What is the international (SI) unit used to describe radioactivity?
Becquerel (Bq)
Three types of natural radiation
Terrestrial, cosmic, and internal
What is the most commonly used dosimeter? (Acronym and written out words)
OSL: optically stimulated luminescence dosimeter
"Scatter" is what this interaction is commonly referred to.
Compton
2-part question: What type of anode is used in modern x-ray equipment? What is the range of this piece of equipment?
Rotating anode; 3,000-10,000 rpm
What is the maximum annual whole-body effective dose limit for radiographers? What are the skin and extremities?
50 mSv; 500 mSv
Gamma radiation has a _____ wavelength and therefore a _____ frequency than microwaves.
Shorter; higher
Which dosimeter is primarily used in nuclear medicine and where is it worn?
TLD; finger of dominant hand facing palmar side
What are the two diagnostically contributing interactions?
Photoelectric and Compton
Name the three components with their function and name that are needed to produce an X-ray.
Source of electrons (Cathode), rapid acceleration (voltage), sudden deacceleration (target/anode)
What is the general rule that applies to the public population's doses compared to radiation occupational workers?
Doses are approximately 1/10th the dose
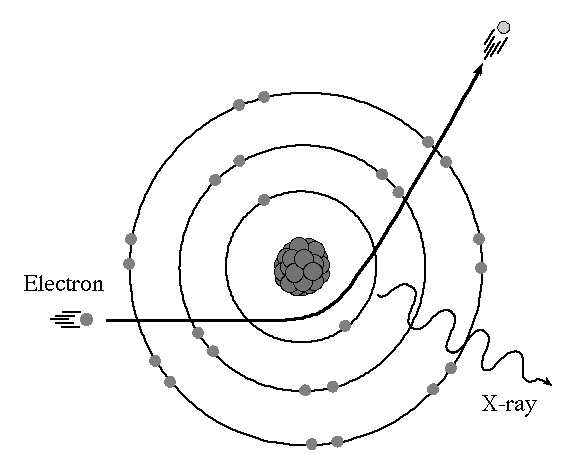
What type of x-ray is produced in this image? What is its emission spectrum represented by?
Bremsstrahlung; continuous/nonthreshold/bell-shaped
What are thermoluminescent (TLD) dosimeters made of?
Lithium fluoride crystals
What are 5 other names for a Coherent interaction?
Thompson, Rayleigh, Classical, elastic, unmodified

Which number represents where element atoms undergo ionization?
8
Which NCRP Report suggests the annual exposure dose limits used today?
Report #116
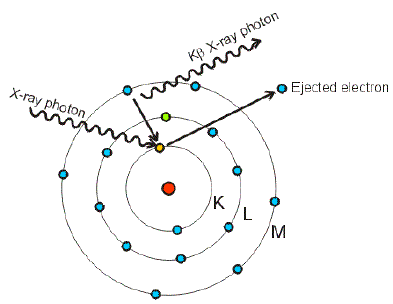
What is the type of x-ray that is produced by the above interaction? What is this considered toward the radiographic image?
Characteristic; "useful"/diagnostic
What is the monthly dose limit for a fetal dose?
0.5 mSv
Pair production takes _____ to ______.
Photodisintegration takes ______to ______.
Pair production: Matter to energy
Photodisintegration: Energy to matter
What two different interactions result in a "cascade" effect that produces secondary X-rays?
Characteristic and Phtoelectric
What is the equation to calculate an equivalent dose?
Absorbed dose x tissue weighting factor x radiation weighting factor
What effect would occur to the X-ray emission spectrum if the 15% rule is applied to an original technique of 70 kVp and 6 mAs to reduce a patient's dose?
Shifts to the right and amplitude descreases
What dosimeter can record doses as low as 1 mrem (10 microsieverts) and what filters does it contain?
OSL; aluminum oxide, copper, tin
If kVp is increased, the ______ (interaction) increases, the _____ (interaction) decreases, patient dose _____, and contrast ______.
Compton, Photoelectric effect, decreases, decreases
Which generator produces the most efficient X-ray beam? What is its voltage ripple?
High-frequency; <1%