Transport & Exchange
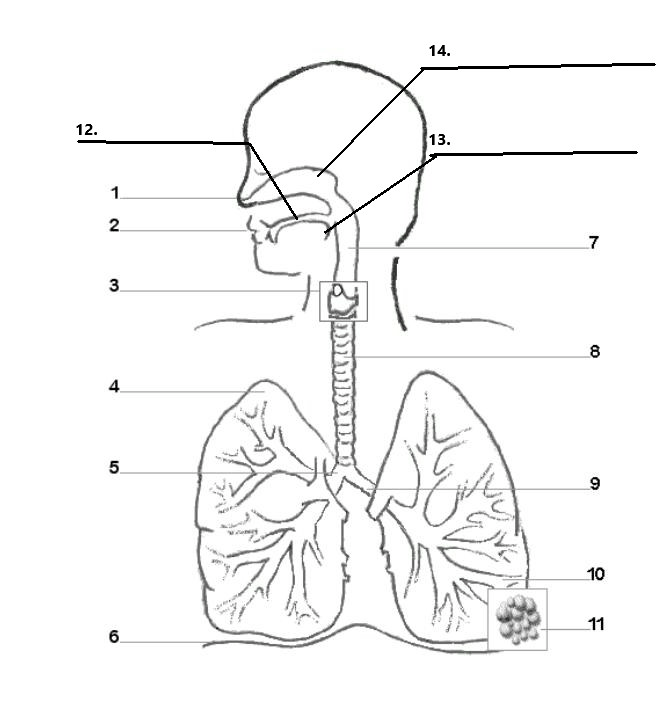
Label parts 1, 2, 12, 13, and 14 of the diagram:
1. Nostrils
2. Mouth
12. Hard Palate
13. Soft Palate/ Uvula
14. Nasal cavity
Where are the vocal cords located?
The vocal chords are located in the larynx.
What is the primary muscle responsible for breathing, and how does it work?
Diaphram. As it contracts, it creates more space in the thoracic cavity which brings in air through the nostrils and/or mouth.
Respectively, filling the lungs and forcing air out of the lungs are called _____________ and ____________
Inspiration and Expiration
What is the major molecule responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body?
Hemoglobin
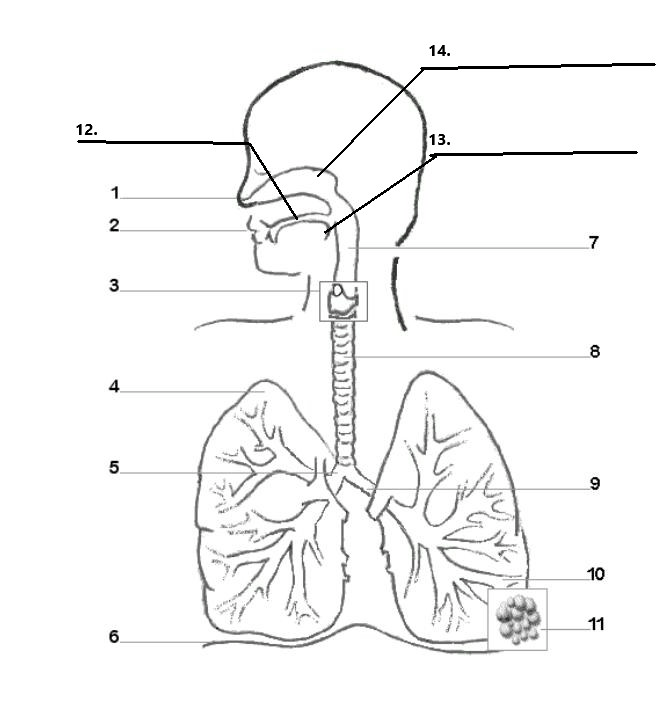
Label parts 3, 7, and 8 of the diagram:
3. Larynx
7. Pharynx
8. Trachaea
Bonus! What are the c-rings of the trachaea made of, and what is there function?
How many lobes does each lung have? Why are they different?
The right lung has 3 lobes, while the left lung has 2 lobes, making space for the heart.
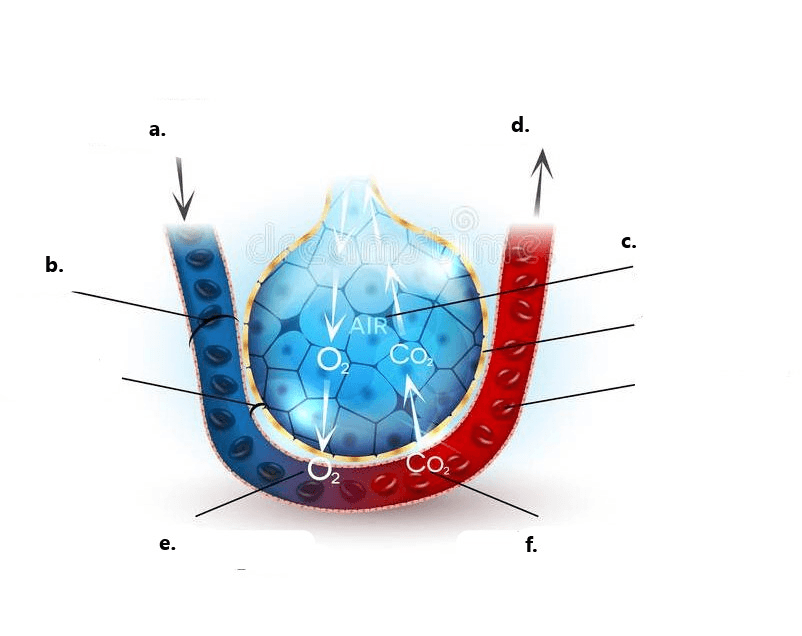
What type of respiration occurs between the alveoli and the capillaries?
External Respiration
The amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs during normal breathing is called the _____________
Tidal Volume
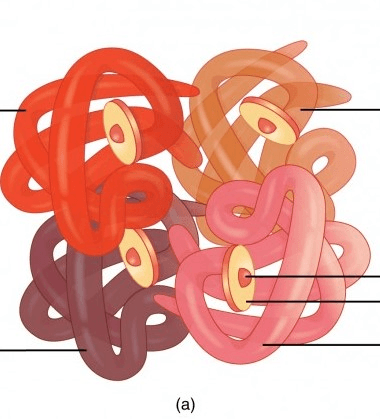
Where does Oxygen bond in the hemoglobin diagram above? How many oxygen molecules can one red blood cell transport?
Heme. Four.
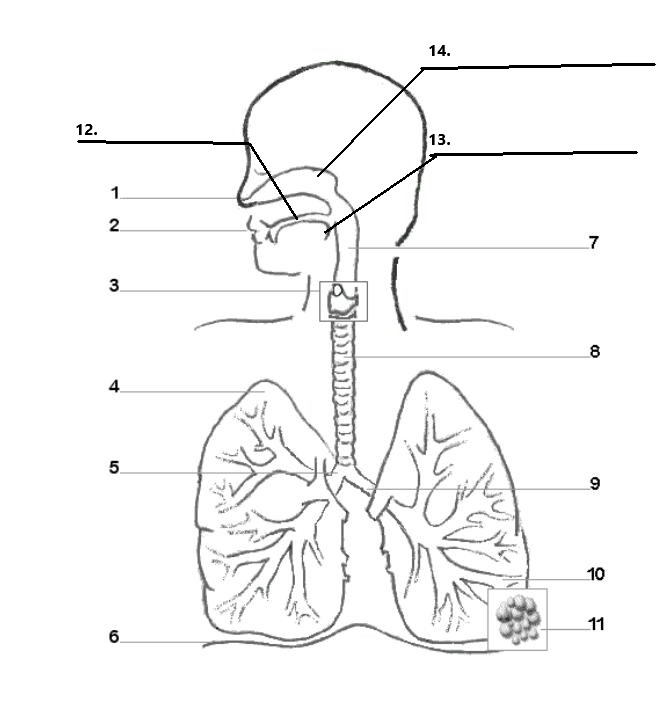
Label parts 4, 5, and 9 of the diagram:
4. Right Lung
5.Right Bronchus
9. Left Bronchus
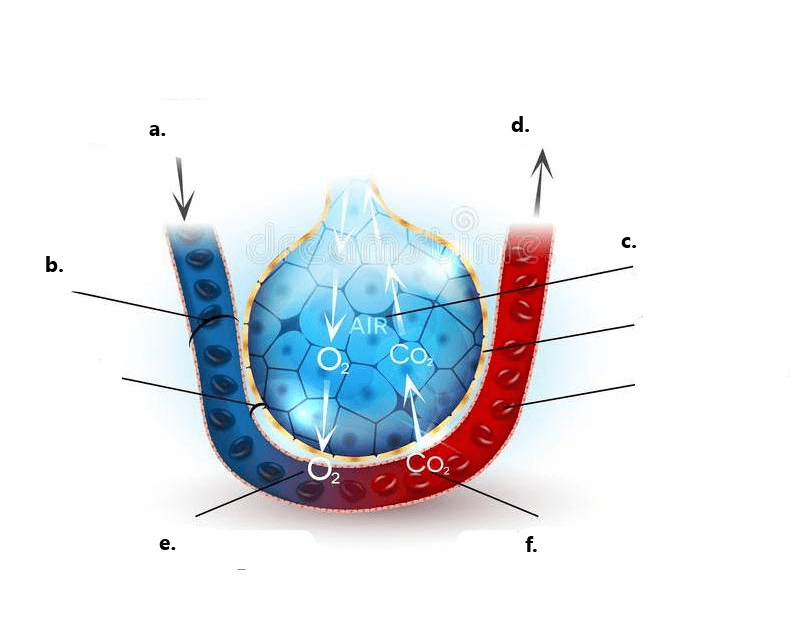
Label a, b, c, and d in the diagram above.
a. Pulmonary artery
b. Capillary
c. Alveolus
d. Pulmonary vein
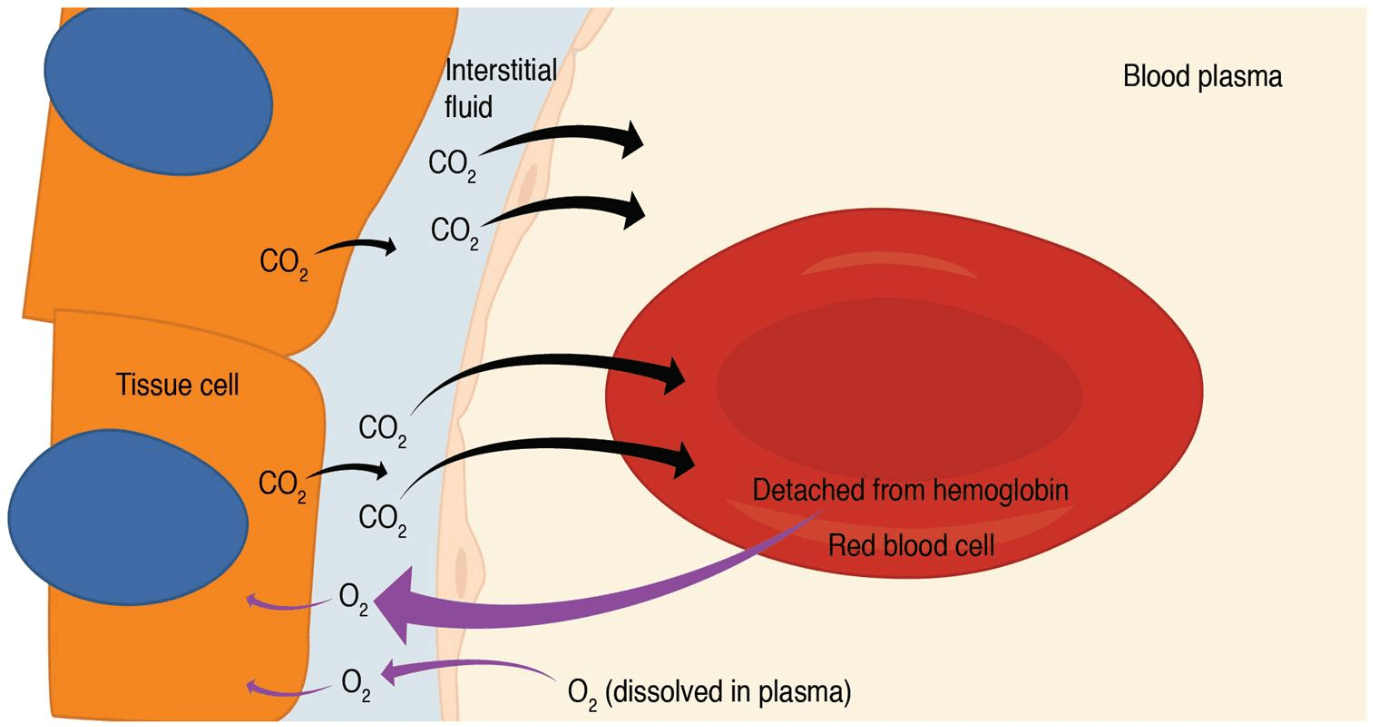
What type of respiration is occurring in the picture above between red blood cells and body cells?
Internal Respiration
____________________________
and
____________________________
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
Expiratory Reserve Volume
True or false:
Red blood cells can carry both Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide. Most of the carbon dioxide is carried by the red blood cells through the body.
False. Most carbon dioxide flows as bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) throughout the body.
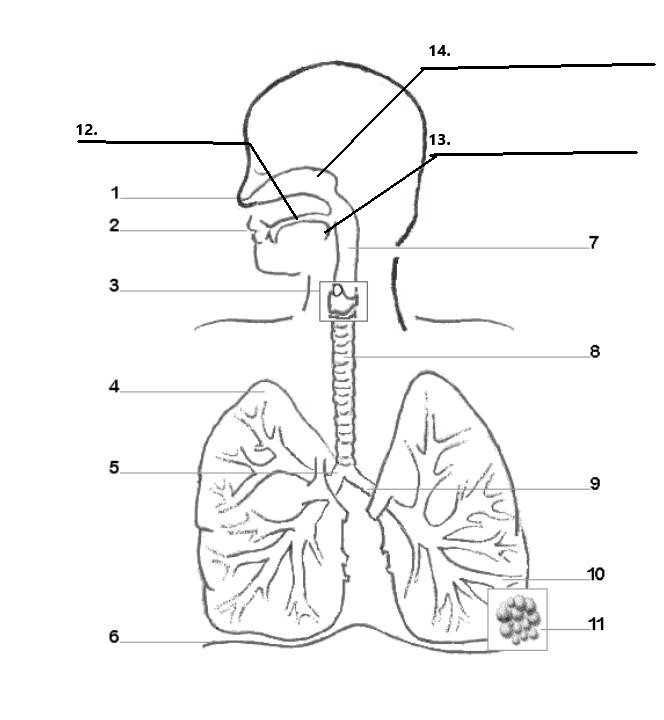
Label parts 6, 10, and 11 of the diagram:
6. Diaphram
10. Bronchiole
11. Alveoli
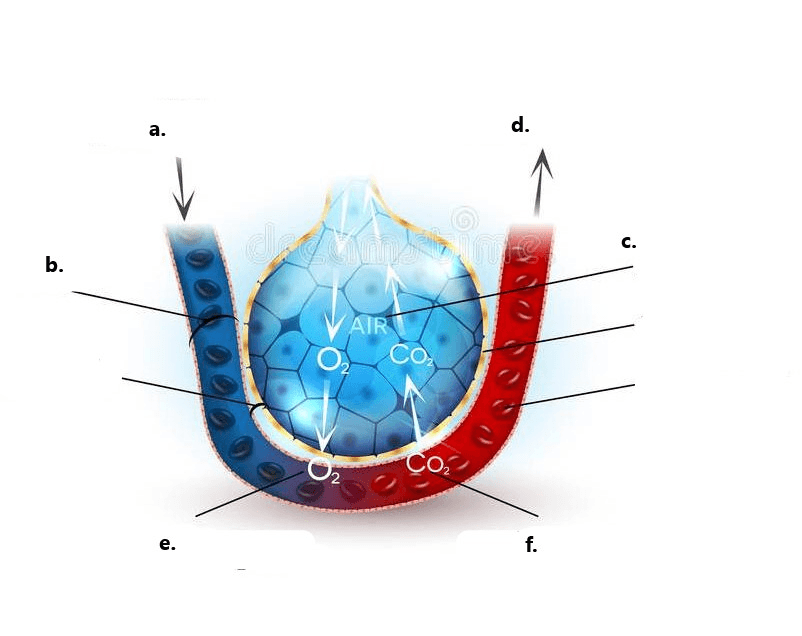
This process causes Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
Diffusion

What is this organelle? What type of respiration occurs here?
Mitochondrion. Cellular Respiration.
Vital Capacity (VC) = the same of what volumes?
Tidal Volume + Inspiratory Reserve Volume + Expiratory Reserve Volume
(TV + IRV + ERV)
True or False
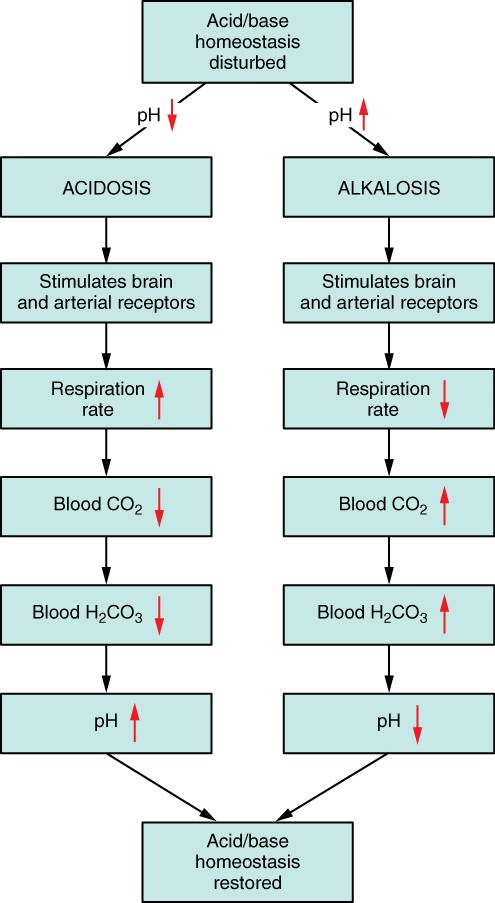
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) are acidic in when dissolved in blood and help regulate the pH of the blood.
True.
What 4 major bones and 2 muscles groups are represented in mechanical model from the video?
Bones: Radius, ulna, Metacarpals, phalanges
Muscles: Finger flexors & extensors
Name at least 7 major muscles involved in a back flip (see video).
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
1. Quads
2. Hamstrings
3. Glutes
4. Gastrocnemius
5. Rectus Abdominus
6. Triceps
7. Biceps

What are the ingredients and products of cellular Respiration.
Ingredients: Glucose and Oxygen
Products: Water, energy (ATP), Carbon Dioxide
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) is the sum of
__________________ + ____________________
Vital Capacity (VC) + Reserve Volume (RV)
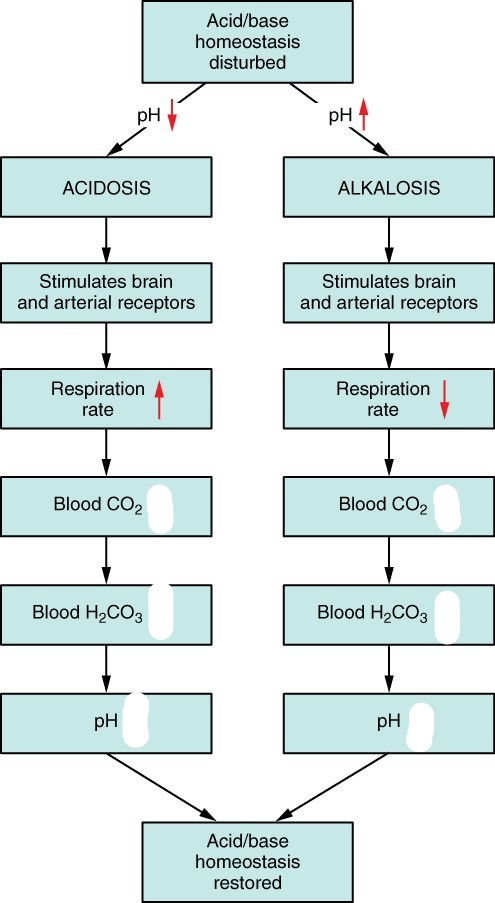
Fill in the blanks with an up or down arrow to show how the body responds to changes in pH.