Klebsiella pneumoniae stains gram negative, with this morphology.

What are rods? (or bacilli)
Dopaminergic and CB1 receptor pathways are implicated in "antimotivational syndrome", caused by this substance.
What is cannabis?
This risk of this disorder causing a stroke is reduced with anticoagulation.
What is atrial fibrillation?
Younger women have a higher risk of pulmonary embolism because of this class of commonly used medications.
What are oral contraceptives?
This patient presented with syncope and hypotension. He is not responding to infusions, what intervention might next be needed?
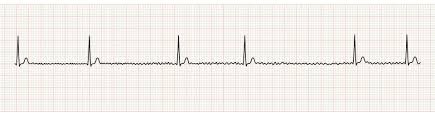
What is pacing?
Respiratory viruses are generally transmitted via this mechanism.
What are droplets?
If this character developed pulmonary hypertension, there is a good chance it was caused by this drug.

What is methamphetamine?
This manifestation of left middle cerebral artery stroke describes inability to process language.
What is aphasia?
This imaging modality is the most commonly used in diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
What is CT angiography?
SSS, an acronym for this, is a common indication for permanent pacemaker placement.
What is sick sinus syndrome?
This microaerophilic organism has minimal oxygen requirements, allowing it to survive in the human lung for decades.
What is Mycobaterium tuberculosis?
This molecule binds to the mu receptor with 50 times more potency than heroin.
What is fentanyl?
This intervention given more than 4 1/2 hours after a stroke may lead to the finding below
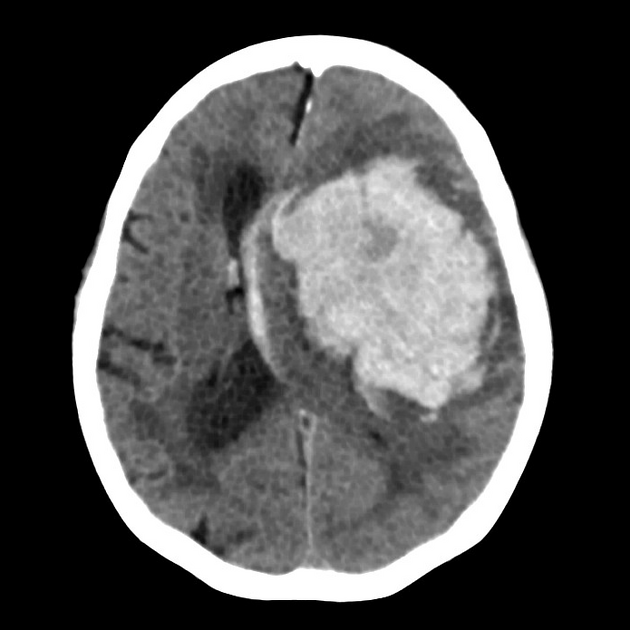
What is thrombolysis?
This parenteral medication used for pulmonary embolism is not typically monitored, but can be with anti-Xa assays.
What is enoxaparin?
Common adverse reactions to this antiarrhythmic medication include interstitial lung disease, thyroid dysfunction, and liver toxicity.
What is amiodarone?
This organism has adapted to adhere to hardware and heart valves, sometimes requiring prolonged duration of antibiotic therapy.

What is Staph aureus?
This effect of cocaine on coronary arteries can mimic myocardial infarction.
What is vasospasm?
Not so fast with that labetalol . . . this strategy improves perfusion after an acute infarction.
What is permissive hypertension?
Echocardiogram can be especially useful to identify this manifestation of pulmonary embolism, with findings such as D sign and McConnell sign.
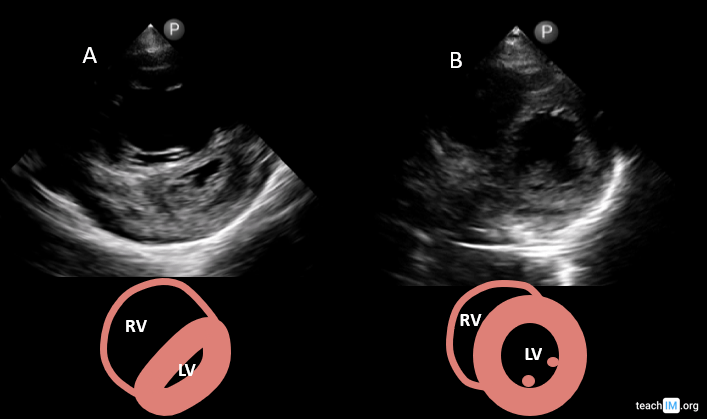
What is right heart strain?
What is electrical cardioversion?
Valley fever occurs when a patient inhales the mold form of this fungus in an endemic area, and then it ruptures in the lungs due to the high temperature, spreading spherules that cause infection.
What is Coccidioides?
Repeat dosing or continuous infusion of this antidote is often needed, because its half life is shorter than many forms of the drug.
What is naloxone (Narcan)?
We might expect this neurologic manifestation to accompany this finding.
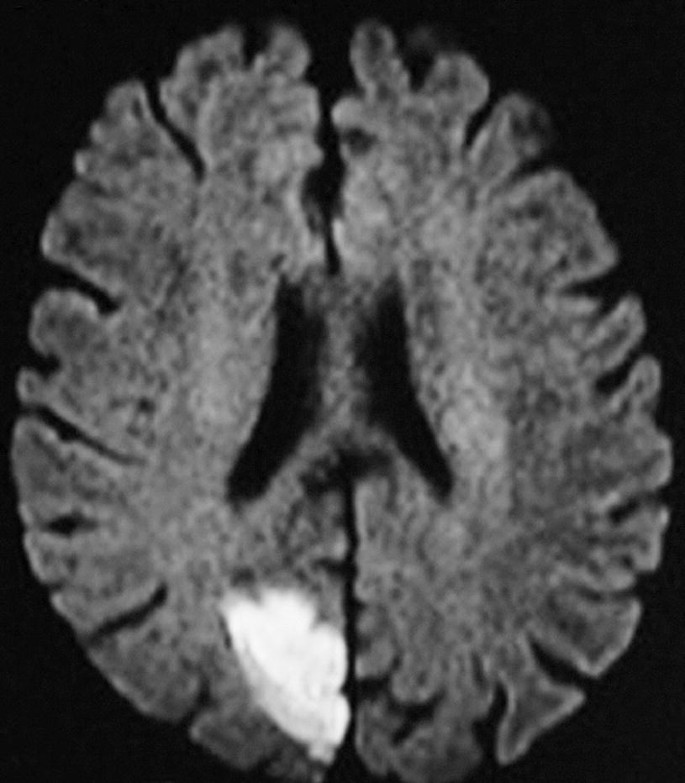
What is left visual field loss?
Pulmonary embolism with shock is the primary indication for this medication.
What is thrombolysis with TPA?
The appendage is a structure in the left atrium commonly implicated in this when a patient has A fib.
What is thrombosis?