The humeral epicondyles should be ______ to the IR for an AP view of the shoulder.
What is parallel?
The foot is rotated internally _____ degrees for an AP Hip
What is 15 degrees?
The centering location for an AP Pelvis
What is a line 2" below the ASIS and centered on the MSP?
Folds on the inside of the stomach
What are rugae?
Joe's middle name
What is Edward?
The name of this position:
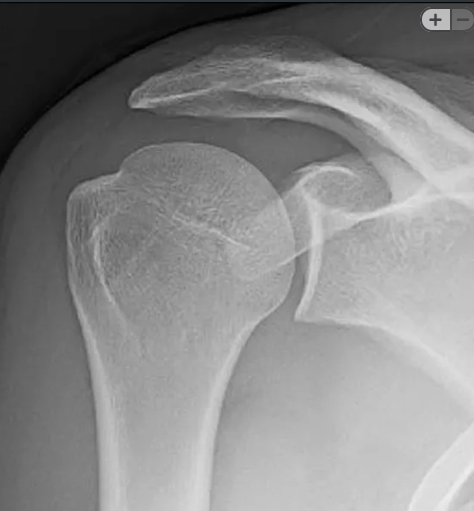
What is Grashey method or posterior oblique?
What does ASIS stand for?
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
This part of the pelvis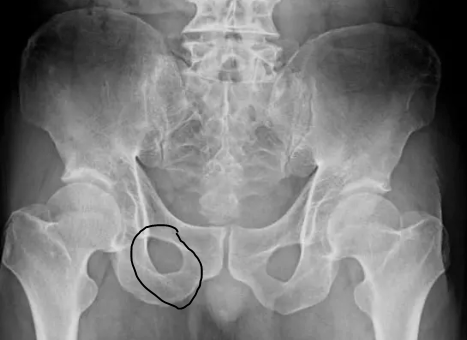
What is the obturator foramen?
Identified by the letter F in this image:
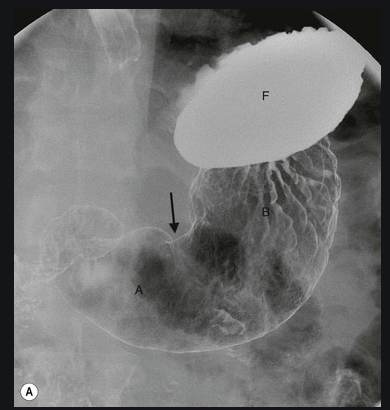
What is the fundus?
What xrays are made up of.
What are photons?
Name this part:
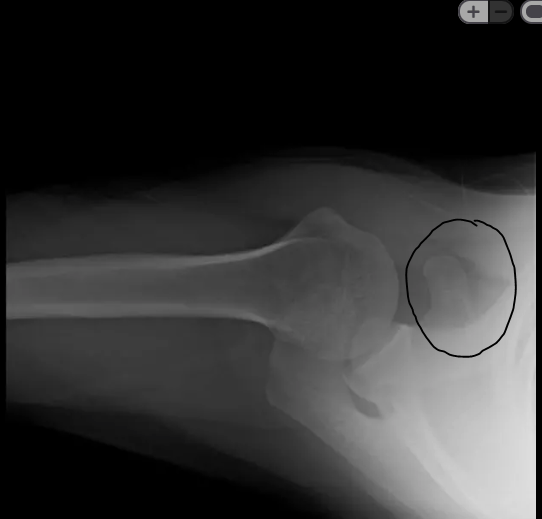
What is the coracoid process?
This part of the femur: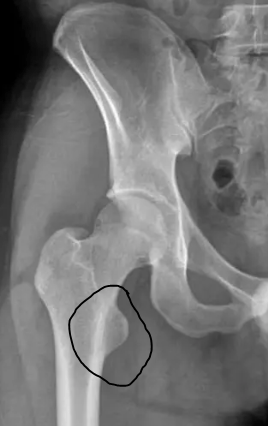
What is the lesser trochanter?
Internally rotated 15 degrees for AP pelvis
What is done with the feet on a AP Pelvis view?
Introduces air into the Upper GI exam
Restricts the size and shape of the beam
What is the function of a collimator?
Humerus Positions done on the trauma patient
What are the neutral AP and trans-thoracic lateral?
This part of the distal femur: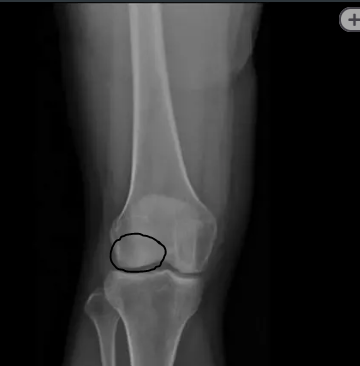
What is the lateral condyle?
The line(s) identified on this image:
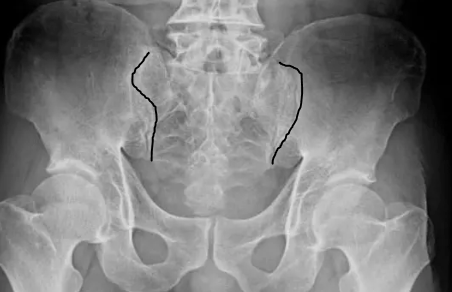
What are the sacro iliac joints
This part of the large intestine:
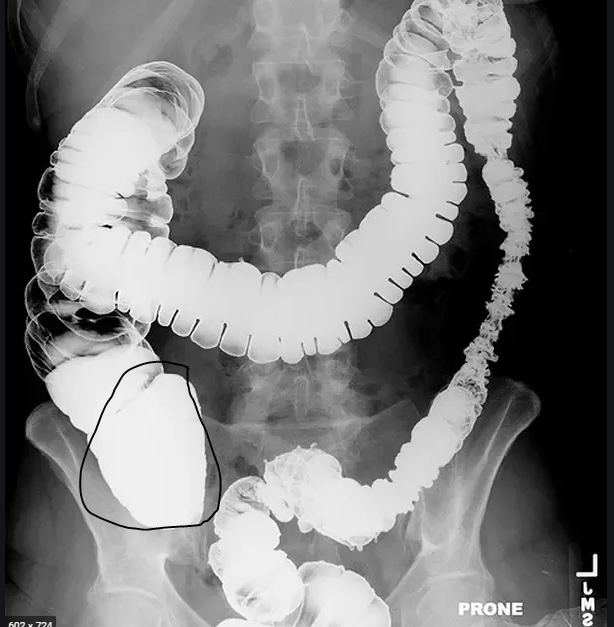
What is the cecum?
Probably the best lab instructor of all time
Who is Joe?
Patient rotated 45 degrees, slightly abduct arm, arm in neutral position. CR is 2" in from shoulder edge and 2" inferior from top of shoulder
What is the patient position and CR centering on a Grashey method shoulder?
This view of the hip is called:
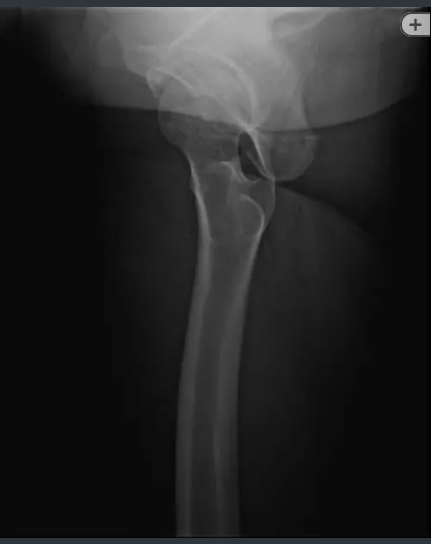
What is a cross table lateral or axiolateral inferosuperior view?
Name this position:
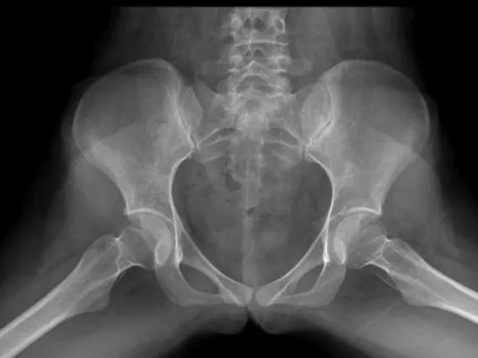
What is a Bilateral frog pelvis?
The path that barium takes during a during a Barium Enema
What is the sigmoid colon, decsending colon, lt colic flexure (splenic), transverse colon, rt colic flexure (hepatic), ascending colon, cecum?
Joes birthday
What is December 9th?