An observation made with your senses
Qualitative
X Axis
Energy of motion
Kinetic Energy
When two things come in contact with one another.
Collision
The variable that stays the same in a science experiment.
Control
Observations that involve numbers or measuring something
Quantitative
What variable is graphed on the x axis?
Independent
Stored energy (energy waiting to be used)
Potential Energy
A push or pull interaction that occurs when an object comes into contact with another object
Contact Force
In a collision, movement of the objects involved is caused by?
Energy Transfer
An educated guess based on what you know
Inference
What variable is graphed on the Y axis?
Dependent
Energy moved from on object to another
Energy Transfer
When an object bends or changes shape
Deformation
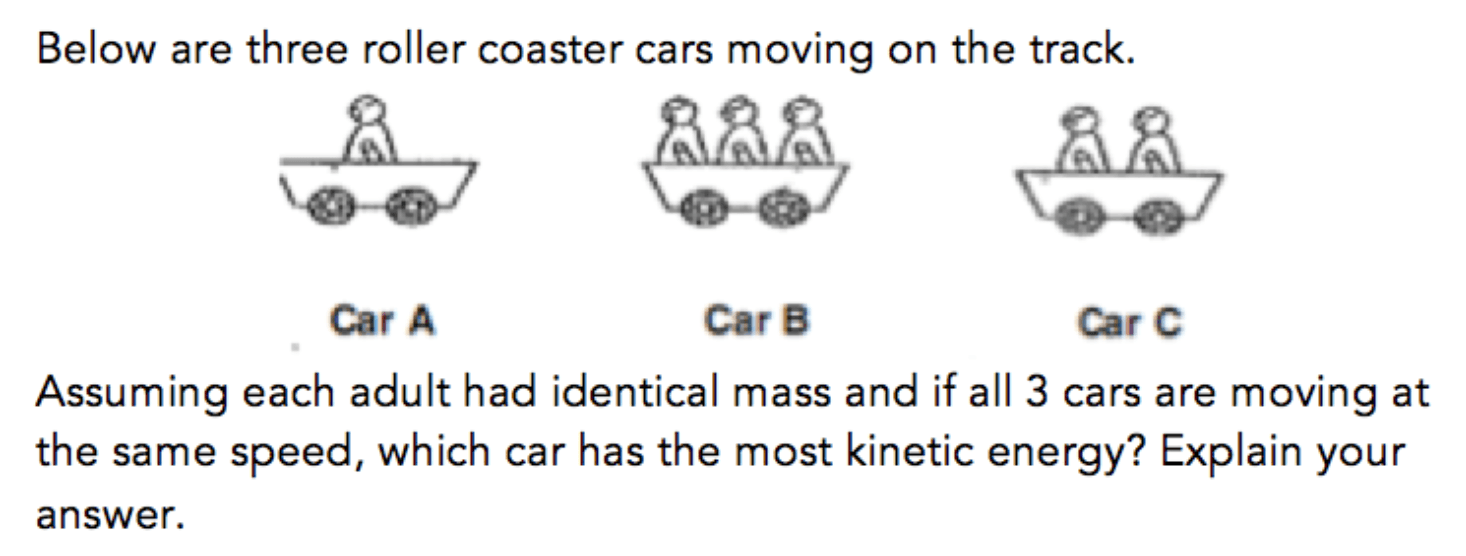
B. More Mass
Independent
Line
Energy changing from on for to another
Energy Transformation
What is elastic limit?
The largest amount of force or deformation a material can withstand before permanent deformation.
The variable we measure or observe the effects on
Dependent
The scientific process has 6 steps.
1. Observe a phenomena
2. Ask a question
3. Make an inference
4. Set up an experiment
5. ?
6. Draw conclusions
Analyze Data (collect evidence)
Other than the data, graphs should include what 3 things:
Labels, Legend(Key), Title
Kinetic Energy is affected by:
1. Mass
2. Speed
Two things occur during collisions that cause damage (whether it is temporary or permanent). These are:
Energy transfer and Force
The force on both objects in a collisions is:
1.
2.
Equal and in opposite directions