What is the smallest unit of matter?
An atom
What is the angle of Earth's tilt?
23.50
What is a biotic factor? Provide an example.
A living component in an ecosystem.
Examples will vary, may include fungi, plants, animals, and or bacteria.
What is a force?
A push or pull done on an object
How many planets are there?
8
What is in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and neutrons
What is the outer layer of Earth called?
Lithosphere
What is the phenomenon depicted in the image? Which is more likely to survive if their environment stays the same? Why?
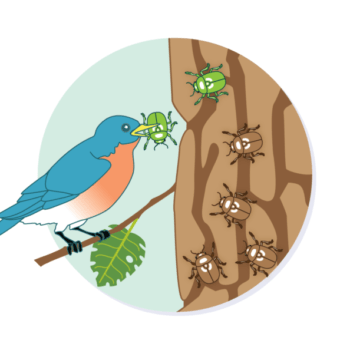
Natural selection; the brown beetles because they blend in with the trees
Newton's first law of motion that states an object in motion will stay in motion unless an external force acts upon it.
What is the nickname for the last 4 planets in our solar system?
Gas Giants
How many groups are there on a periodic table?
18
What are the three types of rocks?
Sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic
Provide an example of a producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, and tertiary consumer.
Answers vary:
Producers are plants
Primary consumers are small herbivores
Secondary consumers are omnivores / carnivores
Tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators
What are the three types of noncontact forces?
Magnetism, static electricity, gravity
What is the unit of measurement used within our solar system? What is the equivalent in miles?
Astronomical units; about 93 million miles
What is the difference between atomic mass and the atomic number?
Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an element while the atomic number is just the number of protons.
Which layer is older in the picture, A or D? How do you know?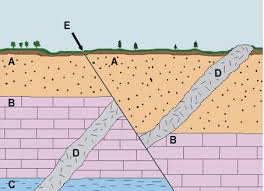
A, because D is cutting through layer A.
What is the difference between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction in terms of genetic trait inheritance?
Asexual reproduction creates identical genetic information to be passed down. Sexual reproduction creates offspring with genetic variation (there can be differences amongst offspring).
Describe the kinetic and thermal energy of the phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
Solid: low kinetic and thermal energy
Liquid: higher kinetic and thermal energy than solids, but less than gases
Gases: highest kinetic and thermal energy
Describe, in depth, what causes seasons?
Because the Earth is tilted at 23.5o, the hemisphere that is tilted towards the sun is either in spring or summer while the hemisphere that is tilted away from the sun is either in fall or winter. If it wasn't for the tilt, there would be no seasons and we would always have 12 hours of sunlight in a day.
DAILY DOUBLE. Answer all of the following questions to earn 1000 points. Get one wrong, lose 500 points.
What is the atomic number, the atomic mass, the number of protons, and the number of neutrons in the element?
What is the element name and symbol?
Atomic number: 19
Atomic mass: 39.10 (or 39)
Number of protons: 19
Number of neutrons: 20
Element name: Potassium
Symbol: K
Why do clouds form in front of a warm front?
The advancing warm air mass slides over a colder air mass, forcing the warm air to rise.
Describe photosynthesis. Use at least two of the following vocab words in your description: pigment, chlorophyll, chloroplasts, glucose, ATP.
The process in which plants convert solar energy into chemical energy.
Did you use any of those terms correctly?
Chlorophyll: provides the green pigment in plants
Chloroplasts: organelle in plant cells that converts light into chemical energy through chemical reactions
Glucose: plant's food source that is produced through the chemical reactions
ATP: produced in the chemical reactions and then used in the Calvin Cycle of plants
List the 7 electromagnetic wavelengths in order from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength.
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x ray, gamma ray
This is technically Earth science, but you'll survive.
List the Geological time scale in order from oldest to youngest (current).
Mesozoic
Cenozoic
Precambrian
Paleozoic
Precambrian
Paleozoic
Mesozoic
Cenozoic