fever may indicate infection or other post-operative complications.
- Administer analgesics: Provide prescribed pain medications, such as opioids or non-opioid pain relievers, while ensuring proper monitoring for adverse effects.
- Non-pharmacological techniques: Offer relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, positioning) or complementary therapies (e.g., heat/cold packs) to help manage discomfort.
- Inspect surgical site: Regularly assess the surgical site for signs of infection (redness, swelling, drainage) or complications (dehiscence, hematoma).
- Drain care: If a surgical drain is in place, ensure proper drainage and that it’s functioning as intended.
- Encourage deep breathing: Prevent atelectasis and pneumonia by encouraging the patient to perform deep breathing exercises and use an incentive spirometer if appropriate.
- Coughing: Teach and assist with coughing techniques to help clear secretions.
- Oxygen therapy: If needed, administer supplemental oxygen and monitor oxygen saturation levels.
- Early mobilization: Encourage early ambulation as tolerated to promote circulation and prevent DVT.
- Compression stockings or devices: Apply pneumatic compression devices or graduated compression stockings as ordered to reduce the risk of clot formation.
- Administer anticoagulant medications as prescribed to prevent clot formation, and monitor for signs of bleeding.
- Monitor output: Keep track of urine output to assess kidney function and fluid status, aiming for adequate urine output (usually >30 mL/hour).
- Assess for signs of dehydration: Check for signs of dehydration such as dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, and concentrated urine.
- Assess nutritional needs: Ensure the patient is receiving appropriate nutrition, either through oral intake or enteral/parenteral nutrition, based on the type of surgery and the patient's condition.
- Keep an eye out for fever, redness, swelling, increased pain at the surgical site, or changes in discharge.
- Hemorrhage: Monitor for signs of excessive bleeding or changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or skin color, which may suggest internal bleeding.
- Cardiac complications: Watch for arrhythmias, chest pain, or changes in heart function.
- Positioning: Position the patient comfortably while maintaining proper body alignment to reduce pressure ulcers, prevent complications, and promote optimal lung expansion.
- Early ambulation: As soon as it is safe, help the patient sit up, dangle their legs, and gradually progress to walking to prevent complications like DVT, constipation, and lung issues.
- Cognitive assessment: Assess the patient's mental status regularly, especially in older adults who are at risk for postoperative delirium.
- Environmental modification: Ensure the environment is calm, quiet, and conducive to rest, minimizing sensory overload or confusion.
- Urinary function: Monitor for adequate urine output. For patients with urinary catheters, ensure the catheter is functioning and remove it as soon as it is no longer needed to reduce the risk of infection.
- Bowel function: Assess for constipation or bowel obstructions, particularly in patients who have undergone abdominal surgery. Encourage mobility, hydration, and the use of stool softeners as appropriate.
- Assess readiness for discharge
What are 2 things that can go wrong with someone who has a chest tube and how can they be addressed?
What are 3 nursing interventions that the nurse must take when managing a patient with a chest drainage system?
Bubbling in the water seal chamber indicating air leak
Atelectasis from hypoventilation- increased dyspnea can indicate
Dislodgement from the insertion site- Apply an occlusive dressing
Disconnection from drainage system- Place the distal end in sterile water
Interventions include:
Keep the drainage device below chest level but not on the floor
Make sure there are no kinks in the tubing
Make sure device is upright
Dont strip the device due to added pressure
Keep clamps at the beside incase of emergency
Mark the time measurement and fluid level at the start and stop of shift
Monitor the clients clinical status
What is chronic bronchitis? What are common findings in someone with chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis is inflammation and chronic muscous secretion usually manifested by a chronic productive cough and sputum production for more than 3 mos.
Symptoms include:
Chronic productive cough,
Dyspnea
use of accessory muscles to breathe
Wheezing, rhonchi
Overweight or obese
Peripheral edema
Cyanosis from hypoxemia
What is cyanosis and pallor and how can they be assessed in dark skin patients?
Cyanosis is a bluish discoloration of the skin which is due to hypoxemia
Pallor -Paleness or loss of color due to decreased oxygen to the tissues
They both can be assessed by checking the palms, soles, conjunctiva, and oral mucosa
What are the 5 ABG components and what are the normal ranges?
pH 7.35-7.45
PaCO2- 35-45
HCO3 21-28
Pao2- 80-100
Sao2-95-100
What are signs of digoxin toxicity and what should be done about it?
Nausea
vomiting
anorexia
dysrhytmias
bradycardia
tachycardia
headache
fatigue
visual disturbances
ototoxicity
hypokalemia
Interventions include:
Assess the patient:
- Check the patient's heart rate and rhythm. If the heart rate is slow or irregular, it could indicate digoxin toxicity.
- Monitor vital signs, especially blood pressure and respiratory status.
- Check for signs of electrolyte imbalances (especially potassium and magnesium).
- Stop administering digoxin immediately if toxicity is suspected. Don’t give more doses until the patient is reassessed and the levels are back to a safe range.
- Contact the doctor immediately, especially if toxicity is severe or if the patient has symptoms like arrhythmias or visual changes.
- A blood test should be done to measure the serum digoxin level. Therapeutic levels are typically between 0.5 and 2.0 ng/mL. Levels above this range may indicate toxicity.
- Correct potassium or magnesium imbalances if necessary, as low levels of these electrolytes can worsen toxicity and arrhythmias.
- In severe cases of toxicity (e.g., life-threatening arrhythmias), digoxin immune fab (ovine-derived antibody) can be administered. This binds to digoxin in the bloodstream and helps remove it from the body
- Continue to closely monitor the patient in a hospital setting, especially for any signs of arrhythmias or worsening toxicity.
What is a cPAP and why is it worn?
A continuous positive airway pressure cPAP is a device applied to the face that is attached to a blower to maintain positive pressure. Usually, 5-15 cm H2O during inspiration and expiration to prevent airway collapse.
When patients can't tolerate a cPAP, an alternative called a BiPAP with is a bilevel positive airway pressure device is available which delivers a higher-pressure during inspiration which the airway is most likely occluded and lower pressure during expiration which may be better tolerated.
Although CPAP is highly effective, compliance is poor.
What is bronchiectasis and how can it be prevented?
Bronchiecstasis is abnormal and permanent dilation of one or more large bronchi. The dilation destroys muscular elements and bronchial elastic fibers that support the bronchial wall. Due to the decreased muscle tone, it is more difficult to clear mucous from the lungs and the lungs experience decreased expiratory airflow.
Avoid smoke, fumes, and irritating inhalants
Smoking cessation
Get appropriate rest and exercise
Surgical removal of the lung portion that is causing the problem is the only cure
What are the normal lung sounds?
Bronchial
Vesicular
Bronchovesicular
What are 5 abnormal lung sounds? Which one is the most life threatening?
Rhonchi (Sonorous wheezes)
Wheezes- (Sibilant wheezes)
Crackles
Pleural friction rub
Stridor- most life threatening
Explain pursed lip breathing, diaphragmatic breathing, and huff coughing?
Pursed lip breathing- Promoted carbon dioxide elimination and prevents collapse of airways. You teach the patient to breathe in (inhale) through your nose and then breathe out (exhale) with pursed lips like you are going to whistle for 4 seconds
Diaphragmatic breathing- Use the diaphragm rather than the accessory muscles to breathe. Slowly breathe in (inhale) and let your abdomen expand, then breathe out (exhale) and let your abdomen go back inward.
Huff coughing- Helps get rid of excess mucous in the airway/lungs. Slowly inhale, hold for a few seconds, and forcefully exhale, repeat a few times
What is the difference between allergic rhinitis and acute rhinitis?
- Allergic Rhinitis: This is caused by an allergic reaction to environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold, or pet dander. When a person with allergic rhinitis comes into contact with these allergens, their immune system overreacts and releases histamine, which leads to the symptoms of the condition.
- Acute Rhinitis: Acute rhinitis is most commonly caused by viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. It can also be triggered by bacterial infections or irritants like smoke or pollutants. Acute rhinitis is typically short-lived and is often part of a broader respiratory infection.
2. Onset and Duration:
- Allergic Rhinitis: The onset of symptoms is often gradual and can occur seasonally (e.g., hay fever due to pollen) or year-round (due to indoor allergens). Symptoms can last for weeks to months, depending on the exposure to allergens.
- Acute Rhinitis: This condition has a sudden onset and typically lasts for a short period (about 7 to 10 days). It is usually associated with the duration of a viral infection, such as a cold.
3. Symptoms:
- Allergic Rhinitis:
- Sneezing, especially in bursts
- Clear, watery nasal discharge
- Itchy nose, eyes, or throat
- Nasal congestion (due to swelling of the nasal passages)
- Watery, red, or itchy eyes (often with conjunctivitis)
- Symptoms often occur in response to specific allergens.
- Acute Rhinitis:
- Runny nose with thicker mucus (which can become yellow or green if a secondary bacterial infection occurs)
- Nasal congestion and post-nasal drip
- Sore throat (from mucus drainage)
- Mild cough
- Mild fever (in cases of viral or bacterial infection)
- No itching of the nose or eyes (a hallmark of allergic rhinitis)
4. Triggers:
- Allergic Rhinitis: Triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, mold, animal dander, or environmental factors like changes in weather or air pollution.
- Acute Rhinitis: Triggered by viral infections (like the common cold) or bacterial infections. Environmental irritants like smoke or strong odors may also cause it.
5. Treatment:
- Allergic Rhinitis:
- Antihistamines: To block the effects of histamine and reduce allergy symptoms.
- Intranasal corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Decongestants: (in some cases) to relieve nasal congestion.
- Allergen avoidance: Identifying and avoiding the triggers is crucial.
- Immunotherapy: In some cases, allergy shots (or sublingual tablets) can be used to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens.
- Acute Rhinitis:
- Symptom management: Since it's often viral, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms (e.g., using saline nasal sprays, decongestants, or pain relievers like acetaminophen).
- Rest and hydration: Adequate rest and fluid intake are important for recovery.
- If a secondary bacterial infection occurs (e.g., sinusitis), antibiotics may be required.
6. Risk Factors:
- Allergic Rhinitis: Individuals with a family history of allergies or asthma are more likely to develop allergic rhinitis.
- Acute Rhinitis: Common in children and adults during the colder months when viral infections (like the common cold) are more prevalent. People with weakened immune systems may also be more prone to infections causing acute rhinitis.
What is another name for sibilant wheezing and sonorous wheezing?
Sibilant wheezing is also known as Wheezes
Sonorous wheezing is also known as Rhonchi
How should upper respiratory infections be managed? List 5
Symptom Management
- Rest: Encourage adequate rest to help the body fight off the infection. Resting supports the immune system and speeds up recovery.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps to thin mucus, soothe the throat, and prevent dehydration. Warm liquids (e.g., tea with honey or broths) can be particularly soothing.
- Pain and Fever Control:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help reduce fever, sore throat, and muscle aches. Always follow the recommended dosage, especially in children, and avoid giving aspirin to children due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.
- Saline Nasal Spray: Saline or saline-based nasal sprays or drops can help relieve nasal congestion by loosening mucus.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or a shower can help open nasal passages and relieve congestion. Humidifiers can also help add moisture to the air.
- Cough Suppressants or Expectorants: Depending on the type of cough, cough suppressants like dextromethorphan may help reduce the urge to cough, while expectorants like guaifenesin can help loosen mucus for easier expectoration.
- Throat Lozenges or Sprays: Sore throats can be relieved with over-the-counter throat lozenges or sprays containing benzocaine or menthol.
- Gargling with Salt Water: Gargling with warm salt water can help soothe a sore throat and reduce inflammation.
- Honey: Honey is a natural remedy that can coat and soothe the throat. It’s especially helpful for soothing coughs and sore throats in adults and children over 1 year old.
- Antibiotics are not effective for viral URIs and should not be used unless a bacterial infection (like streptococcal pharyngitis or sinusitis) is diagnosed. Overuse of antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance and disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body.
- Symptoms of a bacterial infection include persistent fever, pus on the tonsils, or worsening symptoms after a few days. In such cases, a doctor might prescribe antibiotics.
- Good Hygiene
- Cover Coughs and Sneezes: Remind patients to cover their mouth and nose with a tissue or the elbow to reduce the spread of droplets.
- Avoid Close Contact: Advise patients to avoid close contact with others, particularly those who are more vulnerable (e.g., elderly, immunocompromised individuals), until they are no longer contagious.
- If the symptoms worsen or do not improve after 7-10 days, seek medical advice. This may indicate a secondary infection like sinusitis, ear infection, or pneumonia.
- Signs that warrant medical attention include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- High fever (greater than 102°F / 39°C) that doesn't respond to medications
- Severe or persistent sore throat (especially with difficulty swallowing)
- Chest pain or pressure
- Blood in sputum or mucus
- Persistent or worsening headache
- Cough that lasts more than 3 weeks or worsens over time
- Fever in infants and children: For babies under 3 months with a fever, seek medical attention immediately. For older children, fever management with acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be done, but aspirin should never be given to children.
- Saline nasal drops and suction: For infants, saline drops can be used to clear nasal congestion, and a nasal aspirator may help clear mucus.
- Humidified air
- Warm compress
- Avoid irritants: Avoid smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, or other irritants that can worsen symptoms.
What are 5 test taking strategies that can be used during exams?
- Study consistently: Don’t wait until the last minute. Study regularly, and review course materials often.
- Use active learning techniques: Instead of just reading, actively engage with the material. Use flashcards, practice questions, and teach the material to someone else. Also, use concept maps or diagrams to understand complex topics.
- Prioritize your weak areas: Identify your weakest subjects and allocate more time to them. Don’t neglect your strengths, but focus on improving areas where you feel less confident.
- Practice NCLEX-style questions: Since nursing exams often use multiple-choice questions similar to NCLEX questions, practicing these questions will familiarize you with the exam format and improve critical thinking.
- Read instructions carefully: Before starting, take a minute to carefully read any instructions provided. Misunderstanding directions can cause mistakes.
- Time management: Familiarize yourself with the time allotted for each section of the exam. Don't get stuck on any one question—if you don’t know the answer, move on and come back to it later if you have time.
- Read the question thoroughly: Read the question and all the choices carefully. Make sure you understand exactly what’s being asked before choosing an answer.
- Look for key words: Pay attention to keywords such as "most important," "first," "best," or "least likely," as they can change the meaning of the question and the correct answer.
- Eliminate obviously wrong answers: When faced with multiple-choice questions, eliminate answers that are clearly incorrect. This increases your chances of choosing the right one, even if you’re unsure.
- Think critically: Nursing exams often require critical thinking. Consider the patient’s needs, the priority of care, and the nursing process (assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation) when answering questions.
- Use the process of elimination: If you’re stuck between two answers, try to rule out choices that don’t make sense. Consider the reasoning behind each option.
- Trust your first instinct: While it’s important to review answers, second-guessing yourself too much can lead to errors. If you have a strong instinct about an answer, go with it, but always recheck if you have time.
- Don’t overthink it: Overanalyzing questions can lead to confusion and mistakes. Stick to the basics of what you know about nursing practice and patient care.
- Use critical thinking frameworks: When faced with complex questions, try using frameworks like ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation), MASLOW’s Hierarchy of Needs, or the nursing process (assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, evaluation) to guide your decisions.
- Multiple Choice: These questions often have one correct answer and distractors. Use the process of elimination and prioritize safety and the most effective nursing intervention.
- Select All That Apply (SATA): These questions can be tricky, but remember that more than one answer may be correct. Read each option carefully and choose the ones that apply to the situation.
- Priority Questions: These questions assess your ability to prioritize care. Think about Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and ABC (airway, breathing, circulation) principles to decide which option takes precedence.
- Stay calm and positive: Test anxiety can be overwhelming, but it’s important to stay calm. Take deep breaths and stay focused.
- Don’t dwell on a question: If you’re unsure about an answer, mark it and move on.
- Use relaxation techniques: If you feel anxiety rising during the exam, practice deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation techniques to reduce stress and refocus.
- Stay hydrated and eat well: Having a good meal before the exam can fuel your brain. Also, staying hydrated helps you stay focused and alert.
What are the risk factors for a pulmonary embolism? List 5
•THROMBOPHLEBITIS HX
•RECENT SURGERY
•ARRYTHMIAS
•VENOUS CATHETER (CENTRAL)
•ESTROGEN IN CONTRACEPTIVES
•LONG TERM IMMOBILITY
What are 5 medications commonly used to treat respiratory disorders and what do they do?
Antihistamines- BLOCKS HISTAMINE RECEPTORS TO RELIEVE ALLERGY SYMPS SUCH AS SNEEZING AND ITCHING
Decongestants- CONSTRICT BLOOD VESEELS TO REDUCE NASAL SWELLING/CONGESTION
Expectorants- THIN MUCOUS TO HELP YOU COUGH IT UP AND CLEAR YOUR AIRWAYS
Mucolytics- BREAK DOWN MUCOUS TO MAKE IT THINNER AND EASIER TO COUGH UP
Beta Adrenergic Bronchodilating agents- RELAXES AIRWAY MUSCLES TO OPEN THE AIRWAYS FOR EASIER BREATHING
Intranasal Corticosteroids-REDUCE INFLAMMATIN IN THE NASAL PASSAGES, HELP WITH ALLERGIC RHINITIS
Saline Nasal Spray- MOISTURIZED AND RINSES OUT NASAL PASSAGES TO CLEAR CONGESTION
Analgesics- Pain reliever
Mast cell stabilizers- PREVENT THE RELEASE OF HISTAMINE AND OTHER CHEMICALS IN THE IMMUNE SYS
Antipyretics- Fever reducer
Antileukotriene agents- BLOCK LEUKOTRIENES, WHICH ARE INVOLVED IN INFLAMMATIoN AND BRONCHOCONSTRICTION
Cough suppressants- SUPRESS COUGH REFLEX TO RELIEVE DRY COUGH
Anticholinergics- BLOCK ACETYLCHOLINE TO RELAX BRONCHIAL MUSCLES AND IMPROVE AIRFLOW
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors-REDUCE INFLAM IN THE LUNGS AND PREVENTS COPD EXACCERBATION
Immunomodulators-MODIFY THE IMMUNE SYS TO PREVENT ASTHMA FLARE UPS BY BLOCKING IGE
Why should you use caution in given oxygen to patients with COPD?
COPD patients are stimulated to breathe due to their oxygen levels being chronically lower. If you give the too much oxygen, they lose their drive to breathe.
What 2 vaccines should respiratory patients get to prevent infection?
Influenza vaccine and pneumococcal vaccines which lowers their chance of pneumonia.
List 3 nursing diagnosis (NANDA) that are appropriate for respiratory disorders?
§INEFFECTIVE AIRWAY CLEARANCE
§INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERN
§IMPAIRED GAS EXCHANGE
§ANXIETY
§ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE
§IMBALANCED NUTRITION; LESS THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS
List 5 health related changes that occur in the elderly population?
- Bone Density: Bones may become thinner and weaker, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis, particularly in women after menopause.
- Joint Flexibility: Cartilage, which cushions joints, breaks down over time, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis. This can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Muscle Mass: Muscle mass tends to decrease with age, a process called sarcopenia. This can lead to weakness and reduced stamina.
- Heart Efficiency: The heart may become less efficient at pumping blood, which can lead to conditions like heart disease or heart failure.
- Blood Pressure: Blood vessels lose some of their elasticity, which can lead to increased blood pressure (hypertension), a major risk factor for heart attacks and strokes.
- Circulation: Reduced circulation in the extremities can cause cold hands and feet, as well as slower wound healing.
- Lung Capacity: Lung tissue loses some of its elasticity, and the chest wall may become stiffer, which reduces lung capacity and can make breathing more difficult during exertion.
- Weaker Immune Response: The immune system also weakens over time, making older adults more susceptible to respiratory infections, such as pneumonia.
- Cognitive Function: Brain function can slow down, leading to memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and slower processing speeds. In some cases, this can lead to conditions like dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
- Nerve Regeneration: Nerves regenerate more slowly, which can lead to slower reflexes and a reduced sense of touch or balance.
- Sleep Patterns: Changes in sleep patterns, including more frequent waking during the night, can occur as people age. Quality of sleep may also decline.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormone levels change as people age, such as decreased estrogen in women (leading to menopause) or decreased testosterone in men. These changes can affect mood, energy levels, and sexual function.
- Metabolism: The metabolism generally slows down, leading to a higher likelihood of weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
- Skin: The skin loses collagen and elastin, making it thinner and less elastic. Wrinkles, age spots, and dryness become more common, and the skin is more prone to bruising.
- Hair: Hair may thin or become finer, and many people experience graying as melanin production decreases.
- Digestive Efficiency: The digestive system slows down, leading to constipation or discomfort after eating. The ability to absorb nutrients may decrease, which can lead to deficiencies in vitamins or minerals.
- Reduced Appetite: Some older adults experience a reduced appetite, which can contribute to weight loss or malnutrition if not managed properly.
- Immune Function: The immune system weakens over time, making older adults more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and chronic conditions. Vaccinations, like flu and pneumonia shots, become more important with age.
- Kidney Function: Kidney function tends to decline with age, which can lead to problems with fluid balance and the body's ability to filter waste.
- Bladder Control: Many older adults experience bladder control issues, including urinary incontinence or an increased frequency of urination.
- Vision: Vision often deteriorates with age, leading to conditions like presbyopia (difficulty focusing on close objects), cataracts (clouding of the eye lens), and macular degeneration (loss of central vision).
- Hearing: Hearing loss, particularly high-frequency hearing loss, is common in older adults, making it harder to hear certain sounds or conversations.