Name 4 forms of matter
Solids, liquids, gases and plasmas
Why is it ok for scientists to be wrong as it's related to experiments?
There is always something new to be discovered, even from "failure".
What is the definition of Energy?
The capacity or power to do work, such as the capacity to move an object by the application of force.
How does Electrical Energy work?
Created by the flow of ELECTRONS
List 3 main components that make up an atom.
*Bonus
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
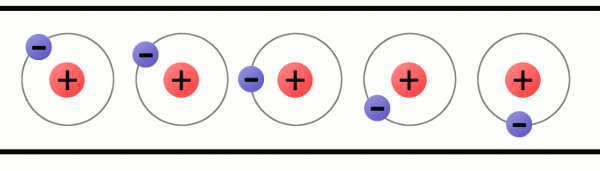
What is this form of matter?
Liquid
What is an Independent Variable?
Bonus: list 3 examples
Something manipulated or changed by a scientist
ex. amount of water, fertilizer for plants, light
Name 7 forms of energy
Light Sound
Electrical Mechanical
Chemical Thermal Nuclear
Name three examples of stored energy waiting to be used.
batteries, food, fuels, muscles
Atomic number is the number of ____________ in an element.
Protons
Define the difference between a solid, a liquid and a gas.
A solid keeps its shape, a liquid takes the shape of the container and a gas goes everywhere.
What is a Dependent Variable?
Bonus: list examples
Dependent on the Independent Variable
Something observed or measured in experiment
Ex. height of plants based on the independent variables
What is the difference between Potential and Kinetic Energy?
Potential energy is STORED energy
Kinetic is energy in MOTION
Define
CONDUCTION
CONVECTION
RADIATION
CONDUCTION- Transfer of Energy, when there is a difference of temperature, from solid to solid
CONVECTION- Transfer of Energy, when there is a difference of temperature, within fluids
RADIATION- Transfer of Energy, when there is a difference of temperature, through the air
This Carbon molecule has _____ electrons.
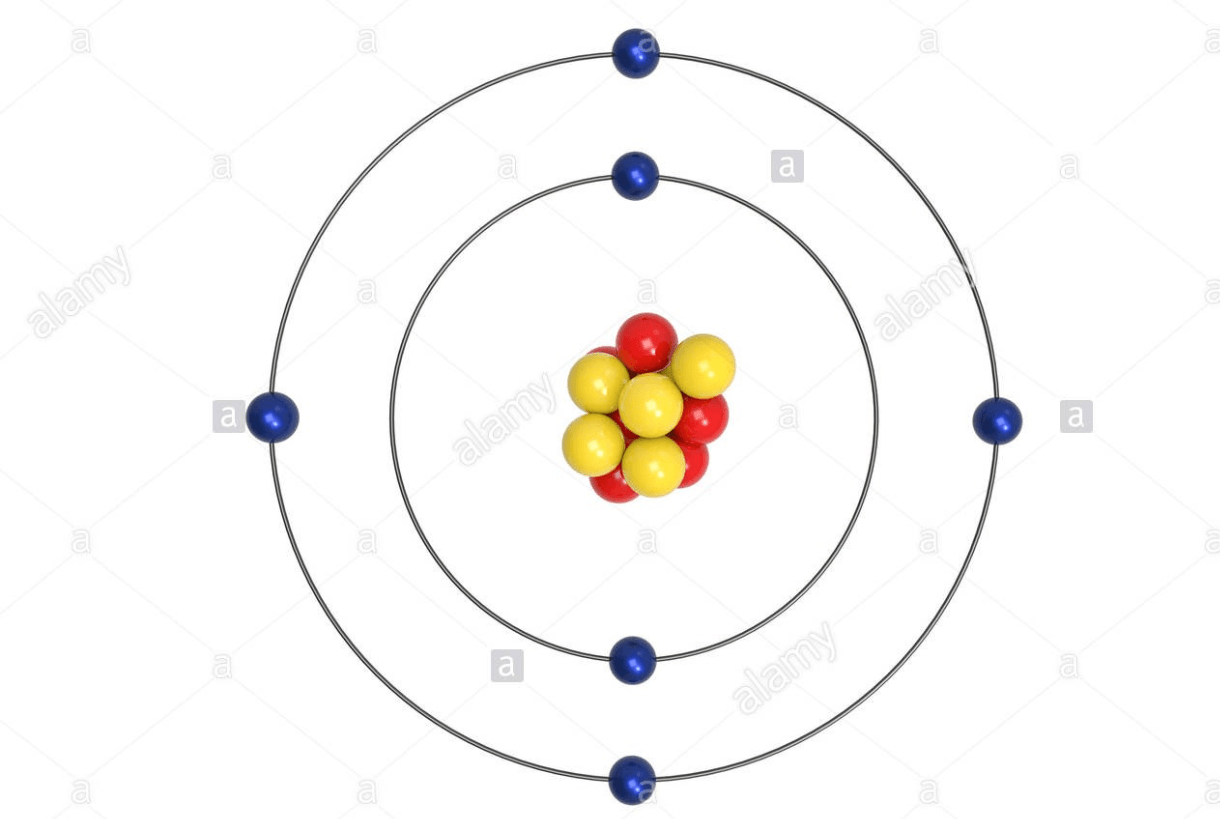
6
Describe the "state change" when something evaporates?
It changes from a liquid to a gas.
List 6 steps of the Scientific method
1. Purpose/Question
2. Hypothesis
3. Materials
4. Procedure
5. Observations/Data
6. Conclusion
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
*Bonus
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed
It can only be transferred or changed from one form to another.
A car weighs 1 ton and is traveling 50 mph
A truck weighs 2 tons and is traveling 50 mph
What is the difference in Kinetic Energy between the two?
The truck has __2___ times the kinetic energy as the car.
What is the Atomic Number of this Element?
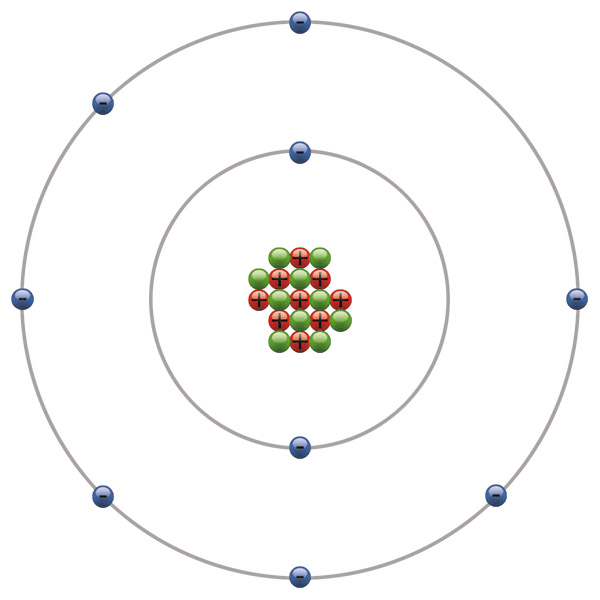
9
Explain how nuclear energy works and is used to power homes and businesses.
*Bonus
How do you change one state of matter to another?
Nuclear energy originates from the splitting of atoms – a process called fission. This generates heat to produce steam, which is used to turn a turbine generator to generate electricity.
Bonus: Add heat/energy
Lauren wants to know which location in her apartment is best for growing Moroccan Sunflowers. She has three small Moroccan Sunflowers. She puts one on the balcony, one by the kitchen window, and one on the mantel in the living room. Each plant has the same size pot and the same soil, and Lauren gives each plant the same amount of water.
What is the independent variable?
Location of the plant
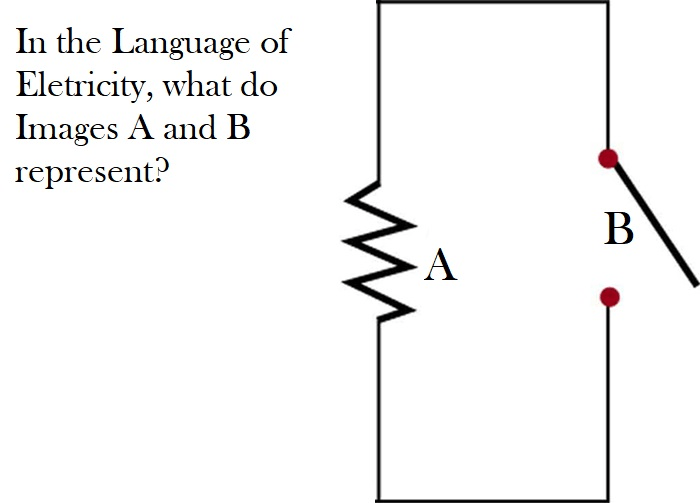
A = resistor, B = switch
Using this equation, calculate how much more Kinetic Energy the race car has than the regular car.
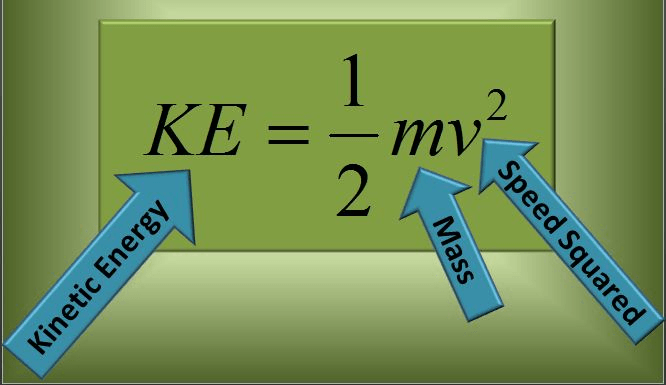
Regular car: 1 ton and is traveling 50 mph
Race car: 1 ton and is traveling 100 mph
The race car has __4___ times kinetic energy as the blue car.
Atomic Mass is the number of __________ + _____________ in an element.
*Bonus chance:
Atomic mass of Florine
Protons + Neutrons
18