This type of RNA has anticodons and helps bring amino acids to the ribosome. A valid sequence might include UAC or GGU.
Transfer RNA
a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and thymine together form this.
What is a DNA nucleotide
This number of bases makes up one codon in mRNA.
What is 3?
In the image, each tRNA is carrying this molecule at the end opposite the anticodon.
What is an amino acid?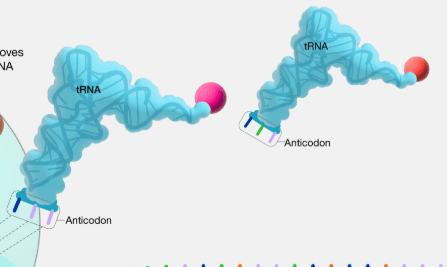
This type of molecule can be radioactively labelled and binds to a complementary DNA sequence to help locate a specific gene.
What is a DNA (or RNA) probe?
This part of a DNA nucleotide is a five-carbon sugar found only in DNA and is bonded to both a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
What is deoxyribose?
This process involves repeating denaturation, annealing, and extension to amplify DNA exponentially.
What is a PCR cycle?
This is the term for the energy needed to start a chemical reaction, which enzymes help reduce.
What is activation energy?
These biological molecules speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required for both synthesis and breakdown processes.
What are enzymes?
This heat-resistant enzyme is used in PCR to build new DNA strands by adding free nucleotides to primers after the DNA has been denatured.
What is Taq polymerase?
This part of a gene is transcribed into pre-mRNA but removed before translation.
What is an intron?
This gene segment is kept during RNA processing and codes for amino acids during translation.
What is an exon?
To produce human insulin using genetically modified bacteria, this step comes first:
A. Insert gene into plasmid
B. Culture transformed bacteria
C. Determine the amino acid sequence of insulin
D. Add recombinant plasmid to bacteria
What is C – Determine the amino acid sequence of insulin?
In this model of DNA replication, each daughter DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesised strand. It is represented in the diagram by the section where each double helix is half dark blue and half light blue.
🧠 Identify the name of this replication model. 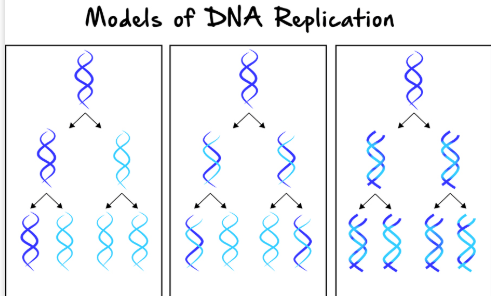
What is the semi-conservative model?
This is the specific region on an enzyme where the substrate binds and the reaction takes place.
This term describes what happens to an enzyme when it is exposed to temperatures above its optimum, causing it to lose its shape and function.
What is the active site?
What is denaturation
Name the purpose of each of the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis:
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
Answer: What is —
mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome;
tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome;
rRNA forms part of the ribosome and catalyses protein synthesis?
This is the term for the process where the enzyme changes shape slightly to better fit the substrate during binding
What is induced fit?
This DNA base is most commonly methylated to regulate gene expression
What is cytosine?
Explain how epigenetic changes, such as increased DNA methylation in genes that control cell division, can lead to cancer
What is — DNA methylation can silence tumour suppressor genes that normally prevent uncontrolled cell division. When these genes are turned off, cells may divide uncontrollably, increasing the risk of tumour formation and cancer?
Changing this part of a protein, such as p53, can change its shape and prevent it from performing its role in regulating the cell cycle.
What is the amino acid sequence?
CRISPR-Cas9 requires this to accurately cut DNA at a specific target site without affecting other parts of the genome.
What is a unique base sequence?
What is a unique base sequence?
A unique base sequence is a specific order of nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G) in a DNA strand that only appears once in the entire genome.
an enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific recognition site.
Restriction enzyme
Role of components in PCR
(i) Primers
Short single-stranded DNA sequences that bind to the target DNA at the beginning and end of the region to be copied.
They initiate DNA synthesis by providing a starting point for DNA polymerase.
(ii) DNA Polymerase
A heat-resistant enzyme that adds free nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, extending from the primer.
It synthesises new DNA strands complementary to the template strand.
This is the variable that a scientist deliberately changes to observe its effect.
This variable is measured or observed in response to changes in the independent variable.
These variables are kept constant to ensure a fair test and reliable results.
What is the independent variable?
What is the dependent variable?
What are control variables?