This is the major cause of maxillofacial trauma.
What are assaults, MVCs, falls, sporting injuries, animal bites, and industrial injuries.
This may cause or be associated with spinal injury.
What are the forces associated with blunt trauma?
All patients with head or neck trauma should be evaluated for this.
What is spinal cord injury?
This is an alteration in brain function, or other evidence of brain pathology, caused by an external force.
What is a traumatic brain injury?
These are the injury rating systems discussed in the book.
What are the Glasgow Coma Scale and the Revised Trauma Score?
If a portion of the outer ear has been avulsed the paramedic should do what?
What is retrieve all pieces of the avulsed ear and wrap the tissue in moist gauze.
These are the types of brain hemorrhages.
What is epidural, subdural, subarachnoid, and cerebral?
This artery branches off of the external carotid artery providing oxygenated blood to the face.
What is the facial artery.
For the purpose of evaluation, the neck can be divided in to 3 zones. This is included in Zone II.
What is the clavicles or carotid cartilage cephalad to the angle of the mandible? This includes the cervical spine and main vasculature.
This is the most common scalp injury. Please define.
What is an irregular linear laceration?
Traumatic Brain injury can be broken into 2 categories. These are the categories and how they are defined.
What is primary and secondary brain injury?
Primary is direct trauma to the brain. Secondary results from intracellular and extracellular derangements initiated by time of injury.
GCS is calculated using this criteria.
What is eye opening, verbal response, and motor response?
This occurs when a tear or puncture of a structure's membrane is caused by trauma.
What is traumatic perforation?
An epidural hematoma accounts for what percentage of all head injuries?
What is 0.5-1%?
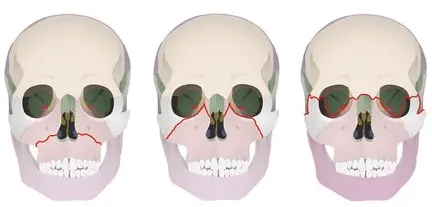
In 1901 a cadaver study was performed that revealed 3 patterns of midface fractures. These fractures were named after the physician who performed the study. What was his name?
Who is Le Forte.
This is often associated with soft-tissue injury to the neck caused by blunt trauma.
What is hematoma, edema, direct tracheal or laryngeal injury, and airway compromise?
This is a star-shaped wound that can be caused by close contact with a ballistic weapon.
What is a stellate wound?
This is the percentage of intracranial space the brain occupies.
What is 80%?
According to the text, what has been shown to affect GCS negatively?
What is hypoxemia and hypotension?
This is when a person is exposed to changes in barometric pressure great enough to produce inflammation and injury to the middle ear.
What is barotitis?
A patient with an epidural hematoma may have transient loss of consciousness followed by a lucid interval. How long does this lucid interval usually last?
What is 6-18 hours?
Signs and symptoms specific to mandibular fractures can include this feeling that their teeth do not "feel right," numbness in the chin, and inability to open the mouth.
What is dental malocclusion?
This may be necessary when direct intubation is impossible because of blood, vomitus, or progressive edema.
What is cricothyrotomy?
These are signs that usually appear 1-3 days after injury.
What are Battle signs and raccoon eyes?
In many TBIs, they incorporate these two injury components. Both injuries can cause intracranial hemorrhage, ischemia, edema, and perfusion abnormalities.
What is focal and diffuse brain injuries?
Which scoring method was published in 1989?
What is the revised trauma score?
This is a rare complication of external trauma to the eyeball causing it to bulge.
What is retrobulbar hematoma?
This type of hemorrhage is classified by intracranial bleeding into the CSF.
What is subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Signs and symptoms of facial fractures include this. (must list all in book)
What is asymmetry of cheekbone prominences, crepitus, dental malocclusion, discontinuity of orbital rim, displacement of nasal septum, ecchymosis, lacerations and bleeding, limitations of movement of mandible, limited ocular movement, numbness, pain, swelling, visual disturbances.
These wounds require aggressive airway therapy and ventilatory support.
What are deep laceration and puncture wounds?
These are symptoms of trauma to cranial nerve VIII.
What are deafness and basilar skull fracture?
If forces are applied are enough to cause the brain to be displaced against the irregular surfaces of the skull, tiny blood vessels in pia matter may rupture. What are the injuries called that cause this?
What are coup and contrecoup?
Your patient has eye opening to pressure, disoriented conversation, and localizes to pressure. What is their GCS?
What is 11?
This type of vision results from images falling on the macula of the retina not the ability to see objects that reflect light waves on areas of the retina other than the macula.
What is central vision?
This type of hemorrhage is most commonly in the frontal or temporal lobes.
What is intracranial hematoma?
During management of a patient with facial fractures, this should be considered.
What is airway management with suction or advanced airway and cervical spine immobilization?
These injuries may be associated with subcutaneous emphysema, neck hematoma, and bleeding of the mouth and nose.
What is esophageal injury?
These are the symptoms of cranial nerve III injuries.
What are ipsilateral, dilated, fixed pupils especially with compression of the temporal lobe. Mimics direct ocular trauma?
Cushing's triad indicates increasing intracranial pressure. What are the parts of the triad?
What is increased systolic blood pressure, bradycardia, and irregular breathing?
You patient has eye opening to pressure, have nonsensical speech, and localizes to pressure. What is their GCS score?
What is 10?
This is blunt trauma to the eye or its adjacent structures may result in a contusion causing bleeding into the anterior chamber.
What is traumatic hyphema?
This type of DAI results in tiny petechial bruising of brain tissue. These injuries account for 20% of all severe head injuries.
What is moderate DAI?
This is contraindicated in the presence of Le Forte fractures I, II, and III.
What is NPAs, nasogastric tubes, and nasotracheal intubation?
This is most prudent when crushed or severed airways totally or partially block attempts for oral or nasal intubation.
What is rapid transport and high concentration oxygen?
List and describe all types of skull fractures listed in the chapter.
What are linear, basilar, open vault, and depressed.
You want to find your patient's cerebral perfusion pressure. The MAP is 70 and the intracranial pressure is 9 mmHg. What is your CPP, is this normal, and was are the normal values for each?
What is 61 mmHg?
Normals= MAP 70-95mmHg, ICP 10-15mmHg, CPP 70-80 mmHg.
Your patient has a GCS of 8, a systolic BP of 86, and a respiratory rate of 9. What is their revised trauma score?
What is 7?
These are the two most common types of dental trauma. Please define both.
What are fractures and tooth avulsion?
Fracture is a crack or breaking apart of the tooth. Tooth avulsion is when the tooth is completely knocked out of the socket.
This type of DAI often causes patients to exhibit abnormal posturing and signs of increased intracranial pressure.
What is severe DAI?