What is a glacial erratic?
A large rock left behind from the last glaciation period when continental glaciers covered most of North America
What are the 3 rock types?
Igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary
What type of plate boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other?
Transform boundary
What is a half-life?
The amount of time that it takes one half of the parent radioactive atoms to decay into daughter isotopes. Every radioactive isotope has a specific half-life.
What machine records earthquake waves?
Seismograph
The era that spans the greatest geological time in Earth's History is...
Precambrian era
What are 4 types of fossils?
mould, cast, trace, body/fossil remains
What is the semiplastic layer of earth that tectonic plates move across called?
Asthenosphere
What is an isotope?
Two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei.
which type of wave travels the fastest?
Primary Waves
The geological eras in order from oldest to most recent are....
Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic
Which type of igneous rock will have larger crystals--intrusive or extrusive?
Intrusive
Which plate boundary results in the destruction of crust?
convergent (subducting)
What is the half-life for the following unknown element?
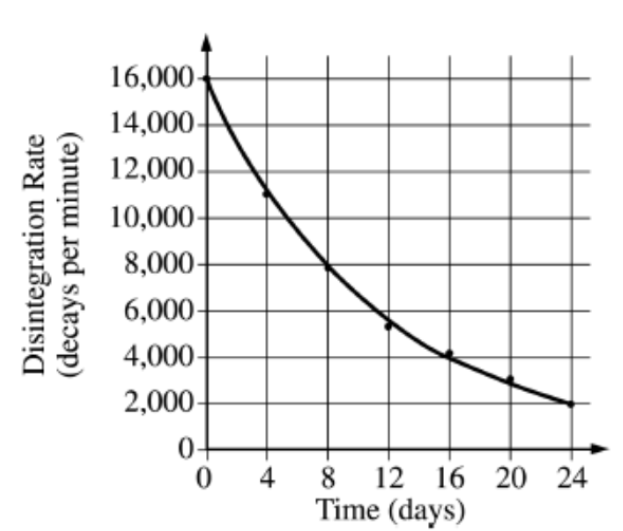
8 days
If a seismograph determines that the time between p and s-waves is 55 seconds, how far away is the station from the epicentre?
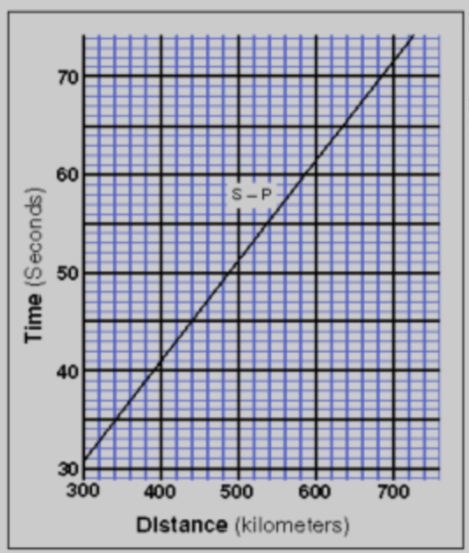
540 km
What microorganism left behind fossilized structures called stromatolites?
cyanobacteria
What are the three things that make a good trace fossil?
Distinctive (easily recognizable)
Abundant (many fossils can be found)
Wide geographic distribution over short time
How we know that the Earth's magnetic poles have reversed multiple times throughout geological history?
Paleomagnetism

Radio carbon dating is done by estimating in a specimen:
a.) The amount of ordinary carbon still present.
b.) The amount of radiocarbon still present.
c.) The ratio of the amount of C-14 to C-12 still present.
d.) The ratio of the amount of C-12 to C-14 still present.
c.) The ratio of the amount of C-14 to C-12 still present.
What are the most damaging types of waves?
Surface waves, love and raleigh
When was the last glaciation? What was it called?
About 12-20 000 years ago, Wisconsin Glaciation
What are the 4 laws of relative dating?
Law of Superposition, Original Horizontality, Lateral Continuity, and Cross-Cutting Relationships
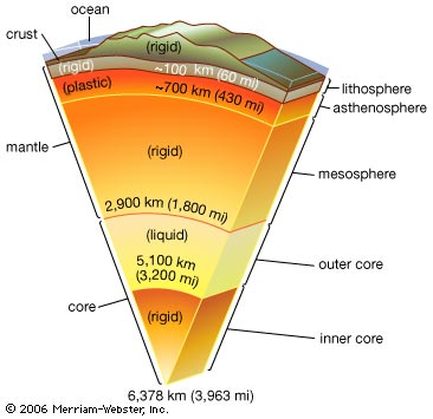
What are the 4 layers of earth listed from thickest to thinnest?
Mantle, outer core, inner core, crust
A geologist determines the percentage of uranium-238 and lead-206 found in a titanite. She finds that 88% of the sample is lead-206. Determine the age of the titanite.
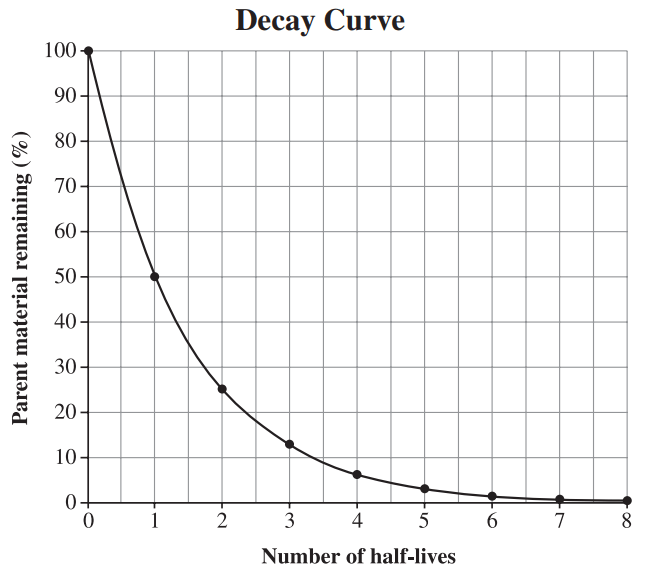
Approximately 13 billion years old.
1.3 x 10^10 a
What is the difference between P and S-waves?
P-waves can travel through solids and liquids while S-waves can only travel through solids.