 The breakdown of rock into sediments due to rain, wind, and snow.
The breakdown of rock into sediments due to rain, wind, and snow.
Weathering
 Type of rock formed when lava or magma is cooled
Type of rock formed when lava or magma is cooled
Igneous
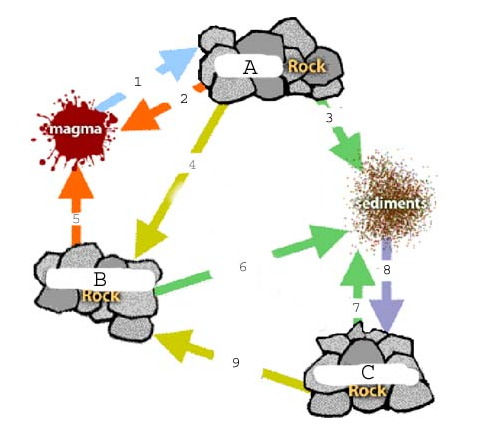 What type of rock is at "A"?
What type of rock is at "A"?
Igneous
Which layer is the youngest?
E
Explain the difference between weathering and erosion.
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks into sediment by wind, water, gravity, etc. Erosion is the transport of sediment after weather occurs.

Erosion
 Rock can be weathered into tiny particles called ______.
Rock can be weathered into tiny particles called ______.
sediment
What type of rock is at "C"?
Sedimentary
 How old is "A" compared to "B" and "C"?
How old is "A" compared to "B" and "C"?
"A" is the oldest compared to "B" and "C"
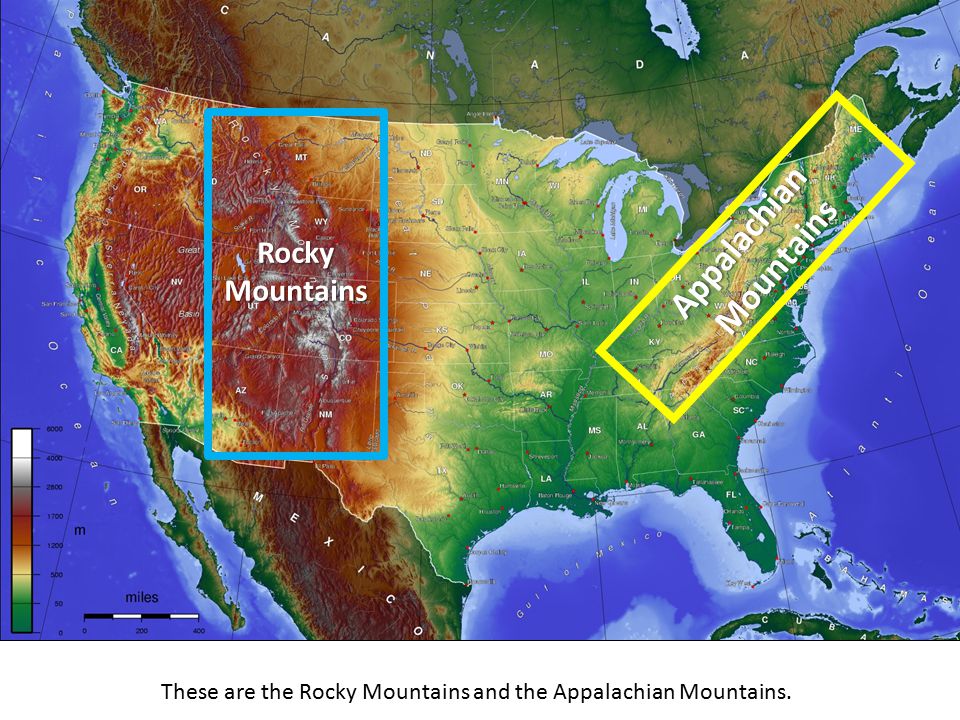 Why do shorter, more rounded mountain ranges tend to be older compared to taller, jagged mountains?
Why do shorter, more rounded mountain ranges tend to be older compared to taller, jagged mountains?
Older mountains are exposed to weathering for a longer period of time which wears them down.

Compaction
 Compaction and cementation form this type of rock.
Compaction and cementation form this type of rock.
Sedimentary
 What's happening at the green arrows?
What's happening at the green arrows?
Weathering
How does the age of D compare to B and C?
After making a claim, a scientists must support the claim with ______ and _______.
evidence, reasoning
 Sediments glued together by water and minerals.
Sediments glued together by water and minerals.
cementation
 Rock formed by heat and pressure
Rock formed by heat and pressure
Metamorphic
 What's happening at the orange arrows?
What's happening at the orange arrows?
Melting
List the order of these layers from oldest to youngest.
A, B, C, D, E
Knowing that the moon has no liquid water and no atmosphere, what rock transformation processes would NOT occur on the moon?
Weathering and Erosion

Moving rocks below earth's surface (hint: does not change the type of rock)
Subduction
What types of rocks are formed by processes caused by energy from Earth's interior?
Igneous and Metamorphic
What's happening at the purple arrow?
arrow?
Compaction and cementation
 Which layer is older? C or A? and why
Which layer is older? C or A? and why
The older Layer is A because C was deposited on top of the rock structure after A was formed
The moon does have volcanic activity. What does this tell you about the majority of the rock on the moon?
A majority of the rocks on the moon are igneous rock.