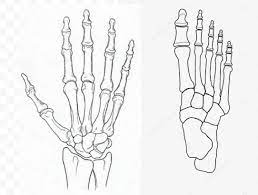
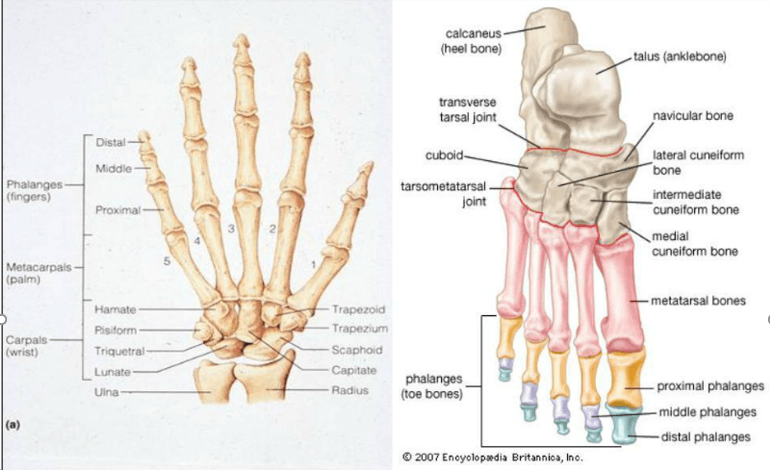
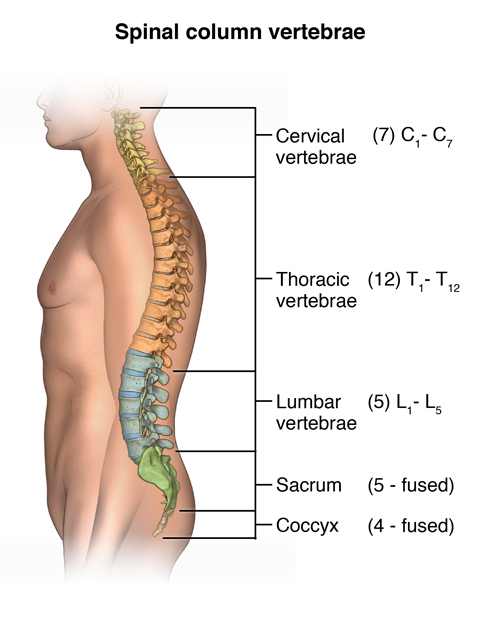
The overarching principle guiding the study of A&P - involves how things work and what they look like
What is the Principle of Complementarity of Structure and Function?

The process of cell replication and its stages
What is mitosis and prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase?
Important parts: DNA replication, chromosomes visible, link to kinetochores by microtubules, line up on metaphase plate, pulled apart, cytokinesis
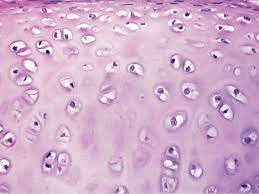
What is hyaline cartilage?

Parts of an atom
What are the neutron (0), proton (+), and electron (-)?
Atomic number = # o protons,
Atomic mass = protons + neutrons
The overarching principle guiding the actions of organs and organs systems that keeps things (e.g. pH, gases, energy, etc.) within a set range of values
What is homeostasis?





Types of chemical bonds
What are ionic, covalent (both polar and non polar), and hydrogen?

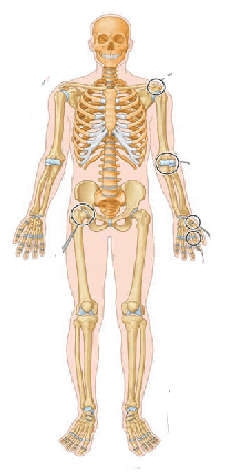
The anatomical words associated with the neck, lower leg, groin, chin, and the back of the knee
What are cervical, crural/sural, inguinal, mental, and popliteal?

The process of gene expression
What is (simply) DNA --> RNA --> protein?
(A little less simply)
Transcription: RNA pol binding, RNA pol linking, Detachment of RNA
Then: mRNA processing
Translation: initiation, elongation, termination

What is pseudostratified ciliated epithelium?
(This is a trachea slide)
Types of energy
What are potential and kinetic?
Levels of organization of life, from smallest to largest
What is chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism?



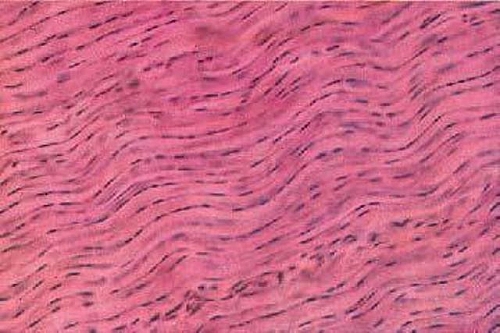
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Range of the pH scale, and the desired pH of blood
What is 0-14, and 7.35-7.45?

The different systems that work together to make the human body
What is integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, lymphatic/immune, respiratory, digestive, and urinary?



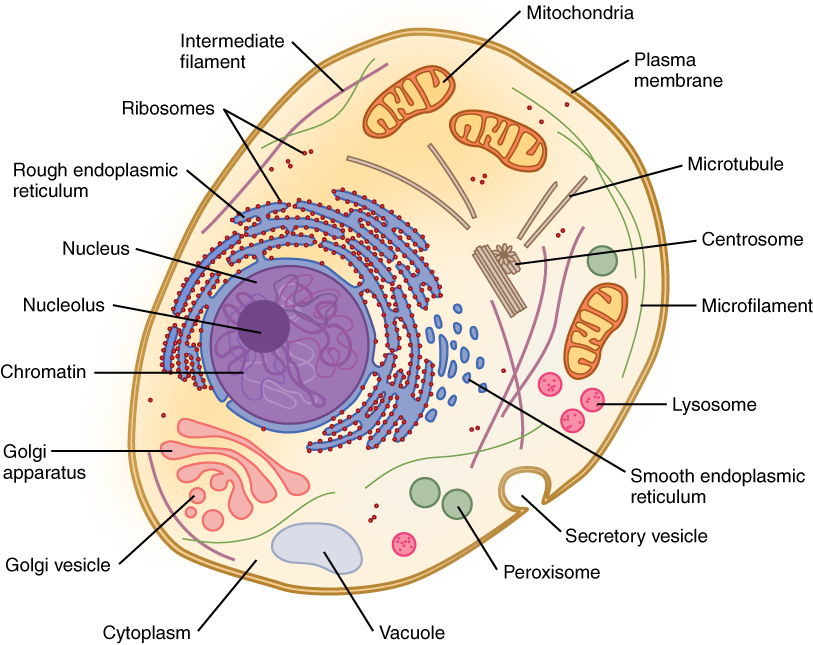
The four types of tissue and examples
What are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous?
Epithelial: squamous, cuboid, columnar, transitional, glands, accessories
Connective: LCT = adipose, areolar, reticular; DCT = elastic, regular, and irregular; fluid = blood and lymph; supporting = cartilage (elastic, hyaline, and fibro) and bone (spongy and compact)
Muscle: cardiac, smooth, skeletal
Nervous

What is reticular connective tissue?
Macromolecules and their monomers
What are carbohydrates (polysaccharides) and monosaccharides; lipids and glycerol + fatty acid tails (or steroids, eicosanoids, glycerides, and phospholipids); proteins (polypeptides) and amino acids; and nucleic acids and nucleotides?