What are cells made up of?
Organelles
True or False: Asexual Reproduction produces offspring that are an exact genetic copy of the parent
True
What are the 4 phases of mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
What are reproductive cells of an animal or plant cell called?
Gamete
What type of cells does meiosis produce?
Reproductive Cells
What is the base pair for Guanine in DNA?
Cytosine
Where in the cell is DNA held and protected?
Nucleus
What are the 5 types of asexual reproduction?
Binary fission, budding, fragmentation, vegetative reproduction, spore formation
What is the longest phase of the cell cycle?
Interphase
What are the 3 phases of sexual reproduction?
Mating, Fertilization and Development
How many phases are in meiosis?
8 (PMAT1, PMAT2)
What is a gene mutation?
A change in order of nucleotide bases that make up the gene
Name 2 differences between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have:
1. chloroplasts
2. cell wall
3. large vacuoles
Give an example of an organism that reproduces through budding
ex. Hydra
In what phase do the sister chromatids separate at their centromeres and move toward opposite ends of the cell?
Anaphase
How many chromosomes are in a zygote?
Diploid (2n)
Half points: 46
In what phase do homologous chromosomes cross over?
Prophase I
What is the word for "causes of mutations"?
Mutagens
What is the structure of DNA?
Double Helix
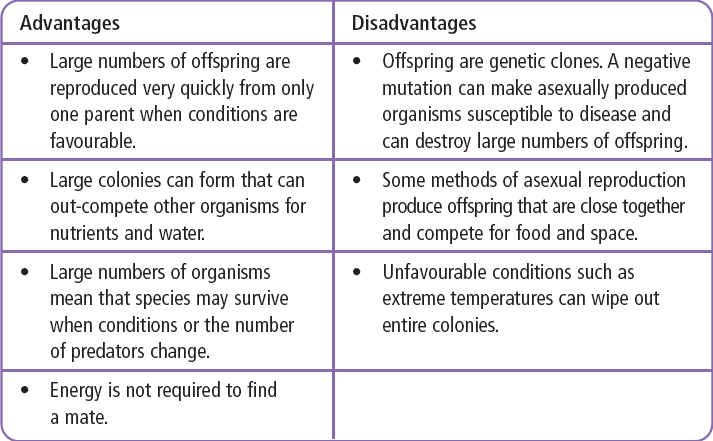
Name one advantage and one disadvantage of asexual reproduction
What structures release long, stiff fibers called microtubules?
Centrioles
What is external fertilization? Name one organism who it is common in.
ex. Salmon, Sea Urchins
What phase is shown below?

Telophase I
What is a neutral mutation? Give one example
When a gene mutation has no effect on the individual.
ex. Kermode Bears with white coats
What organelle makes proteins in the cell?
Ribosomes
Why is a negative gene mutation especially bad for asexually reproducing organisms?
Since all offspring are genetic clones, then this mutation will leave ALL the offspring of the mutated organism susceptible to disease and the negative effects of that mutation
What are the microtubules that split the cell apart during cell division made of?
Tubulin
What are 2 requirements for embryonic development?
Enough nutrients
Temperature must be warm enough so proteins and enzymes will function properly
Sufficient moisture so embryo doesn’t dry out
Protected from predators and environmental factors (ex. UV radiation)
What 3 events lead to Genetic Diversity from Meiosis?
Crossing Over
Independent Assortment in Metaphase I
Independent Assortment in Metaphase II
How does gene therapy work?
A virus is engineered to carry a normal gene
The virus must somehow be targeted to the cells with the defective gene
The normal gene must then replace the defective gene
The normal gene must then be “switched on” so that the replacement normal gene produces the proper healthy proteins. It is also important that the normal gene make the correct amount of healthy protein.