Commonly called the windpipe, this structure is strengthened by rings of cartilage.
trachea
This term describes the volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal, relaxed breath.
tidal volume
The carbohydrate that is required for cellular respiration
glucose
identify the vessels in which gas exchange occur
the capillaries
process of lungs exchanging air with environment
ventilation
These air passages divide from the windpipe at the bottom of the trachea.
bronchi
The formula VC = IRV + TV + ERV defines this lung capacity. (hint what is VC?)
What is vital capacity.
The vessel that returns oxygenated blood to the heart
pulmonary vein
during exhalation, these muscles relax the rib cage
intercostal
the process of exchanging CO2 and O2 to produce energy (ATP)
respiration
What is the name of the large muscle (singular) that pulls air into the lungs?
The diaphragm
Identify letter C
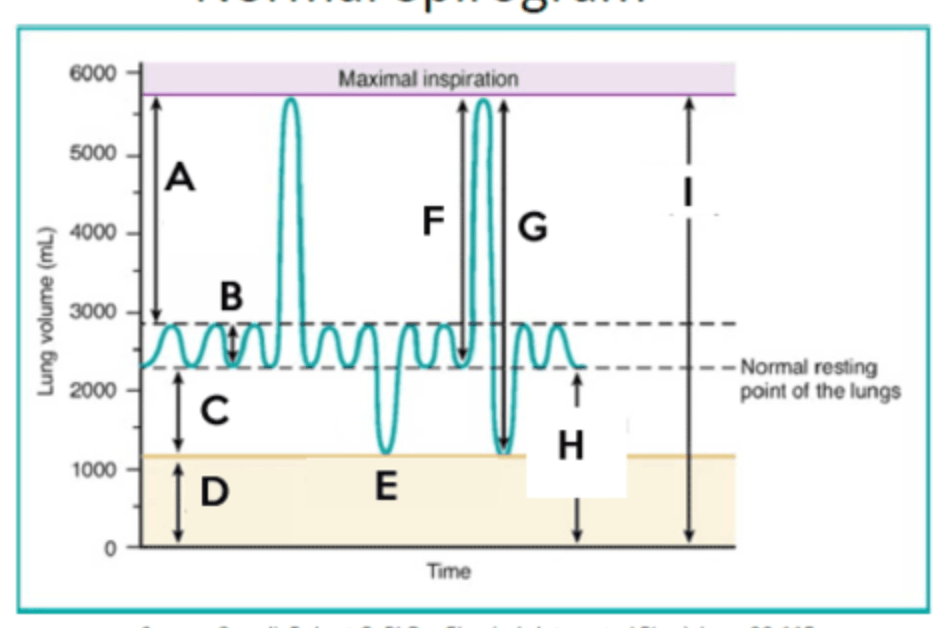
Expiratory reserve
The location of the brain that controls breathing
medulla
during inhalation, what occurs to the volume of the lungs
it increases
the process of taking air into the lungs
inspiration
This is a flap that covers the windpipe and helps keep food and water from entering the lungs.
Epiglottis
Total lung capacity is Vital Capacity + this volume
medical term for yawning
ostication
during inspiration this muscle inferior to the lungs contracts
diaphragm
exhalation
passive process of expelling air from the lungs
What are the tiny balloon-like sacs at the end of the bronchioles; location of gas exchange
Alveoli
What is the tool that is used to breathe in and measure lung capacity?
spirometer
classification of a respiratory disease such as bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchial tubes)
obstructive
the organelle in which cell respiration occurs
mitochondria
also known as systemic gas exchange; exchange of gases between blood and tissue (two words)
internal respiration