This is how leaders demonstrate commitment to safety and promote a safety culture.
What is H&S Leadership?
A product of shared values, beliefs, attitudes, perceptions, competencies and patterns of behaviour related to safety.
What is safety culture?
Plan, Do, Check, Act
What are the steps of the PDCA cycle?
Something with the potential to cause harm to people, the environment or damage company assets.
What is a hazard?
Moral, business and legal
What are the three groups of reasons for H&S?
Pathological, reactive, calculative, proactive, generative
What are the steps in the Safety Culture Maturity Ladder?
A formal written commitment from senior leadership to prevent injuries and illnesses.
What is a Health & Safety Policy?
The combination of likelihood and severity of harm.
What is risk?
To Know, To Participate, and To Refuse unsafe work.
What are the three fundamental employee rights in Health and Safety?
What leaders say, do, measure, and prioritize shapes how others think about safety.
What is the Leadership Shadow?
Criteria that measure improvement to prevent incidents
What are leading indicators?
Vision, hearing and other sensory barriers; perception selectivity
What can influence your risk perception?
Lost time, damage, stress, and insured and uninsured losses.
What are the real costs of workplace incidents?
When a leader’s actions and attitudes influence others’ behaviour, those influences spread throughout the team and the organization, like a pebble dropped in water.
What is the Ripple effect of leadership?
For an accurate understanding of H&S performance management requires both of these.
What are lagging and leading indicators?
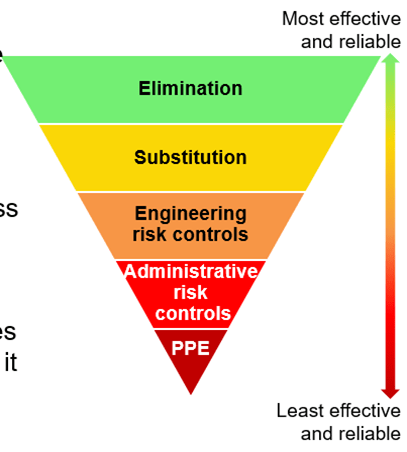
What is the Hierarchy of Risk Controls?
Feeling respected, supported and safe to speak up and knowing your mental health is protected at work.
What is psychological health and safety?
This social behaviour occurs when workers copy unsafe practices because “everyone else does it,” rather than following procedures.
What is group conformity?
When a team asks, “Which PDCA step did we skip or rush?”, they’re applying this key principle of health and safety management systems.
What is continual improvement?
When unsafe practices gradually become accepted as normal.
What is risk normalization?