This image represents what process
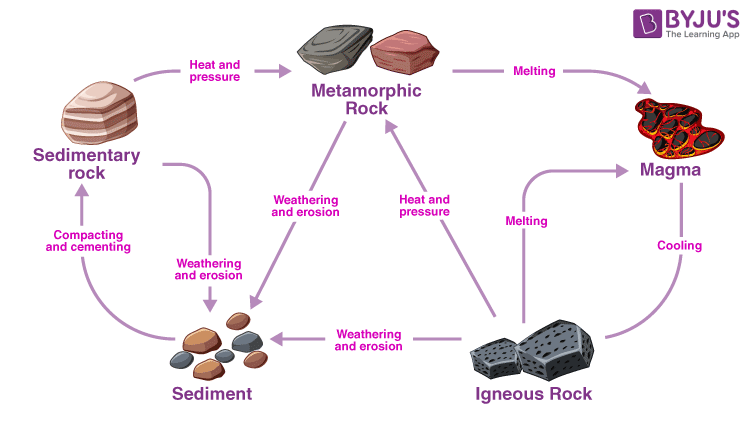
The Rock Cycle
Igneous rock type formed from magma and cooled UNDERNEATH the earth's surface
What is intrusive rock
Small particles that make up sedimentary rock.

What is sediments
Under pressure, shale forms what metamorphic rock, often used for roofing?
Slate
What is magma? How does magma differ from lava?
Magma refers to molten rock, which is found at depth, while lava refers to molten rock that is found on the surface of the Earth.
The type of rock that forms from magma or lava
What is igneous rock
Why do crystals in a magma stop growing during cooling?
They run out of space
The first step in turning a rock into a sediment is ________.
weathering alters the rock
| Two forces required to create metamorphic rock | 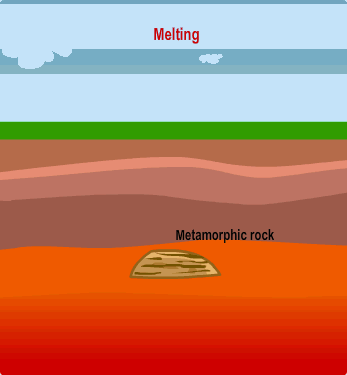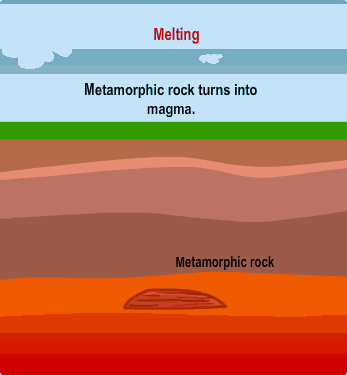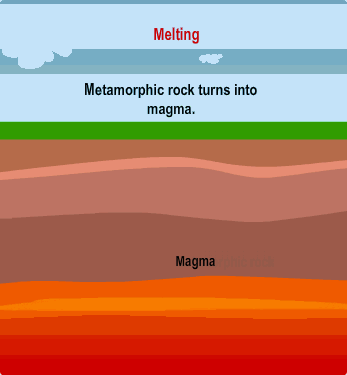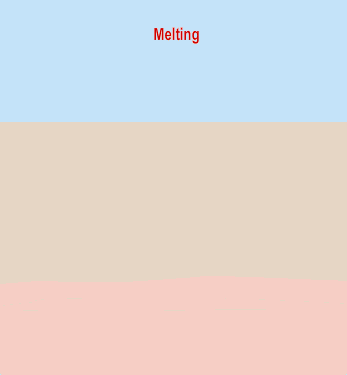 |
What is heat and pressure
The terms intrusive and extrusive are used to describe which one of the three rock groups?
Igneous Rocks
What are the 3 major groups of rocks

igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic
This action causes vesicles (open pores) to form in extrinsic rock when it is formed.

Gases are released.
Why are sedimentary rocks important?
Sedimentary rocks contain almost all of the fossil record. Sedimentary rocks make up about 75% of continental rock outcrops and contain clues to the history of the Earth’s surface. They also have economic importance; for example coal is a sedimentary rock and other natural resources are extracted from sedimentary rocks.
Texture of this metamorphic rock

Foliated
What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive?
Intrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in larger crystals due to slow cooling, while extrusive igneous rocks form when lava cools rapidly on the Earth's surface, creating smaller crystals; essentially, the key difference is where the magma cools - underground for intrusive and on the surface for extrusive.
True or False: Under the right circumstances, any rock can be transformed into another type of rock in the rock cycle.
True
Type of rock formed from lava ON the earth's surface.

What is extrusive rock
Type of this sedimentary rock (not name)
Biochemical
Under extreme temperature or pressure limestone becomes this metamorphic rock.

What is marble?

What is the most characteristic feature of sedimentary rocks?
Stratification - Layering of sediments
This is the starting process by which Igneous rock transform to sediment.

What is weathering or erosion
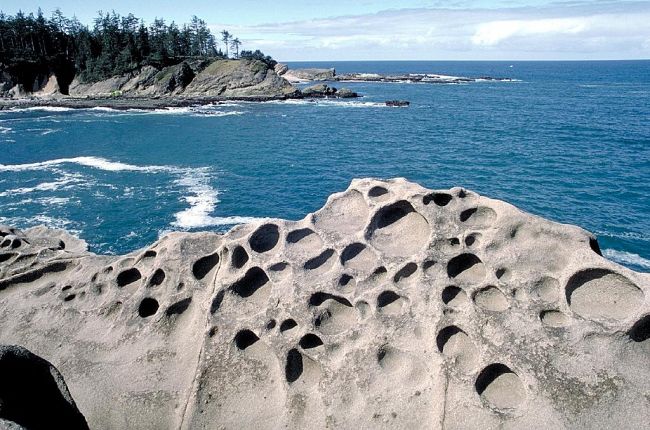

Intrusive igneous rocks are often characterized as coarse-grained because ________
the slow cooling at depth allows large crystals to grow
Sedimentary rock made up of broken pieces of other rocks

Clastic or Conglomerate
Regional metamorphism often occurs during this tectonic process
Mountain building
What type of rock is generated when rocks that formed near the surface become deeply buried and exposed to intense pressure and/or heat (but do not melt)?
Metamorphic Rocks
This is the process by which layers of sediment become compacted and cemented together.

Lithification
What happens to crystals in igneous rocks when lava cools very quickly.
They have very small crystals

Process by which sediments become sedimentary rocks
Lithification
How forces are applied to rocks under confining pressure.
Forces are applied equally in all directions
When determining rock composition, describe the test that can be used to determine whether it contains the mineral calcite.
Placing dilute hydrochloric acid on the rock to see if it reacts (fizzes) with the calcium
What is the most common place for sediment to be deposited and why?
Oceans
There are a few explanations. First, 2/3 of the Earth's surface is oceans so it is most likely that anything on the Earth's surface will be in an ocean. In addition, most streams end in the oceans and the streams are one of the important mechanisms for moving sediment. I would also add that gravity moves things downhill and the ocean basins are generally lower than the continental surfaces.
Igneous texture characterized by two different crystal sizes?

What is porphyritic?
Describe the process of lithification.
- Compaction occurs where pressure is placed on loosely packed sediment. Volume of the sediment is reduced and water is squeezed out.
- Cementation occurs when mineral-bearing water circulates among the grains, hardens, and cements the sediment grains together. This process is most effective for lithifying sand and gravel-sized sediments.
Primary agent of contact metamorphism
Heat
The texture of the following igneous rock?

Aphanitic
Use the rock cycle to explain the statement “One rock is the raw material for another.”

The rock cycle illustrates that any rock type can be transformed into any other rock type. As an example, igneous rocks may be weathered and compacted into sedimentary rocks. Those sedimentary rocks may be subjected to heat and pressure to become metamorphic rocks. Depending upon the conditions, rocks can be continually transformed into different types of rock.
A porphyritic texture where large crystals are embedded in a matrix of small crystal may form when ________. 
a magma that has partially crystallized slowly moves to a different location where it then cools rapidly.
Breccia is likely to have traveled only a short distance before compaction and cementation. How do we know this? Explain.

The fragments are angular so they didn't bounce off the other objects which would have rounded the corners.
Mountain building causes metamorphism because ________.
Mountain building creates differential pressure on the parent rocks
mountains are heavy and they push shallow, cool rocks to depths where they get heated
mountains form by the gradual buildup of material that comes from other areas and this can produce an uneven pressure on rocks
True or False: Glassy igneous rocks form when magma cools too fast for mineral grains to grow.
True
Why does magma rise toward the Earth's surface?
Because it is less dense than the material around it
Obsidian exhibits a ________ texture.
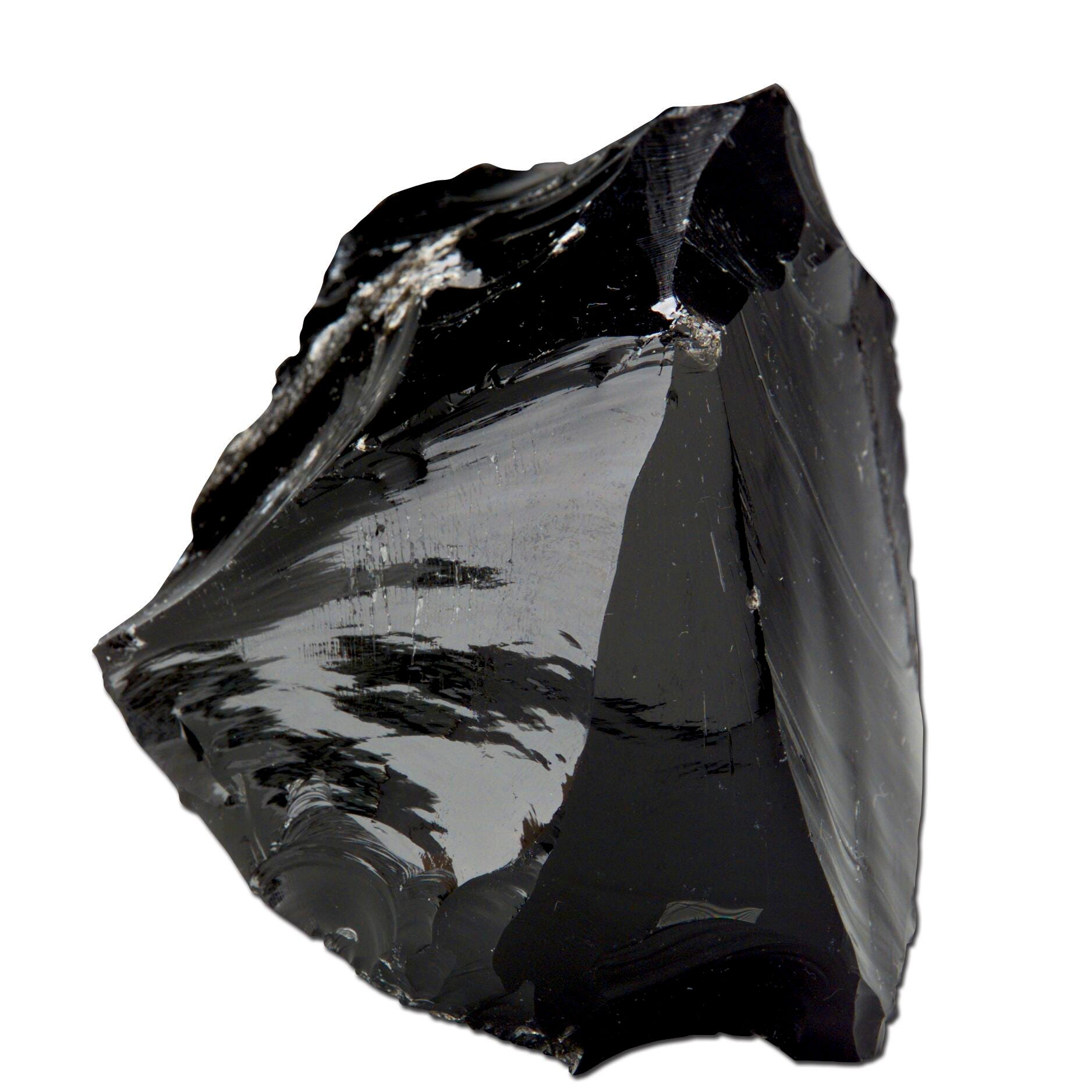

Glassy
The most abundant chemical sedimentary rock is ________.
limestone
What is foliation?
Foliation in metamorphic rocks refers to a visible layering or banding pattern formed by the parallel alignment of mineral grains within the rock, caused by extreme pressure during metamorphism,
Which sample(s) in the image exhibit(s) a porphyritic texture?
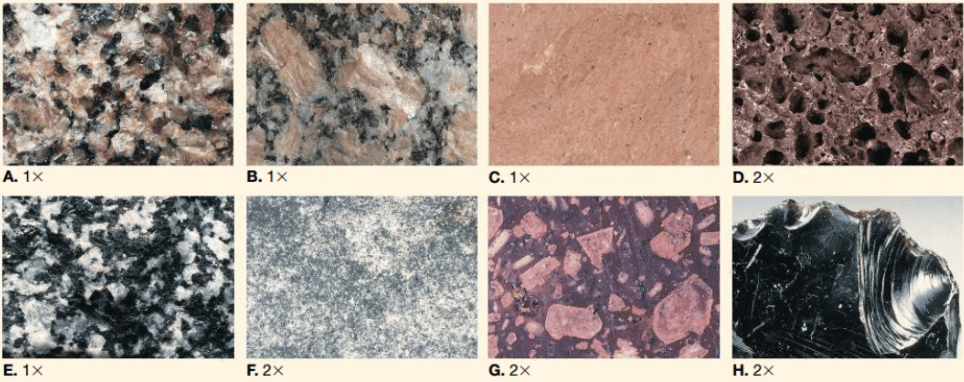
B and G
What is required for an igneous rock to weather?
It must be exposed at the surface of the Earth.
What is the texture of the following rock?

Phaneritic
True or False: Frost wedging is a form of chemical weathering
False
Distinguish between regional and contact metamorphism.
Regional metamorphism is associated with mountain building and involves large amounts of pressure and high temperatures. It results in large-scale rock deformation. Contact metamorphism occurs when rock is in contact with hot magma. In these cases, metamorphism is heat-related.
What term is used to describe the larger crystals in a Porphyritic igneous rock?
Phenocrysts
Which rock in the image displays the best example of a vesicular texture?

D
Which sample(s) in the image exhibit(s) a phaneritic texture?

A and E
Describe the environment in which a fine-grained igneous rock forms
When molten lava solidifies on the surface, it cools rapidly and produces a fine-grained igneous rock
Every metamorphic rock has a ________________, the rock from which it was formed.
Parent Rock
Describe the environment in which a coarse - grained, phaneritic igneous rock forms.
When molten magma solidifies at great depths, it cools slowly, forming course grained igneous rock.
_________________ shows the interrelationships among the three rock types
The Rock Cycle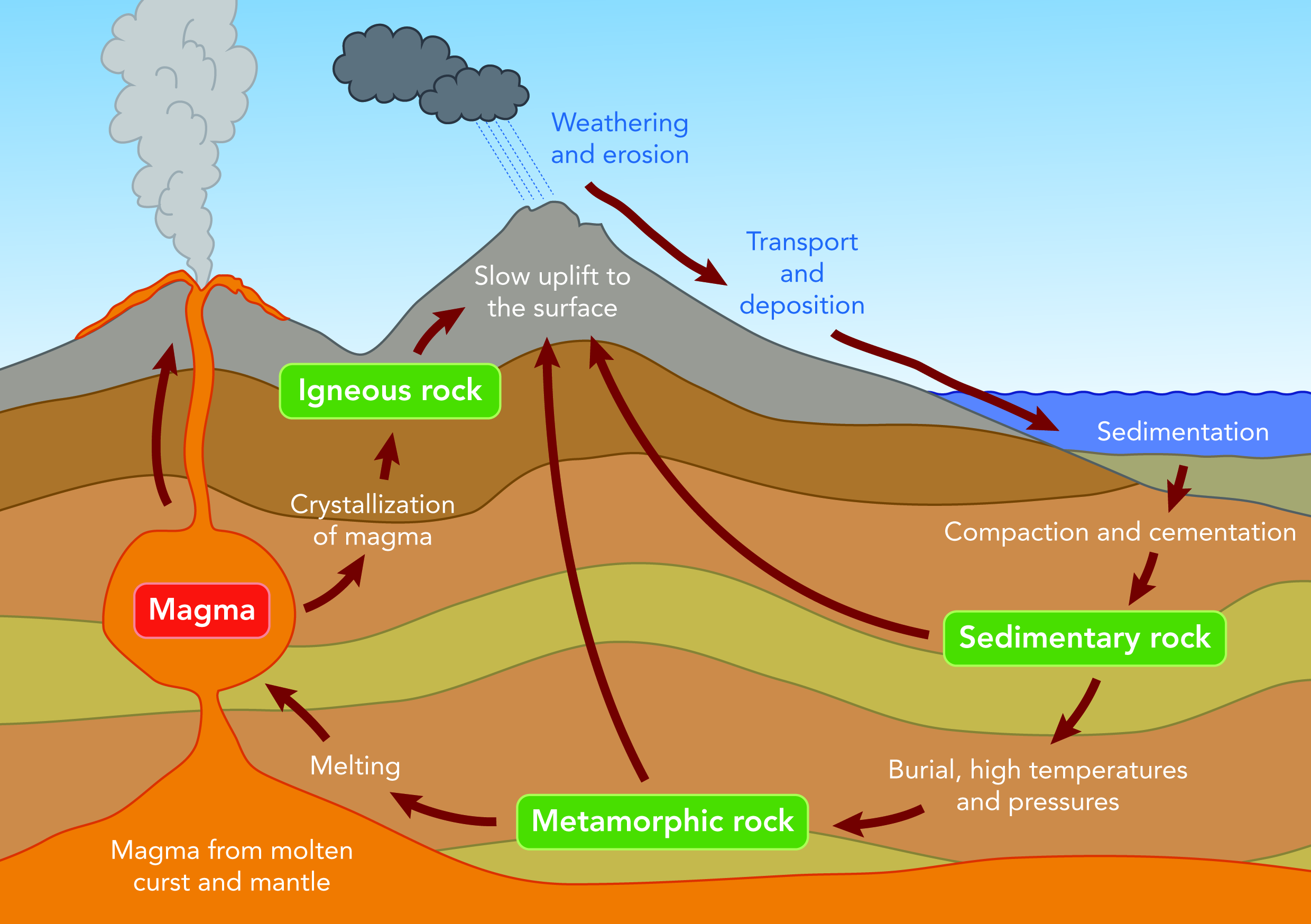
Be sure to know the difference between low-grade and high-grade metamorphism.
Metamorphic grade refers to the range of metamorphic change a rock undergoes, progressing from low (little metamorphic change) grade to high (significant metamorphic change) grade. Low-grade metamorphism begins at temperatures and pressures just above sedimentary rock conditions.
