Altered by pH and temperature, the part of an enzyme that makes it specific to its substrate.
What is an active site?
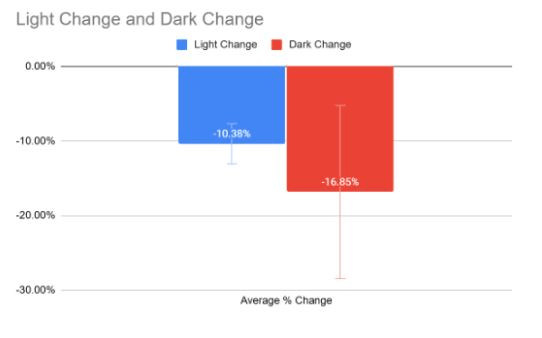 This conclusion could be made about the difference between light and dark conditions for plant transpiration.
This conclusion could be made about the difference between light and dark conditions for plant transpiration.
What is no significant difference?
Bulky and polar. This part of a nucleotide attaches to the 3’ end of another.
What is phosphate?
These would be the ways to describe the only types of particles that can pass in and out of a cell membrane without a protein.
What are small, non-polar molecules?
These two molecules are byproducts of the Electron Transport Chain, being “used up” so they can be recharged in glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle.
What are NAD+ and FADH?
For the sake of random assortment, this beautifully named description shows how each gamete carries only one copy of each allele!
What is the law of segregation?
When heterozygotes of two traits are bred, we expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio. But sometimes they do not sort independently because of this phenomena which would produce the following data.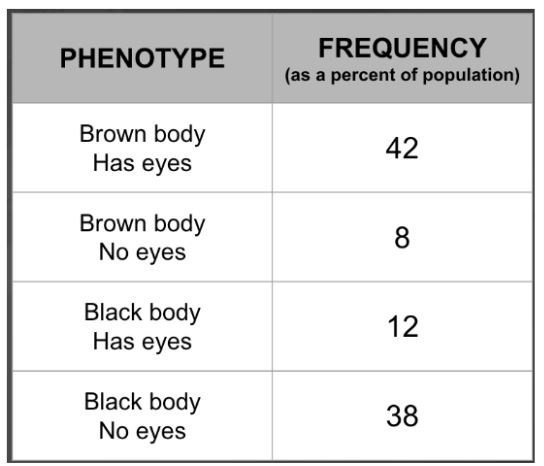
What is gene linkage?
With gelatin we saw that size matters, but so does shape because comparing absorption between cubes doesn’t work when this type of variable to describe something like the shape, isn’t accounted for.
What is confounding?
This term describes an unintentional process that begins from random mutations and takes generations to see.
What is adaptation?
This little bud of membrane helps carry proteins and other substances in and out of a cell!
What is a vesicle?
After light reactions occur, Rubisco fixes carbon from CO2 into G3P in this section of a chloroplast.
Where is the stroma?
Roses are red. Violets are blue. Sometimes when crossbred we get purple it's true! We just need a term to describe it from you.
What is incomplete dominance?
A plant with no water at 50 g. It withers down to 40 g after several days to experience this percent change.
What is -20%
Big pharma be advised. In dosing diseased cells with two different drugs to compare efficacy, cells under these conditions would best be your negative control.
What are diseased cells without a drug?
Activate. Inactivate. A conformational change in protein, and therefore, function, occurs due to this signal cascade process.
What is phosphorylation?
When a membrane sac from the extracellular matrix merges with the cell membrane and adds materials into the cytoplasm.
What is endocytosis?
What’s pretty sweet about GLP-1 and other blood sugar drugs is that several of these proteins come from the exact same DNA sequence through this editing process.
What is alternative splicing?
Data does not always give us what we expect from change. A null hypothesis assumes everything is from chance. A x2 value under the critical value means we must do this to that null hypothesis.
What is fail to reject the null hypothesis?
Yellow wildflowers in the yard. Winds blow and bring in pollen from red ones. Now my my yard is giving… Monarch from this population changing process.
What is gene flow?
Genetics goes beyond simple dominant and recessive, such as this unique form of inheritance shown in the pedigree below.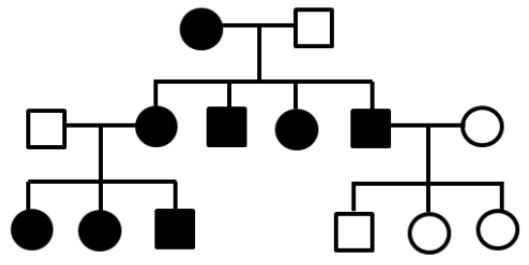
What is mitochondrial inheritance?
Cursed genetic drift. How you change a population… Not through natural selection we see a change in this measure of population diversity.
What is allele frequency?
Based on the diagram, what process allows glucose to enter the cell?
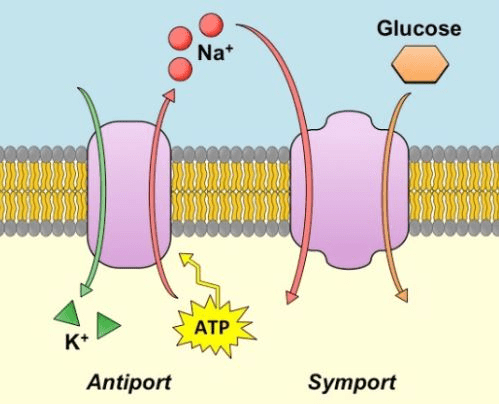
What is secondary active transport?
Cells are shown with different amounts of a protein despite having the same DNA for this reason.
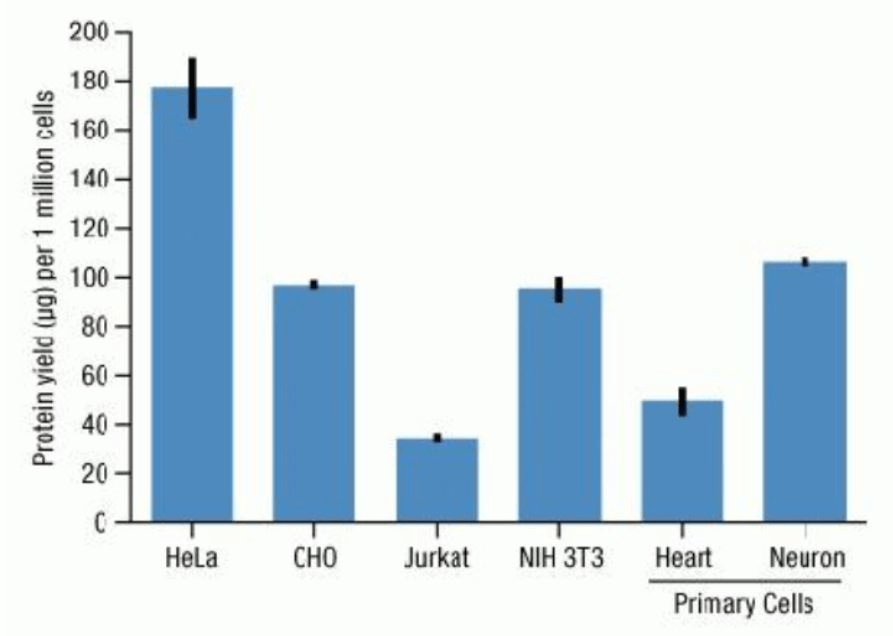
What are different amounts of transcription factors in their environment?
Sometimes potatoes lose mass in concentrated sucrose solution when water leaves it to dilute the concentrated solution. Sometimes, the potato’s mass stays the same in sucrose solution because of this reason.
What are isotonic conditions?
The G-cap is protection. But it lasts not forever. And through this process do nucleotides sever.
(And break down from the RNA polymer into individual monomers)
What is hydrolysis?
E.coli can be transformed by being given plasmids, or DNA with certain traits encoded in. If a trait for glowing in the dark was being studied, scientists usually add in antibiotic resistance for this reason.
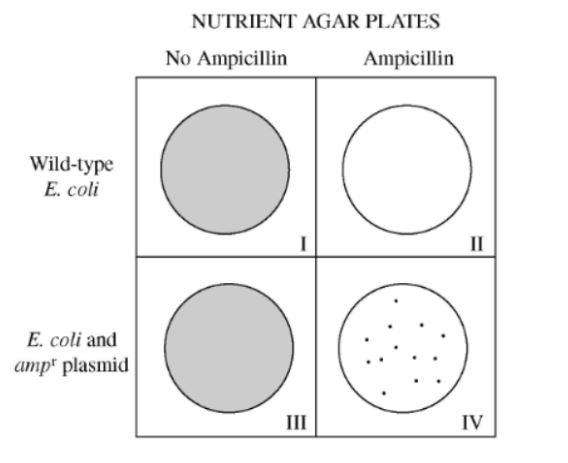
What is to only let transformed e.coli grow?
Alcohol! Lactate! These are the boons of the metabolic process of yeast, bacteria, and sometimes… us.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Only the messenger goes through a nuclear pore and this modification to mRNA tags it for its exit to the cytoplasm in eukaryotes.
What is the poly-A tail?
This tidy organelle is found mostly in animal cells and not often in plants because the cell wall (amongst other structures) makes it relatively redundant in keeping things clean.
What are lysosomes?
According to the cladogram, these class of species are the 2nd most closely related to reptiles after the birds.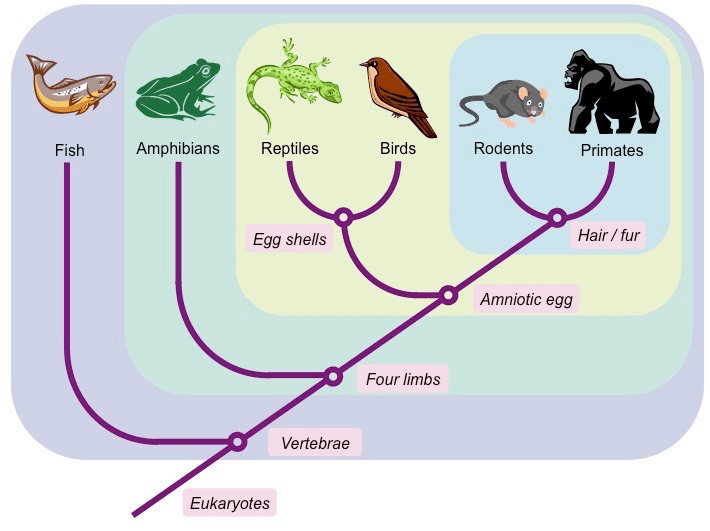
What are the rodents AND the primates?