What type of matter is made of only one kind of atom?
Element
What element has the symbol Na?
Sodium
What property causes water molecules to stick to each other?
Cohesion
What is the pH of pure water?
7
What law states matter is not created or destroyed?
Law of Conservation of Mass
What happens to acceleration when force increases?
It increases.
Which law explains inertia?
Newton’s First Law
What wave property measures height?
Amplitude
What is the first stage in a star’s life cycle?
Nebula
What type of galaxy is the Milky Way?
Spiral
What is the main energy source for Earth’s weather?
The Sun
What happens to warm air?
It rises
What are tropical cyclones called in the Atlantic?
Hurricanes
Why is salt water considered a homogeneous mixture?
It is evenly mixed throughout.
How many oxygen atoms are in CO₂?
2
What property allows water to move up plant stems?
Adhesion
Are substances with pH 3 acidic or basic?
Acidic
If reactants have a mass of 30 g, what is the mass of the products?
30 g
What happens to acceleration when mass increases?
It decreases.
Which law explains action–reaction forces?
Newton’s Third Law
What wave property is measured in Hertz?
Frequency
What type of star is the Sun?
Main sequence
Name the three types of galaxies.
Spiral, elliptical, irregular
What Earth system absorbs and releases heat slowly?
The hydrosphere (oceans)
What causes wind?
Differences in air pressure
What ocean temperature is needed for cyclone formation?
About 26.5°C (80°F)
Classify air as element, compound, homogeneous mixture, or heterogeneous
Homogeneous mixture
Which tool helps identify the atoms involved in chemical reactions?
The periodic table
Which property allows insects to walk on water?
Surface tension
Which has a higher pH: lemon juice or soap?
Soap
What happens to atoms during a chemical reaction?
They rearrange.
What equation represents Newton’s Second Law?
f=ma or a=f/m
Why do seatbelts protect passengers during sudden stops?
Inertia
What happens to wavelength when frequency increases?
It decreases.
What is the final stage of a low-mass star?
White dwarf
Where is Earth located in the universe
On the Orion Arm
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather is short-term; climate is long-term.
What effect causes winds to curve?
Coriolis Effect
Where do tropical cyclones get their energy?
Warm ocean water
How is a compound different from a mixture?
Compounds are chemically combined; mixtures are physically combined.
How many total atoms are in C₆H₁₂O₆?
24 atoms
Why does water form droplets on a waxy surface?
Cohesion and surface tension
Compare the properties of acids and bases.
Acids have low pH and produce H⁺; bases have high pH and produce OH⁻.
Why must chemical equations be balanced?
To show mass is conserved.
Calculate acceleration: 20 N force on a 4 kg object.
5 m/s²
How do Newton’s laws apply to amusement park rides?
Forces, acceleration, and action–reaction all act together.
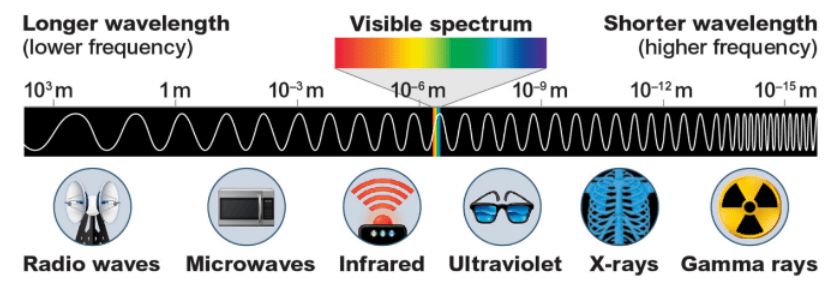 Which EM wave has the most energy?
Which EM wave has the most energy?
Gamma rays
What information does the H–R diagram show?
Temperature and brightness
Which galaxy type has mostly older stars?
Elliptical
Why do coastal areas have milder climates?
water moderates temperature
Name one global wind belt.
Trade winds / Westerlies / Polar easterlies
Why do hurricanes weaken over land?
Loss of warm water and increased friction
A substance contains only carbon and oxygen in a fixed ratio. How should it be classified and why?
Compound; elements are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio.
Explain why chemical formulas are important for understanding reactions.
They show which atoms and how many are involved.
Explain how cohesion and adhesion work together during capillary action.
Adhesion pulls water up surfaces; cohesion pulls additional water molecules along.
Why is water used as the reference point on the pH scale?
It is neutral.
Explain how photosynthesis demonstrates conservation of mass. 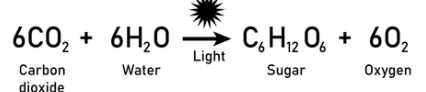
Atoms from CO₂ and H₂O rearrange to form glucose and oxygen.
Explain how force and mass together determine acceleration.
Acceleration depends on the net force applied and the object’s mass.
Explain how all three laws act during a rocket launch.
Inertia resists motion, force causes acceleration, and exhaust pushes downward while the rocket moves up.
Compare radio waves and gamma rays in wavelength and energy. 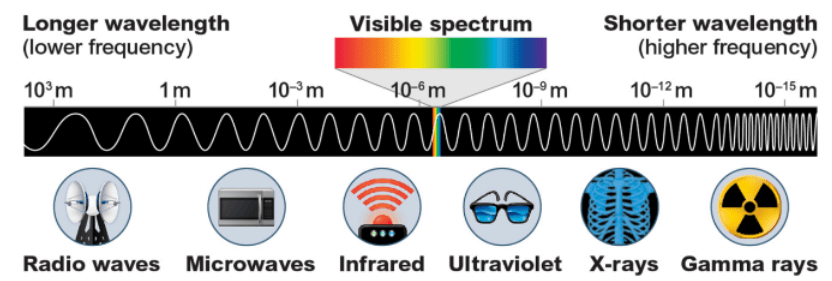
Radio waves have long wavelength and low energy; gamma rays have short wavelength and high energy.
Why do high-mass stars have shorter life spans?
They burn fuel faster.
Why are spiral galaxies a good spot for new star formation?
The have a lot of dust which can form into a star due to gravity
Explain how uneven heating of Earth causes weather patterns.
It creates pressure differences that move air and water.
Explain how global winds influence local weather.
They transport heat and moisture
Explain how ocean currents and air masses work together to form tropical cyclones.
Warm water heats air, causing rising motion and low pressure.
A student mixes iron filings and sulfur powder, then uses a magnet to separate the iron. What conclusion best describes the original mixture?
It was a heterogeneous mixture because the substances kept their properties
How does the periodic table helps scientists analyze chemical reactions?
It identifies the atoms involved using element symbols
Water rises through a paper towel placed partially in a cup of water. Which two properties are responsible for this observation?
Adhesion and cohesion
Sample A - pH 1
Sample B - pH 4
Sample C - pH 2
Sample D - 10
which is the strongest Acid
sample A
A chemical reaction occurs in a sealed container. The mass before the reaction is 120 g. What will be the mass after the reaction?
Exactly 120 g
Two objects are pushed with the same force. Object A has more mass than Object B. What is the correct assumption if both are pushed with equal force
Object B will accelerate more
A roller coaster starts from rest, speeds up, and then slows down. Explain how more than one of Newton’s laws applies.
Newton’s First Law explains that the coaster remains at rest until a force acts on it. Newton’s Second Law explains that when forces such as gravity act on the coaster, it accelerates. Newton’s Third Law explains that as the coaster pushes against the track, the track pushes back with an equal and opposite force.
Two waves carry different amounts of energy but travel at the same speed. Explain which wave property accounts for the difference.
The difference in energy is due to amplitude. A wave with greater amplitude carries more energy even if it travels at the same speed.
Two stars appear equally bright from Earth, but one is farther away. Explain what this suggests about their luminosity.
The star that is farther away must have a greater luminosity because it produces more energy to appear just as bright from a greater distance.
Astronomers observe two galaxies.
Galaxy A has a flat disk with arms and active star formation.
Galaxy B has a round shape with mostly older stars.
Identify the type of each galaxy and explain the evidence used to classify them.
Galaxy A is a spiral galaxy because it has a disk shape with arms and ongoing star formation.
Galaxy B is an elliptical galaxy because it has a round shape and contains mostly older stars.
Explain why two cities at the same latitude can have different climates.
Coastal cities have milder climates because nearby water absorbs and releases heat slowly, while inland areas heat and cool more quickly.
Explain how rising and sinking air creates wind.
Warm air rises and cool air sinks, creating differences in air pressure. Air moves from high pressure to low pressure, producing wind.
Explain why a storm weakens over cooler water.
Tropical cyclones need warm ocean water for energy. Cooler water reduces evaporation and heat transfer, causing the storm to weaken.
What observation best supports the claim that a substance is a compound rather than a mixture?
The substance is chemically combined and forms a fixed ratio of elements
A chemical reaction includes the formula 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O.
What evidence best shows the usefulness of the periodic table in understanding this reaction?
It identifies the types and number of atoms involved
What situation demonstrates surface tension as a result of water’s molecular structure?
Varied answer
Example: Insects walking across a pond
True or false:
Acids and bases can conduct electricity
True or False:
When a reaction is over, the number and type of atoms changed when the product is formed
False
An object with a mass of 30 g is pushed with a force of 150 newtons, what is the acceleration?
5 m/s2
Explain how all three of Newton’s laws act together during a rocket launch.
Newton’s First Law explains that the rocket remains at rest until a force acts on it. Newton’s Second Law explains that the thrust force causes the rocket to accelerate upward based on its mass. Newton’s Third Law explains that gases are pushed downward while the rocket is pushed upward with an equal and opposite force.
Radio waves vs X rays. Explain how their positions on the electromagnetic spectrum relate to wavelength and energy.
Radio waves have long wavelengths and low energy, while X-rays have short wavelengths and high energy. As wavelength decreases, frequency and energy increase on the electromagnetic spectrum.
A star moves off the main sequence on the H–R diagram. Explain what this indicates.
This indicates the star has begun to run out of hydrogen fuel in its core and is entering a new stage of its life cycle, such as becoming a red giant or red supergiant.
A student claims that irregular galaxies are “unfinished spiral galaxies.”
Evaluate this claim using scientific evidence about galaxy structure and formation.
The claim is incorrect. Irregular galaxies are not unfinished spirals; they often lack structure due to gravitational interactions or collisions with other galaxies. These interactions disrupt their shape, preventing the formation of spiral arms.
Explain how the Sun, atmosphere, and hydrosphere drive long-term climate patterns.
Energy from the Sun heats Earth unevenly. The atmosphere and hydrosphere move this energy through winds and ocean currents, which influence long-term climate patterns.
Explain how Earth’s rotation affects wind patterns.
Earth’s rotation causes moving air to curve due to the Coriolis Effect, creating global wind patterns that influence local weather.
Explain how ocean currents and air masses lead to tropical cyclone formation.
Warm ocean currents heat the air above them, causing warm, moist air to rise. This creates low pressure, draws in more air, and strengthens the storm through continuous energy transfer.