Identify A. [1 mark]
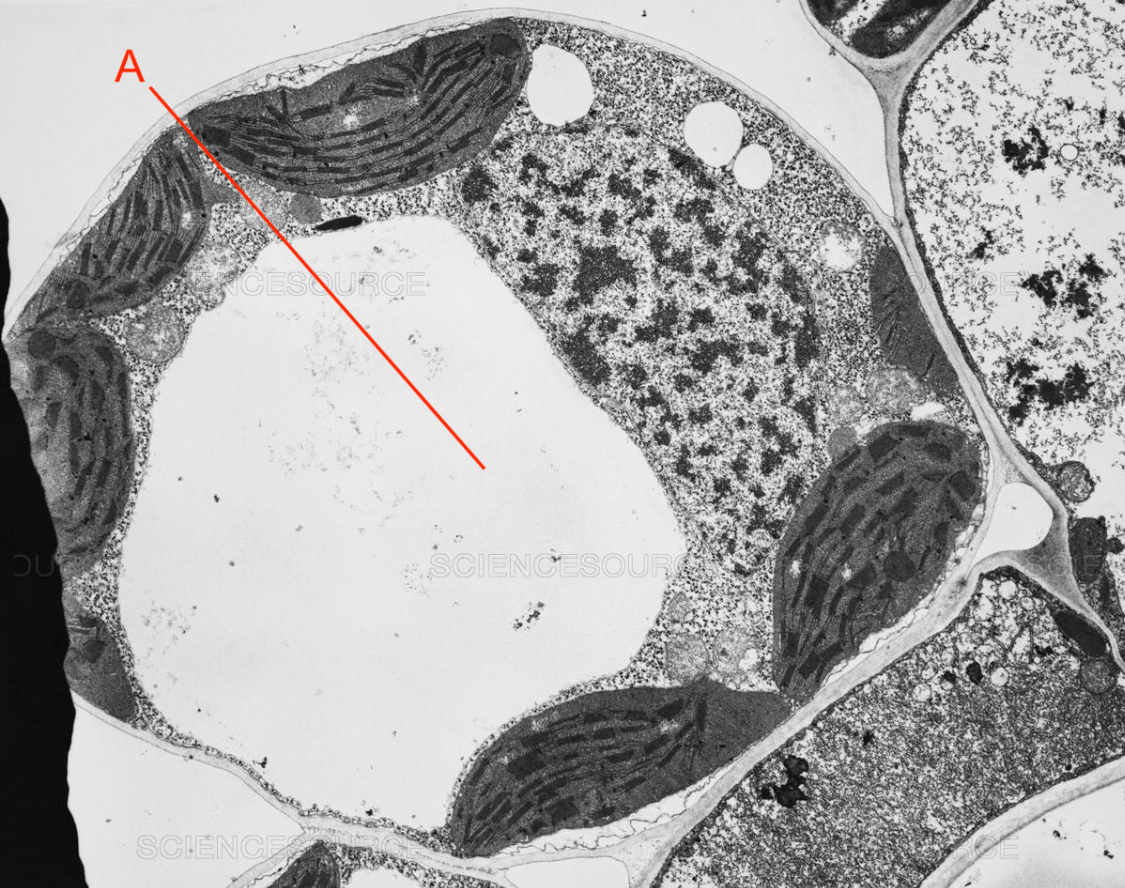
Vacuole
The diagram below shows the cooling curve of substance X, which freezes at 5°C. What state(s) is/are present at point C?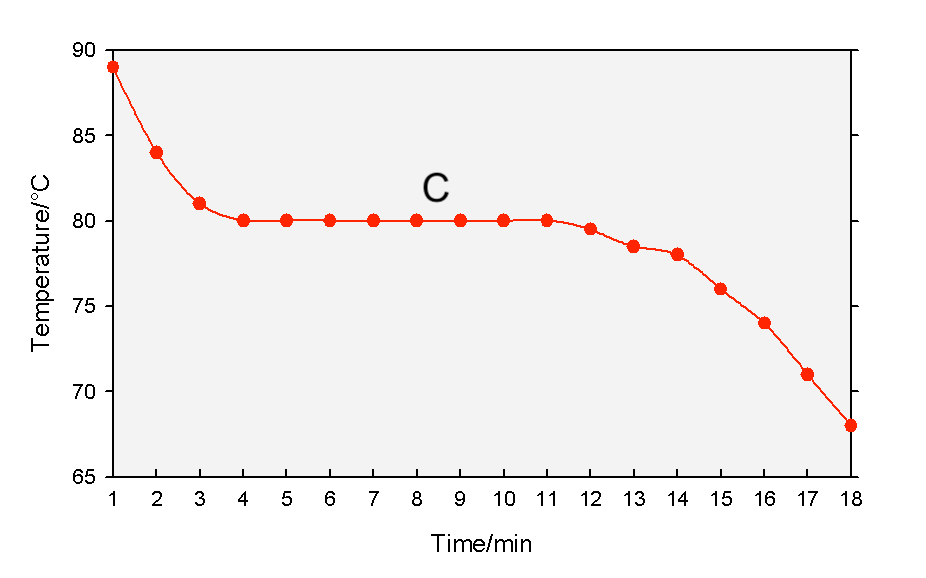
Gas and liquid
Explain how the red blood cell is adapted to its function of transporting oxygen around the body. [2 marks]
It lacks a nucleus so there is more space to carry more haemoglobin, increasing its oxygen carrying capacity. (REJECT: more space to carry more oxygen)
It has haemoglobin which can bind reversibly to oxygen, allowing oxygen to be transported to all body cells
It has a circular biconcave shape to increase rate of absorption of oxygen by red blood cells.
Using the particulate nature of matter, explain why the density of a substance is greater in the solid state than in gaseous state. [2 marks]
Particles in a solid are very closely packed, while those in a gas are spaced far apart.
Thus there are more particles per unit volume in a solid than a gas of the same substance.
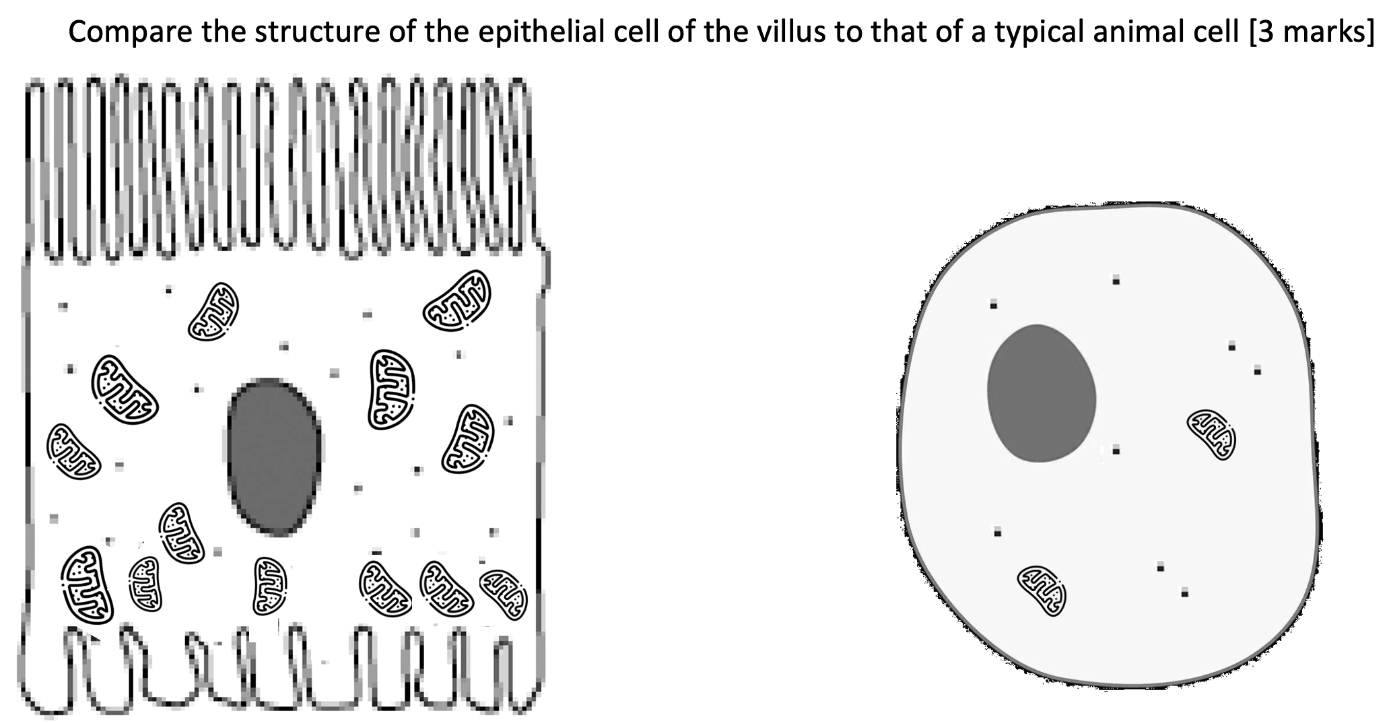
Compare: need to include both similarities and differences
Similarity 1/2/3: presence of cell surface membrane/ nucleus/ cytoplasm
Difference 1: epithelial cell of villus has finger-like projections, while typical animal cell do not
Difference 2: epithelial cell of villus has more mitochondria than typical animal cell (use of comparative terms)
Substance X has a melting point of -203 degree celsius and boiling point of -18 degree celsius. Make a sketch to show the arrangement of particles in substance X at -19 degree celsius. [3 marks]
No particles in isolation
Particles should not form orderly rows/columns (cannot draw straight line through the rows/columns)
At least 3 rows drawn
Particles to be of same size
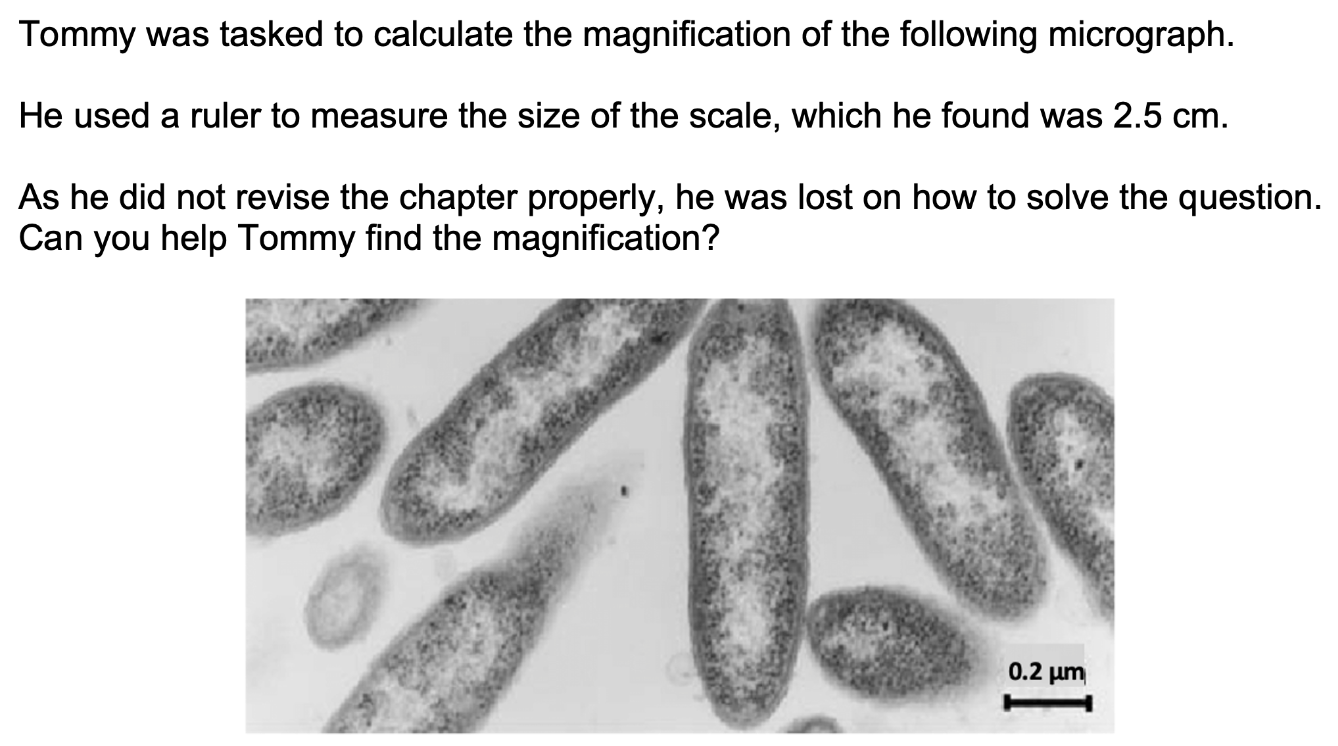
[2 marks]
Magnification
= size of image / actual size
= (2.5*10000) / 0.2
= 125000.0 X (to 1 d.p.)
Substance X has a boiling point of 10 °C. When X was heated from 25 °C to 40 °C, predict what would happen to the gas syringe. Explain your answer. [4 marks]
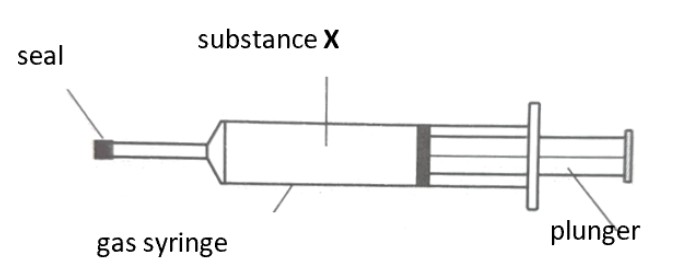
The plunger will move outwards.
When heated from 25 °C to 40 °C, the gas particles gain energy and move more vigorously,
causing the distance between particles to increase,
occupying a larger volume, pushing the plunger outwards.
Draw cell C, labelling the nucleus, cell surface membrane and tail.
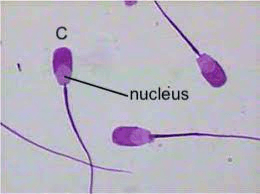
Proportion/accuracy (nucleus/tail proportional, thickness of tail)
Line (no shading, no gaps, no stray lines)
Labels (straight label line, correct labels)
Size (>1/2 of space given)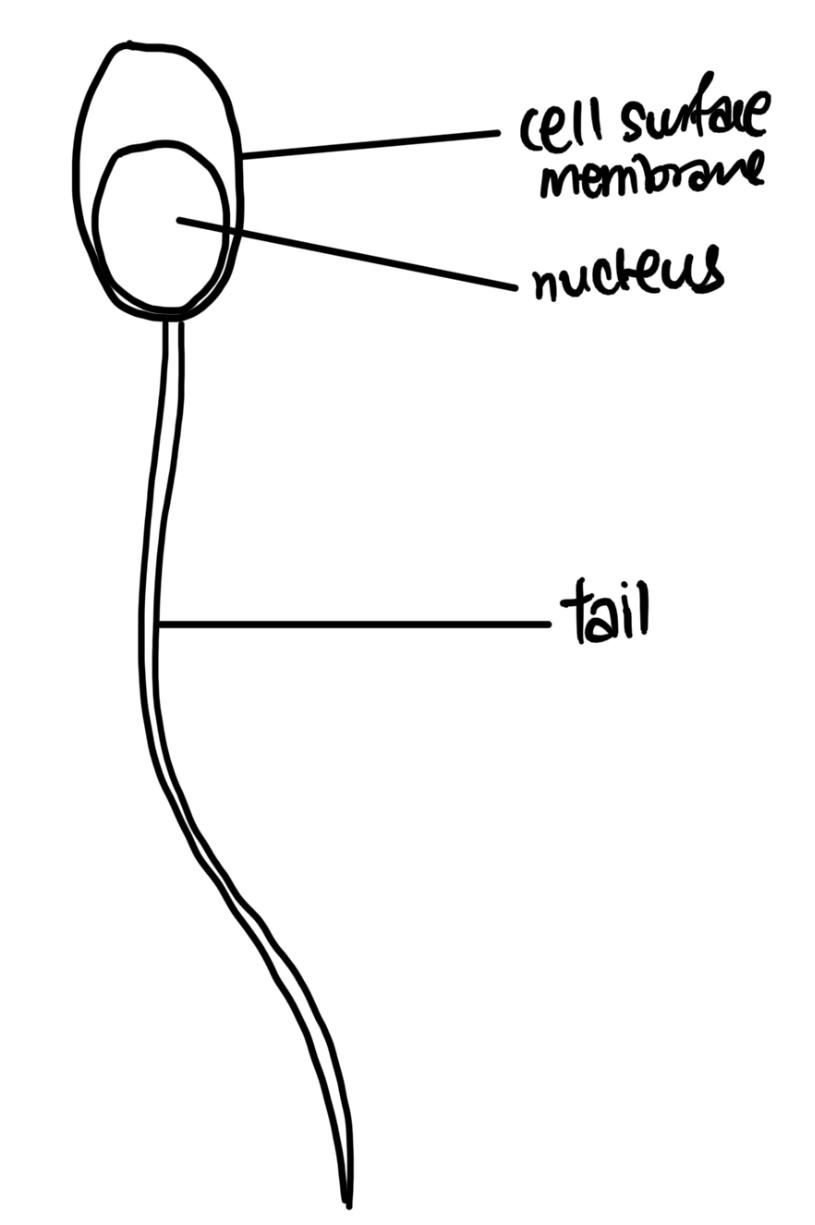
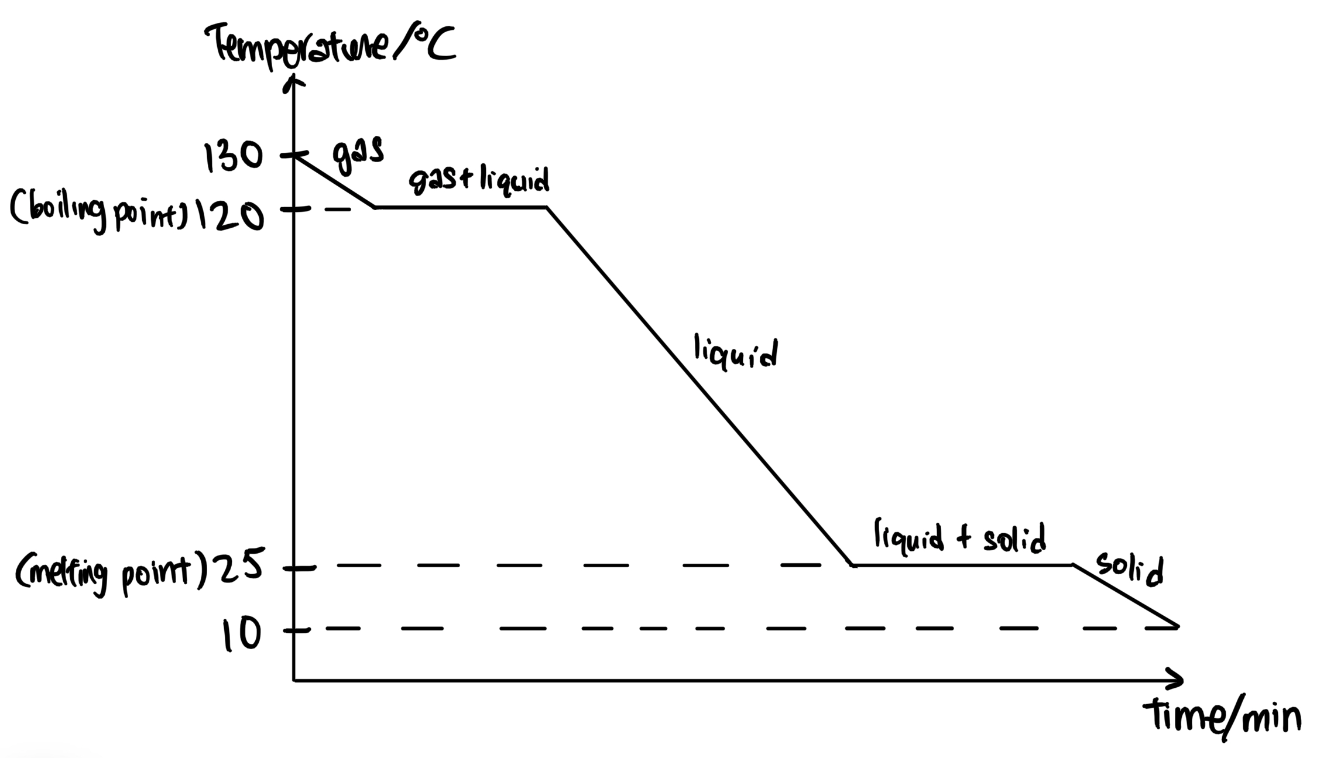
Substance Y has a boiling point of 120 °C and melting point of 25 °C.
Draw a graph of temperature against time when substance Y is cooled from 130 °C to 10 °C. Label the melting point, boiling point and states present. [5 marks]
Points
Axis
Line
Size
Mixture of states