List 3 lab safety rules.
No eating or drinking
Always waft
Wear goggles
Follow directions at all times
Always have supervision of a teacher or parent
No horseplay
etc.
What is the measurement at D?
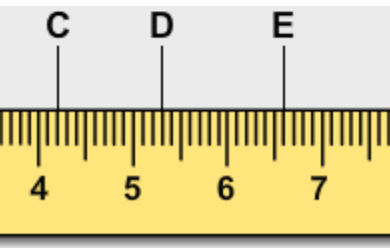
5.3 cm
What is the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION of the HIGH power objective?
10 (eyepiece) x 40 (high power objective) = 400x
What was the responding/dependent variable in our toilet paper experiment?
List 5 features of all living things.
Use Energy
Respond to Stimuli
One or more cells
Life Span
Locomotion (moves)
Maintain Homeostasis (good health)
Adapt - organisms change over time to survive their environment
Reproduce - continuation of the species by making offspring
Grow and Develop
What breaks down dead and decaying organisms and returns nutrients back into the environment?
Decomposers (NOT scavengers, they do not recycle nutrients)
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
Sunlight + CO₂ (carbon dioxide) + H₂O (Water) →
sugar (energy) + O₂ (Oxygen)
What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
A physical change is a change that occurs where a new substance is not created. A chemical change involves the creation of a new substance.
How many electrons are in the each of the 4 energy levels?
1st energy level - 2 electrons
2nd energy level - 8 electrons
3rd energy level - 18 electrons
4th energy level - 32 electrons
Which color wave has the longest wavelength?
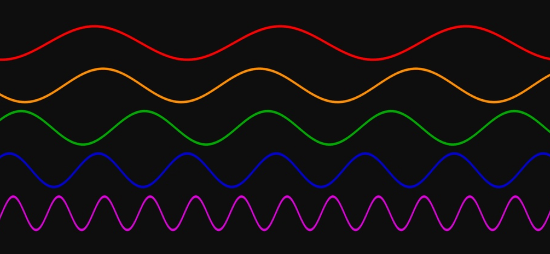
Red
What is the name of the following piece of equipment?

Ruler
What number is the metric system based on?
10
When you move the slide up, the image appears to move _________.
Down
What type of observation uses words to describe something?
qualitative observation
What is an adaptation?
A change within a species developed over time to help them better survive their environment.
What is the main source of energy in any ecosystem?
Sun
What is the job of the nucleus?
It is the brain of the cell and directs cell activities.
Matter is anything that has _______ and _______.
Mass and Volume.
What is a proton and how do you figure out how many there are in an element?
A proton is a positively charged particle and you can look at the atomic number to figure out how many there are in an element.
Which of the following represents the crest?
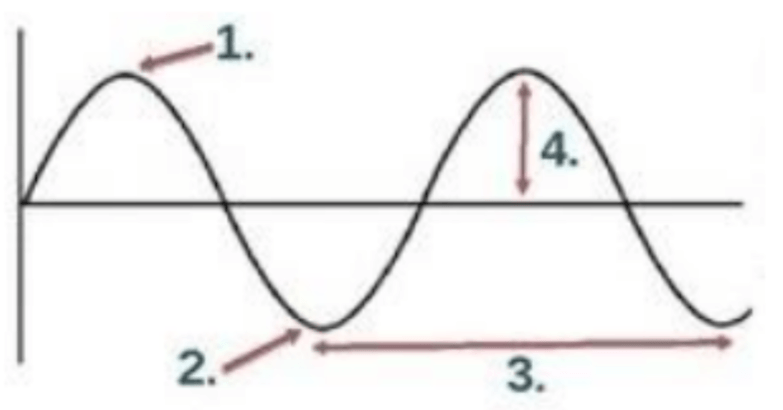
1
What is the name of the following piece of equipment?

Graduated Cylinder
What is mass?
The amount of matter in an object
How do you carry a microscope?
Using two hands, you hold the arm and base.
Define observation.
Gathering information using your senses
What is the difference between a stimulus and a response?
A stimulus is a change in the environment that causes a reaction whereas a response is the reaction.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is the flow of energy from one organism to another. A food web is multiple overlapping food chains.
What are 3 differences in the organelles of plant cells and animal cells.
Plant cells have chloroplast, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts or a cell wall, and have multiple small vacuoles.
Describe the shape, volume, energy, and particle spread for a gas.
Gasses have no definite shape, no definite volume, high energy, and the particles are spread the farthest apart.
What is an electron and how do you figure out how many there are in an element?
An electron is a negatively charged particle and you can look at the atomic number to figure out how many there are in an element.
Which of the following represents the trough?
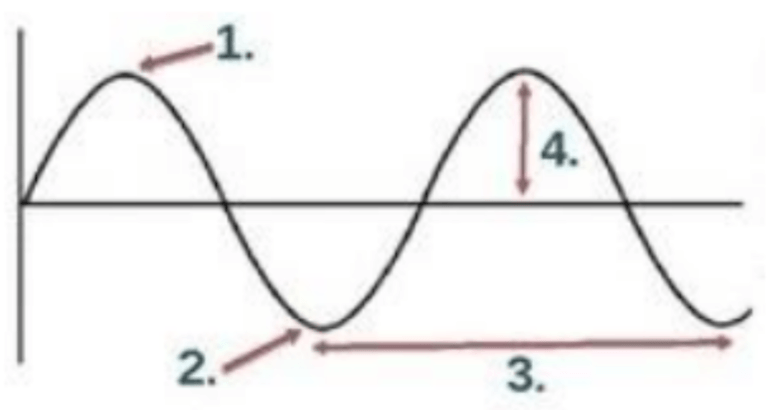
2
What is the name of the following piece of lab equipment?

flask
What is volume?
The amount of space an object takes up
What do you use to change the amount of light coming through the microscope?
Diaphragm
What are the 3 definitions for hypothesis?
An educated guess
A scientific prediction
A potential solution to a problem
Define homeostasis.
An organism’s ability to maintain steady internal conditions when outside conditions change (good health)
What does an herbivore eat? Carnivore? Omnivore?
Herbivore- plants
Carnivore- meat
Omnivore- both plants and meat
List the 3 parts of the cell theory.
1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things
3. All cells come from cells that already exist.
Describe the shape, volume, energy, and particle spread for a liquid.
Liquids have no definite shape, a definite volume, medium energy, and the particles are spread the a bit apart.
What is a neutron and how do you figure out how many there are in an element?
A neutron is a neutral particle with no charge and you can do atomic mass - atomic number to figure out how many there are in an element.
Which of the following represents the amplitude?
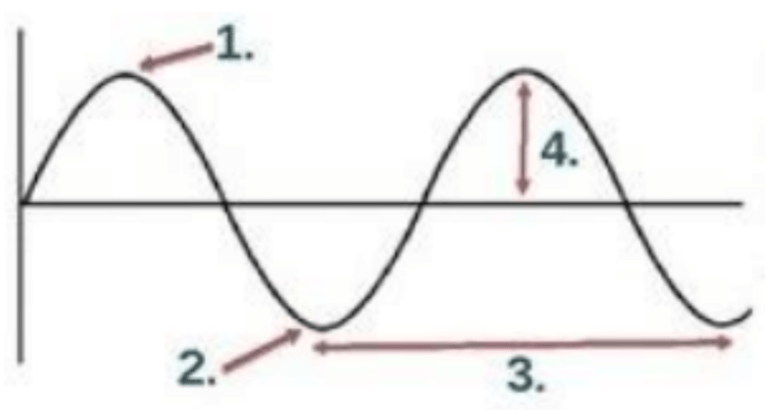
4
Demonstrate Wafting.
*moving smell towards nose by pulling hand towards face*
What is the volume of the rock?
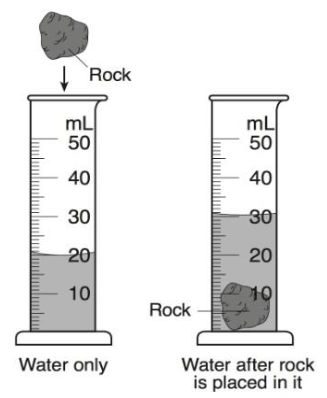
10 mL
Describe the eyepiece and its magnification.
The eyepiece is the top part of the microscope that you look through. It has a lens that magnifies 10x.
List the steps of the scientific method in order.
State the problem
Gather information
Form a hypothesis
Perform an experiment
Collect and record data
Analyze data
Form a conclusion
Which organism is a 1st consumer?

Snail
The first ORGANISM in a food chain or food web is ALWAYS a _________.
Producer (NOT a plant, plants are types of producers but not all producers are plants)
What process does the mitochondria do and for what purpose?
Cellular respiration, in order to produce energy.
Describe the shape, volume, energy, and particle spread for a solid.
Solids have a definite shape, a definite volume, low energy, and the particles are closest together.
Give 3 examples of a heterogeneous mixture.
Cereal in milk
Salad
Fruit Salad
Chex mix
Lucky Charms
Fruit Loops
etc.
Which of the following represents the wavelength?
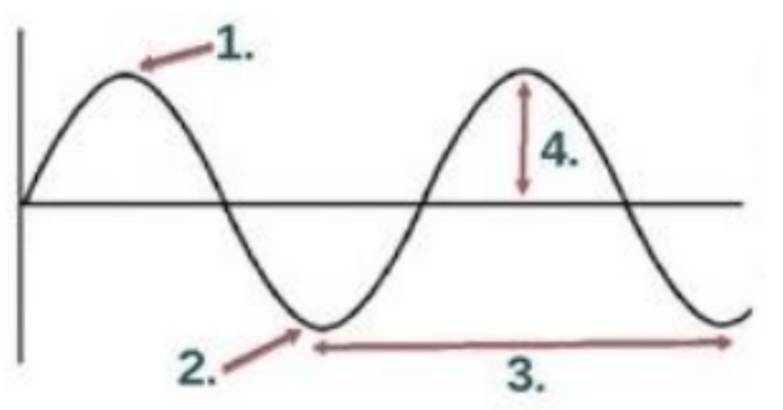
3