Anatomy
Anatomy
The large muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. On the lung model it was represented by a balloon that was cut in half.
What is the diaphragm?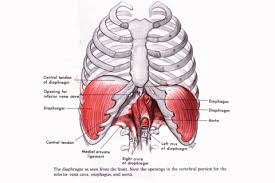
These are the 4 stages of respiration.
What is pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, transport, and internal respiration?
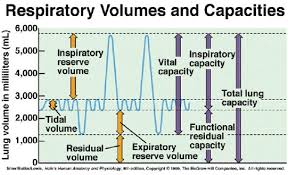
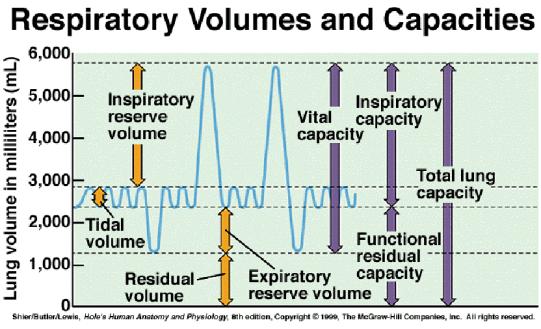
The amount of air that enters and leaves the lungs during a normal respiratory cycle ~500ml
What is tidal volume?
This will happen to your respiration rate if blood CO2 levels increase. What might cause this?
What is increase, exercise?
The mechanism for pushing air out of the lungs and pulling air into the lungs.
What is the pressure gradient (volume of thoracic capacity)?
This is the pathway of air through the following structures during inhalation. Alveoli, bronchi, bronchioles, epiglottis, larynx, nasal cavity, nose, pharynx, trachea
nose 🡪 nasal cavity 🡪 pharynx 🡪 epiglottis 🡪 larynx 🡪 trachea 🡪 bronchi 🡪 bronchioles 🡪 alveoli
How many oxygen molecules can one red blood cell carry, explain
~ 1 billion:
Each red blood cell contains 250 million hemoglobin molecules. Each hemoglobin molecule carries 4 oxygen bound to iron. 250 million x 4 = 1 billion!
This tool is used to measure lung capacities.
What is a spirometer?
If there is a high amount of carbon dioxide inside the body tissues and a low amount within the blood this will happen. What is this called?
CO2 will diffuse from the body tissue into the blood (from high to low concentration). Internal respiration.
This is what the rib muscles do to cause expiration.
What is the rib muscles relax, causing them to move inwards and down on the lungs
This is the respiratory structure where oxygen molecules diffuse and travel to the RBCs.
What is the alveoli?

What protein inside your RBCs binds to oxygen and which Which metallic atom does it contain?
Maximum Forced Exhalation ~ 1.2 L
What is expiratory reserve volume?
This structure is responsible for control of your respiratory rate.
What is the medulla and pons (brain stem)?
This is what the diaphragm does to cause inspiration.
What is the diaphragm contracts, causing it to flatten and push down
The reason why it is healthier to breathe through your nose instead of your mouth.
The nose is full of hair and mucous, which serve to trap bacteria, viruses, fungus, and other harmful agents in the air before they reach the lungs.
This is how most oxygen is transported in the body and what percentage
It binds with hemoglobin on the red blood cell, 95 – 98%
Maximum exhalation after maximum inhalation. 3,000-5000 mL
What is vital capacity?

Describe how gases move across structures in your body (i.e. alveoli -> capillaries)
What is diffusion? A substance (ex. O2 or CO2) moves from high to low concentration
Describe how inspiration occurs (cause and effect, include action of structures)
The diaphragm contracts pulls down and rib muscles contract pull ribs out -> increase the volume of the thoracic cavity -> decreases pressure -> air from the outside world moves from high pressure to low pressure (inside the lungs). This is breathing in!
The trachea is maintained in a open position by these supporting structures.
What is cartilaginous rings?
This is how 70% of CO2 is carried in the blood?
reacts with water in the blood to form bicarbonate ions to travel in plasma.
Air that never leaves the lungs.
What is residual volume?

If there is a high amount of oxygen inside the alveoli and a low amount inside the blood this will happen. What is this called?
Oxygen will diffuse from the alveoli into the blood (from high to low concentration) (external respiration)
The rate that you breathe at voluntary or involuntary? Explain.
Breathing rate is involuntary (you don’t have to think about it), but you can override your system and control your breathing rate (ex. Purposefully breathing faster when you are being goofy, or slower when you are doing yoga or practicing mindfulness).