This chemical hazard type is represented by a yellow diamond in the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) diamond:

Reagent reactivity
These factors are used to calculate the total magnification of a light microscope.
Ocular magnification x Objective magnification
This is the recommended clearance angle for the microtomy blade
3-8 degrees
This is the percentage of 20g of silver nitrate diluted to 100ml
20%
This type of microtome is used for paraffin sectioning at Labcorp Greenfield/Madison
Rotary Microtome
This pictogram for labeling in the Hazard Communication Standard is optional/not required 
Environment
This type of microscope lens typically has an objective range of x2.5 to x4
Scanning lens
Lab temperature may effect this during sectioning
Ability to form a ribbon
This is the °F equivalent to 4°C
39.2°F
This is the function or ovens between microtomy and staining and the issue they help prevent
Ovens dry slides and prevent tissues from washing off during staining
These would be the next steps taken if formaldehyde monitoring results show a TWA of 0.6 ppm
This result is above the TWA action level 0.5 ppm but less than the maximum allowable TWA. Monitoring must be repeated every 6 months and can cease after 2 consecutive monitorings fall below the action level and STEL (short term exposure limits). The employee must be provided with a medical surveillance program.
This microscope can be used to examine substances that are birefringent, doubly refractile, or exhibit anisotropism
Polarizing microscope
This may be experienced during sectioning if the clearance angle is to small
Skipped sections, thick/thin sections or compressed/wrinkled
This is the grams of solute needed to prepare 500mL of 0.55% potassium metabisulfite
2.75g
The microtomy floatation bath should be kept in this temperature range compared to the melting point of embedding paraffin
5-10C below the melting point
This is the STEL (Short Term Exposure Limit) for formaldehyde
2.0 ppm
This is the light source of a fluorescence microscope
Mercury or halogen lamp
How might this microtomy issue be fixed? 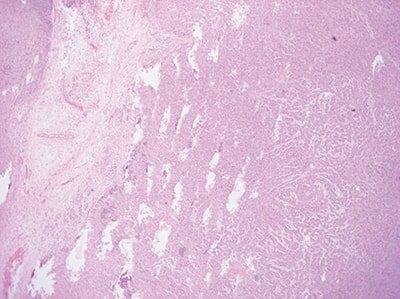
Face slowly/with less micron advances deeper into the block until holes disappear
This is the grams needed to prepare a 1 liter, 2M solution of NaCl; atomic weights Na=22.99g and Cl=35.45g
116.88g
This is the most common temperature for cryostat sectioning
-20C
Some tissues (brain, liver, spleen, etc) section better at -10C while tissues containing fat require colder temps (ex: -25C)
This type of extinguisher should be used on a fire involving electrical equipment
Class C
This is the term for the color fringe effect seen around an imagine in light microscopes if the lens isn't corrected for colors
Chromatic aberration
Bonus content:
Achromatic objective: corrects for 2 colors (red & blue) -most routine lab microscopes
Apochromatic objective: corrects for 3 colors and other lens aberrations
Name two of three possible causes for "parched earth" artifact 
1. Poor fixation or processing
2. Flotation bath too hot
3. Chilling block with cryo spray
This is the grams needed to prepare 200 ml of 0.1N H2SO4 ; atomic weights H=1.00g; S=32.06g; O=16g
0.98g
This is the benefit of buffering solutions (like 10% NBF)
Makes them more resistant to pH changes after dilution or adding small amounts of acids/bases
NBF helps prevent formalin pigment in tissues (seen in tissues fixed with acidic formalin)