What is the charge of a proton, an electron, and a neutron?
Proton: 1+
Electron: 1-
Neutron: 0
Which of the following bases pair together:
adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T) and uracil (U)
A-T
U-T
C-G
You are stopped at a stop light that turns green. You press you accelerator and accelerate at 4.55 m/s2 until you reach the speed limit of 16.67 m/s
Use the following equation to find the change in time:
vf = vi +aΔt
*CA
vf = vi +aΔt
vf-vi/a=Δt
3.66s = Δt

If A is 48o and c is 38 m, what is b?
*CA
b=cos48o×38m
b=25.4m
What are the colors of the German flag?
Red, black, and yellow
What is the element symbol? Atomic mass? Atomic number?
*PTNA
Element symbol: C
Atomic number: 6
Atomic mass: 12
Prokaryotes:
-do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles
-no mitochondria
-unicellular
Eukaryotes:
-have membrane bound nucleus and organelles
-Nucleus contains genetic information
-multicellular
The equation for kinetic energy is K= 1/2mv2
What is the kinetic energy of a 2.3 kg ball rolling at 7m/s?
*CA
K= 1/2mv2
K=1/2(2.3)(7.02)
K=49J
Solve using BEDMAS
(1+52)−16(1/2)3
*CNA
24
What are the 3 secondary colors?
Orange (r&y)
Purple (r&b)
Green (y&b)
What is nCl? (moles of chlorine).
The following values are given:
mCl: 7 grams
mmCl: 35 grams/mol
*PTNA
**CA
What is 0.2 mols?
mol = mass ÷ molar mass
ncl = mCl ÷ mmCl
nCl= 7 ÷ 35
nCl = 0.2 mol
What is the term for the symbiotic relationship between 2 species in which one is benefited and the other is not benefitted nor harmed (neutral)?
Commensalism
In the famous equation E=mc2, what does each variable represent?
Bonus: what constant number does c represent?
E: energy
m: mass
c: speed of light
c=3.00x108m/s
What is the meaning of ! in math?
Solve 4!
*CNA
Factorial means n×(n-1)×(n-2)×(n-3)×...×1
4!= 4×3×2×1
4!=24
What is the term for a duel, but between 3 people instead of 2?
Truel
What element this diagram is representing.

Hint: Each dot represents an electron
*PT allowed
Phosphorus.
Name 3 factors that affect enzyme activity?
-pH
-Temp
-Enzyme [ ]
-substrate [ ]
Velocity is the derivative (slope) of displacement with respect to time (meaning change in position/change in time).
Acceleration is the derivative of velocity with respect to time (meaning change in velocity/change in time).
If displacement1 occurs from 0m@0s to 6m,4s, what is velocity1?
If displacement2 occurs from 6m@4s to 8m@8s, what is velocity2?
What is the acceleration between velocity 1 and velocity 2 (with respect to time)?
*CA
v1= 6-0/4-0
v1 = 1.5 m/s
v2 = 8-6/8-4
v2 = 0.5
a = 0.5-1.5/8-0
a=-0.125 m/s2
In order to find the derivative of an equation, you must follow the following steps:
1. Multiply coefficients by their power
2. Subtract their power by 1
Find the derivative of the following
a) 3x2
b) 4x
c) 2
d) 9x4+7x3+8
*CNA
a) 3x2= (2)3x2-1=6x
b) 4x = (1)4x1-1=4
c) 2 = (0)21-1=0
d) 9x4+7x3+8 = (4)9x4-1 + (3)7x3-1 + (0)81-1 = 36x3+21x2
Which end of the pH scale (0 to 14) is acidic and which end is basic?
0- acidic
14- basic
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a method of drawing molecules based on the repulsion of valence electrons from each other.
Valence electron are the electrons that are shared in covalent molecules. The molecule is shaped so that the electrons of the central atom are as spaced apart as possible.
What is the VSEPR of SO2.
The following information is given:
S has 6 valence electrons
O has 6 valence electron
18 total valence electrons
S forms 2 double bonds with each O atom
Each bond represents 2 electrons
This means that after 4 double bonds are formed, 10 electrons remain unbonded (lone pairs)
Each element's goal is 8 valence electrons
Each atom gets the number of electrons needed to fulfill their goal.
Draw this entire structure with S's valence electrons spaced apart so they are as far away from each other as possible.
*PT allowed
**CA

What is the equation for cellular respiration? only 500 points will be rewarded for exact equation.
(Hint: it is the reverse of photosynthesis)
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
Momentum is a combination of speed and mass, represented by the equation p=mv
Momentum is conserved, meaning the initial momentum before a collision is equal to the final momentum after a collision (pi=pf).
Lastly, in order for a collision to occur, 2 masses must collide. The total momentum is equal to the momentum of each mass (ptotal=p1+p1).
2 masses (95 kg @ 8.5 m/s and 110 @ 6.4 m/s) collide into each other, stick together, and move forward together at the same speed. Use all the equations to find the final speed of the two masses.
*CA
pi = pf
pi1 + pi2 = pf1 + pf2
m1m1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
m1m1i + m2v2i = (m1 + m2)vf
vf = (m1m1i + m2v2i)/(m1 + m2)
vf = 0.505 m/s
To say limx→a f(x) = L means we can make the value of y or f(x) arbitrarily close to L by making x close to a from either side of the graph. It focuses on what happens near a not at a. If the limit from the right of x (x+) and the limit from the left of x (x-) are not equal, the graph is discontinuous, and the limit is DNE.
Example:
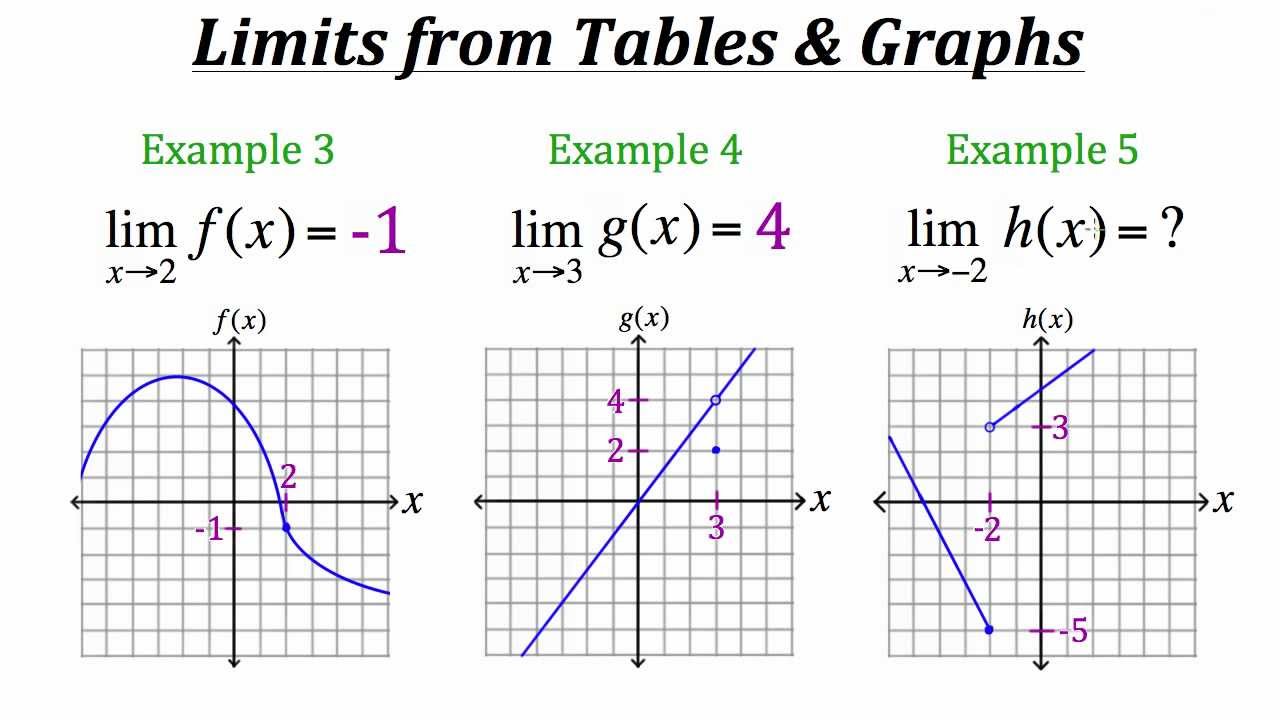
What is limx→2- h(x) =?, limx→2+ h(x) =?, and limx→2 h(x) =?
limx→2- h(x) =-5
limx→2+ h(x) =3
limx→2 h(x) = DNE

Name the phases.
A- waning crescent
B- waning gibbous
C- Last/4th quarter
D- Waxing crescent