This is the articulation formed between the cricoid and arytenoid cartilages.
What is the cricoarytenoid joint?
The cuneiform cartilages rest inside the aryepiglottic folds.
True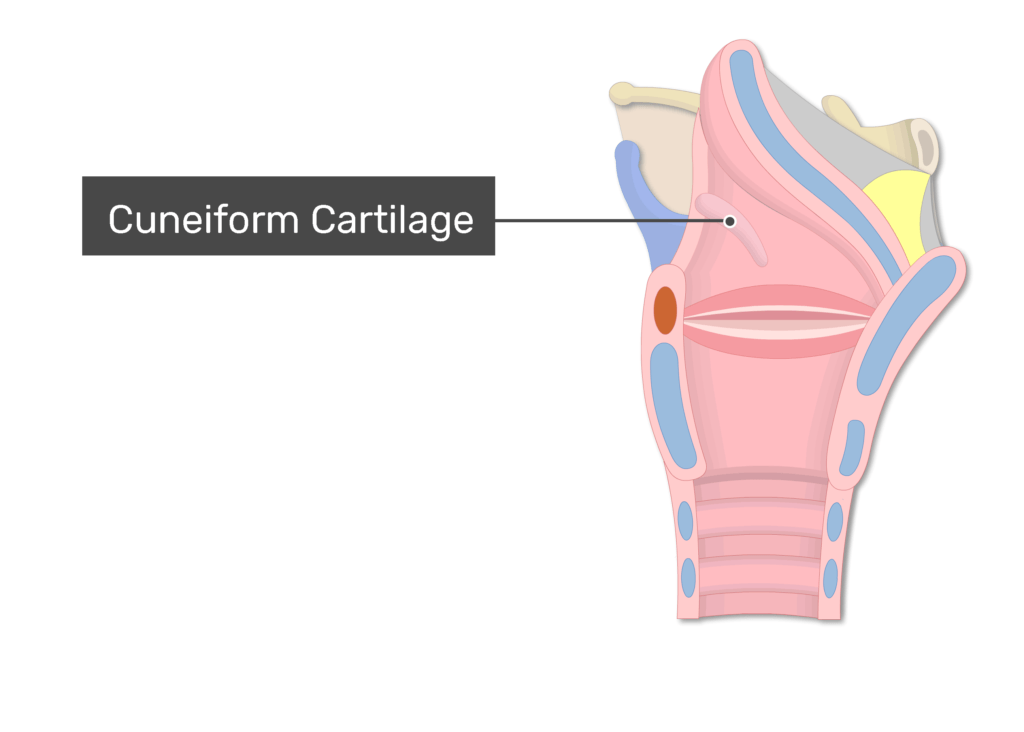
An increase in vocal fold tension is related to an increase in this psychological correlate of frequency.
What is pitch?

Mylohyoid
Elevator

Structure 9
What is the thyroid cartilage?
The thyroid cartilage has two sets of horn-like extensions, also known as this.
 What are the cornu?
What are the cornu?
or
What are the inferior and posterior cornu?
The sternohyoid muscle is a laryngeal depressor with two bellies (a superior and inferior belly).
False
This question describes the omohyoid.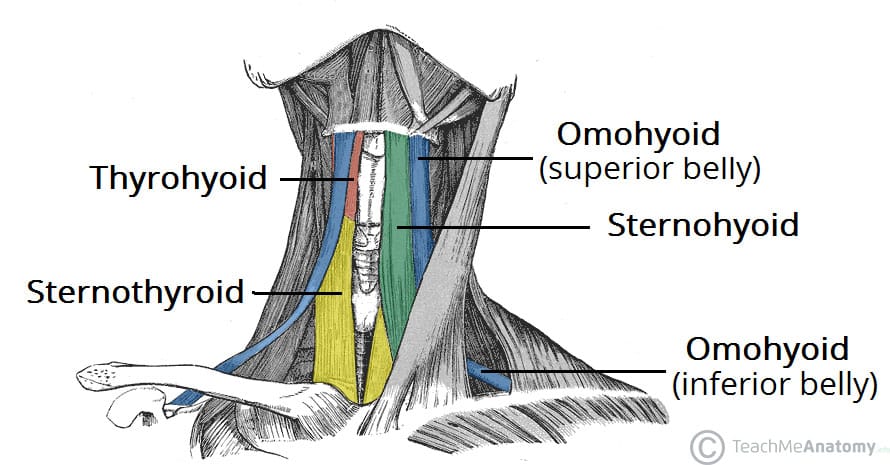
In this type of vocal attack, onset of airflow comes before adduction (coming together) of the vocal folds
What is breathy vocal attack?
 Geniohyoid
Geniohyoid
Elevator
Structure 10
What is the cricoid cartilage?
This sinus is a small indentation between the aryepiglottic fold and thyroid cartilage.
What is the pyriform sinus?
The stylohyoid muscle elevates the larynx and retracts the hyoid bone.
True
This is the frequency of vibration that is most efficient for a person's vocal folds. It depends on gender and age.
What is optimal pitch?

Digastricus
Elevator
 Yellow structure
Yellow structure
What is the transverse arytenoid?
The epiglottis is attached to the hyoid bone by this ligament.
What is the hyo-epiglottic ligament?
In the associated chain theory, a master control mechanism tells muscles when exactly to move.
False
This question describes the central control theory.
This muscle is the primary tensor of the vocal folds.
What is the cricothyroid?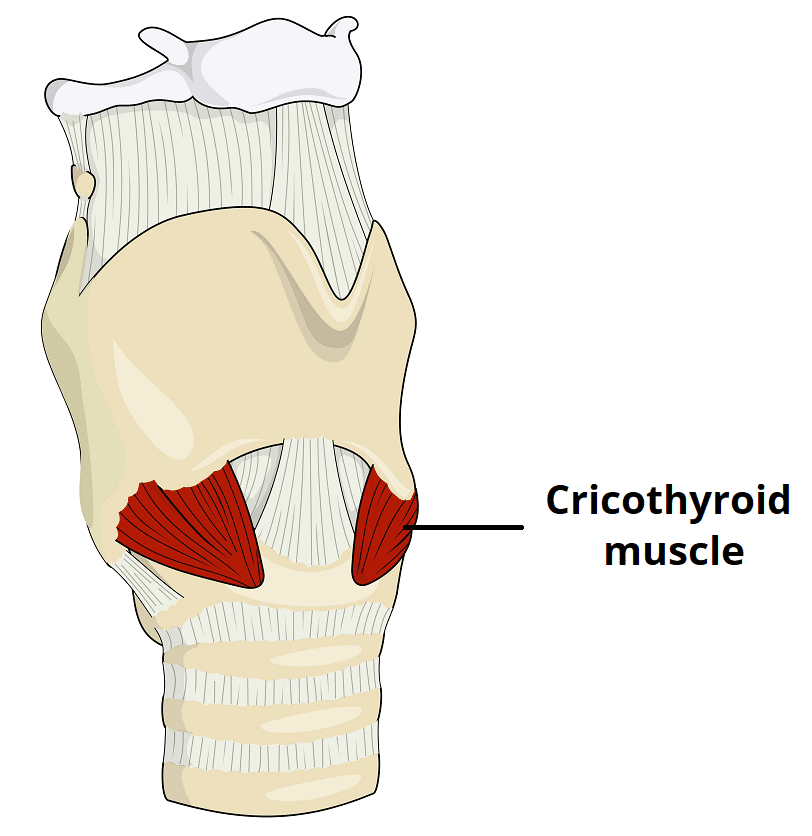
Sternohyoid:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12724/kxW0oZzZVCGCI1VgwGfWw_Musculus_sternohyoideus_01.png)
Depressor

Dark blue structure on bottom
What are the posterior cricoarytenoids?
The arytenoid cartilage rock back and forth, which allows the vocal folds to do this:

What is approximate/make contact?
Children's voices usually have a fundamental frequency of between 80-140 Hz.
False
Male voices: 80-140 Hz
Children's voices: 295-400 Hz
These two structures make up the thyroarytenoid muscle (the bulk of the vocal folds).
What is the thyrovocalis and the thyromuscularis?
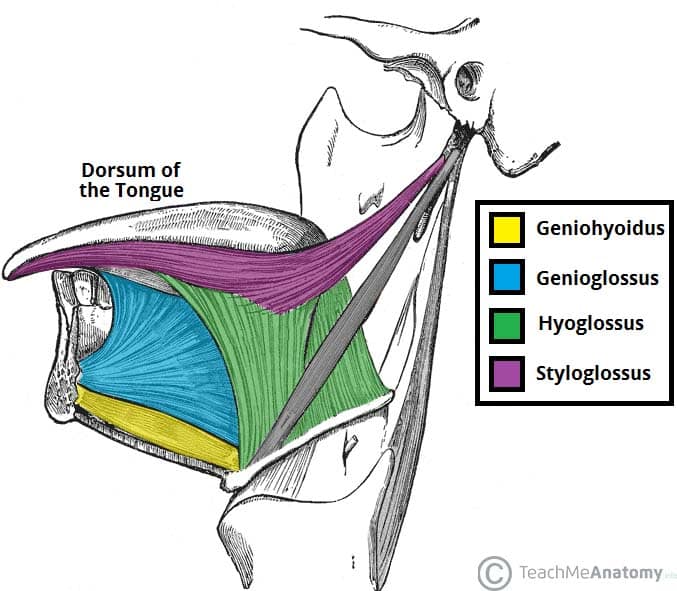
Hyoglossus (in green)
Elevator
(laryngeal elevator, but lingual depressor)

Brown structure
What are the oblique arytenoids?
