The major function of the respiratory system is to:
Supply oxygen to, and remove CO2 from the body
Gold standard test for diagnosis of respiratory compromise
Arterial Blood Gas (Abg)
The normal ph value of an ABG
7.35-7.45
The most commonly used oxygen delivery device
Nasal Cannula
Percussion over the lung fields should produce what sound?
RESONANCE
This type of medication is given to relax smooth muscle and open airways
Bronchodilators
Contains structures such as bronchus, trachea, alveoli
Lower respiratory tract
This diagnostic tool can identify masses, air, or fluid in the lungs
Chest X-ray
What does HCO3 refer to in ABG findings?
Bicarbonate (metabolic buffering systems)
High Flow device most commonly used for accurate control of oxygen concentration on inspiration
Venturi Mask
Difficulty breathing while lying down that resolves with upright positioning is called
Orthopnea
This class of medicine depresses the respiratory drive and should be monitored closely
Narcotics (opioids/Benzos)
The process by which we inhale and exhale
Ventilation
Invasive diagnostic test for visualization of the respiratory tract down to the level of the secondary bronchi
Bronchoscopy
Indication for oxygen therapy using PaO2 measurement?
O2 level <60 mmHg
The oxygen delivery device seen here:

Tracheostomy Collar
Using this device 5-10 times/hour can prevent atelectasis, pneumonia, or worsening of pulmonary issues following invasive procedures
Incentive Spirometer
This medication should be ordered with a dose and a goal of therapy
Oxygen
The exchange of gases at the alveolar level is called
Perfusion
Diagnostic test used to evaluate lung volumes and function
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT's)
Which part of the ABG speaks directly to the process of ventilation?
PaCO2
This O2 delivery device has one way valves and an attached reservoir bag
Non-Rebreather
The finding noted below is called: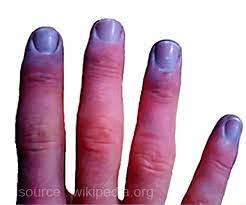
Cyanosis
Name two of three common side effects of albuterol?
Tachycardia
Nervousness/Shakiness
Headache
The two membranes surrounding the lungs are called
The visceral pleura and the parietal pleura
Diagnostic test used to remove air or fluid from the pleural space
Thoracentesis
ABG finding for these values:
ph: 7.31 PaO2: 86% pCO2: 32 mmHg HCO3: 26 mEq/L
Sa02: 91%
Respiratory Acidosis
This oxygen delivery system provides heated and humidified medical gas up to 60L/minute
High-Flow Nasal Cannula
Lung sound frequently described as tubular, moderate intensity, heard on inspiration and expiration
Bronchovesicular
This type of non-respiratory medication commonly causes patients to develop a dry, non-productive cough
Ace Inhibitors
Besides ventilation and respiration, name 3 other responsibilities of the respiratory system
Acid Base balance
Speech
Sensory Input/Output (Smell)
Fluid Balance
A Common side effect of a patient undergoing Thoracentesis is:
Feeling the need to cough
In a patient with COPD, the stimulus for breathing is ___________ , rather than _____________ .
Hypoxia, Hypercarbia
Collapse of the alveoli in the lung is referred to as
Atelectasis
Chest Physiotherapy uses vibration, percussion, and postural drainage to clear airways. List three nursing considerations to include in the plan of care for this patient.
perform 1 hour before /3 hours after meals
Head lower than chest (promote drainage)
Administer bronchodilator/ Mucolytics prior to treatment
Perform over patients gown; use towel or sheet
Provide suction device if needed
Change patients position to percuss all lung fields
This medication is used to treat stridor
Inhaled Racemic Epinephrine