Melting ice
Physical
Number of valence is determined by the ________ number on the periodic table.
Group
Shiny, hard, conducts electricity, attracts magnets
Metals
Metal, nonmetal or metalloid: Calcium
Metal
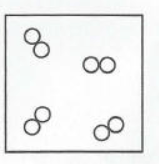 Element, compound, mixture
Element, compound, mixture
Element
Burning magnesium ribbon
Chemical
How can we find number of orbitals for an element using the periodic table?
Find the period (or row) number
Dull, brittle, does not conduct electricity nor attract magnets
Nonmetals
Metal, nonmetal or metalloid: Carbon
Nonmetal
 Element, compound, mixture
Element, compound, mixture
Compound
Egg in vinegar
Chemical
How many valence electrons does Lead (Pb) contain?
4 valence
Mix of metals and nonmetals, shiny, conducts some electricity, hard
metalloids
Name of the nonmetal group that has 7 valence electrons:
Halogens

Element, compound, mixture
Mixture
Boiling water
Physical
How many valence and orbitals are in group 16, period 3?
(Bonus if you also name the element)
Valence: 6
Obitals: 3
Name of the group 1 metals on the periodic table:
Alkali Metals
List 2 characteristics of metalloids:
 Physical or chemical change
Physical or chemical change
Chemical change
Baking a cake
Chemical
What groups on the periodic table are the Transition metals found in?
Groups 3-12
Name of the group 18 non-metals:
Noble Gases
Alkali Metals are group 1, which group would these elements be most likely to chemically bond with:
Non-metal Group 17: Halogens
 Physical or chemical change
Physical or chemical change