What are the three states of matter?
olid, liquid, gas.
What measures the amount of matter?
Mass
What is weathering?
Breaking rock into smaller pieces.
What happens at a divergent boundary?
Plates move apart.
What natural disaster is hardest to predict?
Earthquakes.
Which state of matter has a definite shape and definite volume?
Solid
Which two observations prove a chemical reaction occurred?
-Change in Temperature
-Change in color
-Production of gas
-Production of sound
-Formation of a solid
-Change in smell
What is erosion?
Movement of sediment.
What happens when oceanic crust converges with continental crust?
Oceanic crust subducts.
What causes tsunamis?
Underwater earthquakes or subduction-zone movement.
Look at the particle diagram below. Which diagram represents liquid.
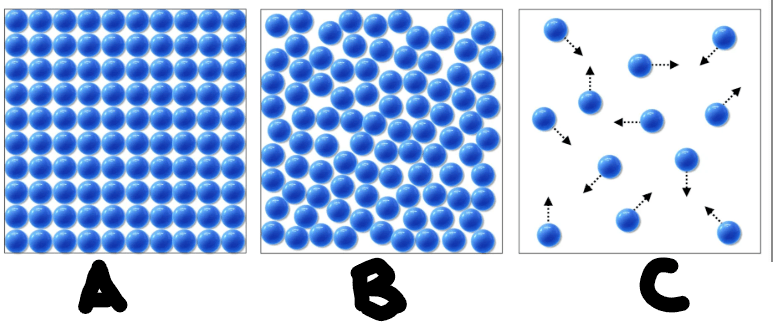
B
Using the model below, count the atoms.
H2 + O2 -> H2O
Reactants: H2 + O2
Products: H2O
No, the products show fewer oxygen atoms unless balanced.
The diagram shows rain hitting rock and breaking it into smaller pieces without moving them.
Is this weathering or erosion, and why?
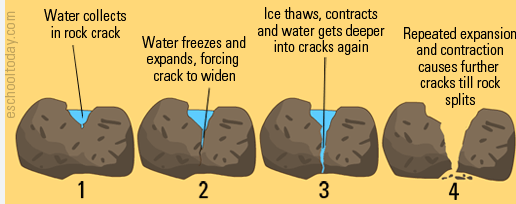
Weathering—rock breaks but does not move.
The diagram shows two plates sliding past each other.
Which boundary is this?
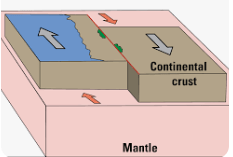
Transform boundary.
Look at the diagram showing a fault suddenly slipping.
Which natural event does this cause?
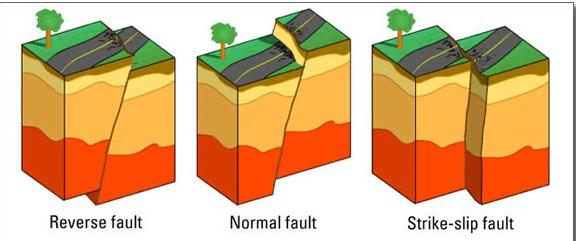
An earthquake.
What two phase changes are endothermic?
Melting and vaporization.
What does the Law of Conservation of Mass state?
Mass cannot be created or destroyed.
What force causes continents to move?
Convection currents.
What is a hot spot?
A stationary area where magma rises to form volcanoes.
What causes both earthquakes and tsunamis?
Motion of tectonic plates.
Explain why melting is endothermic but freezing is exothermic.
Melting absorbs heat to break particle attraction; freezing releases heat as particles lock into place.
Look at the before-and-after reaction diagram.
If the number of particles stays the same but changes arrangement, what does this show?
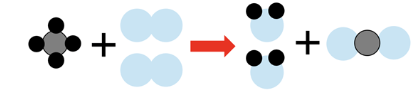
Chemical reactions rearrange atoms without losing or gaining matter.
Look at the fossil map of Glossopteris found in Antarctica, Africa, India, and South America.
What major theory does this support?
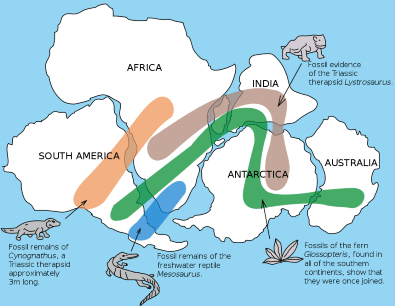
Continental drift (Pangaea once connected these continents).
Look at the hot spot chain diagram.
Why is the volcano directly over the hot spot the youngest?
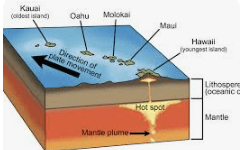
The plate moves, so older volcanoes drift away while new ones form above the hot spot.
A map shows a subduction zone on the Pacific Rim.
If an underwater earthquake occurs there, which coastline is most at risk for a tsunami?
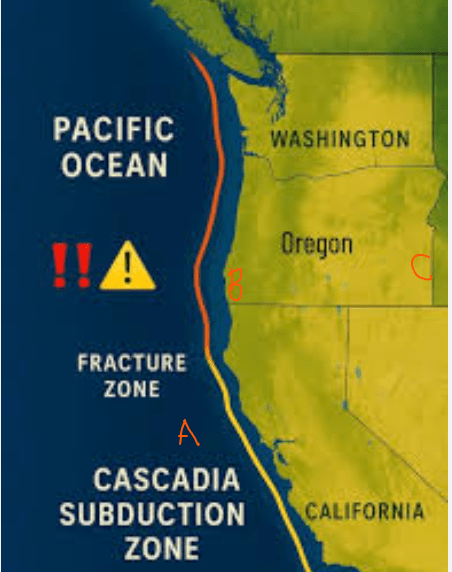
The coastline nearest the subduction zone (Pacific coastal areas).