BELIEF SYSTEMS:
Describe at least 4 of the 5 tenets of Islam.
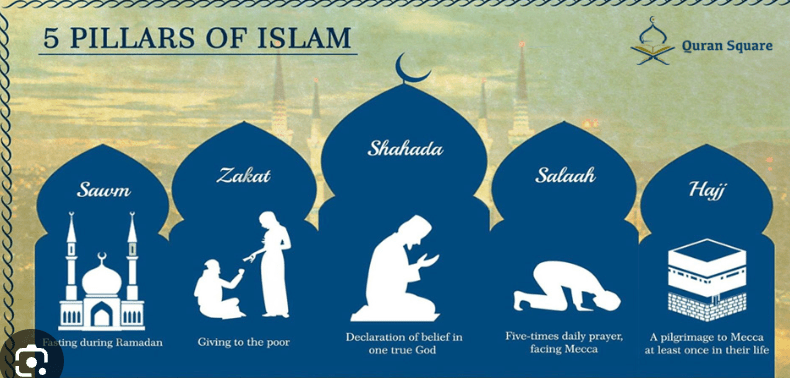
BELIEF SYSTEMS:
1) Describe the Hindu caste system.
3) Where was Hinduism primarily practiced?
1) Individuals were born into a social hierarchy, often based on skin color
2) Primarily in SE Asia (Nepal, India, Sri Lanka, etc.)
BELIEF SYSTEMS:
Describe Confucianism:
a) What philosophy was it created in response to?
b) What are the core beliefs in Confucianism?
c) What is filial piety?
a) Confucianism was made in response to legalism, which advocated for strict punishment to create social order
b) cultivation of virtue, ethics, and hierarchy as a way of creating social order
c) respecting family members (especially males) above all else.
BELIEF SYSTEMS:
Describe the relationship between feudal pope, king, lords, knights, and serfs (vassals). 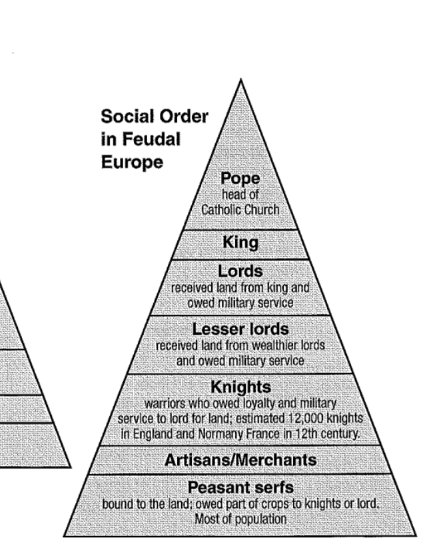
The head of the Catholic Church held most symbolic power in many Feudal societies. Meanwhile, kings and lords would give land and protection to serfs (vassals) in order to receive agricultural service and loyalty.
BELIEF SYSTEMS:
Mansa Musa, who was emperor of ______, embarked on a ______ to ______, because he believed in Islam. Along the way, he distributed gold to different people. Meanwhile, in other parts of Africa like ______, they believed in Christianity.
Mansa Musa, who was emperor of MALI embarked on a HAJJ to MECCA, because he believed in Islam. Along the way, he distributed gold to different people. Meanwhile, in other parts of Africa like ETHIOPIA, they believed in Christianity.
BELIEF SYSTEMS:
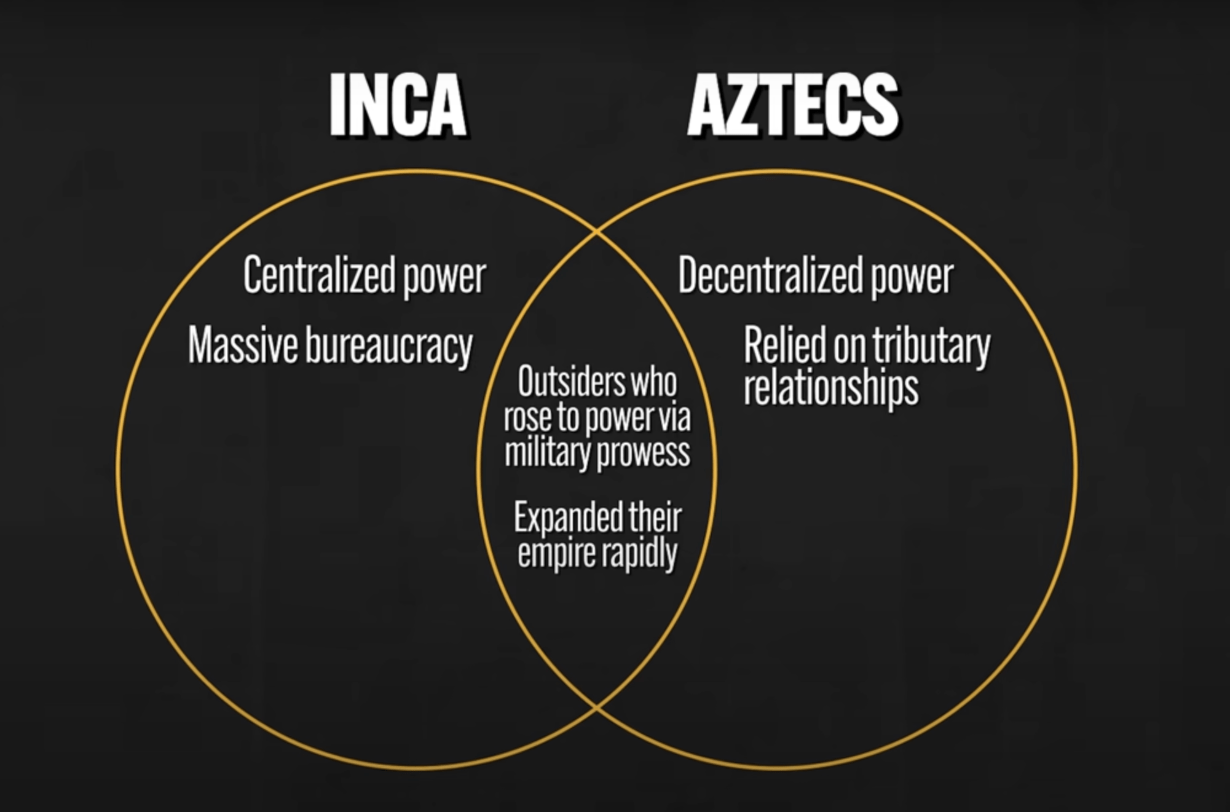
Aztecs and Incas were _______, meaning that they built their societies around the worship of many gods.
Aztecs and Incas were POLYTHEISTIC, meaning that they built their societies around the worship of many gods.
POWER MAINTENANCE:
Describe 2-3 technological advancements in Dar-Al-Islam which spread through trade & merchants.
Irrigation technology
Trade introduced new plants and animals
Inventions -water pump worked by animals
Preserved Greek and Roman texts
Education and research centers (math, science, astronomy, medicine)
POWER MAINTENANCE:
Describe the concept of "purdah": what was it, and what religion was it predominantly found in?
Purdah = the seclusion of women from society; mostly Hindu practice whereas Muslim women would work and socialize
POWER MAINTENANCE:
The Chinese state built legitimacy though inventions which transformed society. Describe at least 3-4 inventions from Song China.
1) Gunpowder
2) Moveable type (precursor to type writer)
3) Paper money (to facilitate trade more easily)
4) Compass
5) Civil Service Exams to become part of the government
POWER MAINTENANCE:
Describe the principal of PRIMOGENITURE.
The idea that a parent's lands would be inherited by their first born child (son); important in determining the passing of feudal lands.
POWER MAINTENANCE:
West African empires during this period of time often arose to power due to growing city & trade. Describe at least 2-3 things they traded in.
Salt = preserved food
Enslaved people
Gold
Cattle in South Africa & Zimbabwe
POWER MAINTENANCE:
In Mesoamerican cultures, ne way of instilling fear and control into domestic people and enemies was ________, which was often nominally for the purpose of appeasing Sun Gods and keeping the cycle of the earth going.
In Mesoamerican cultures, ne way of instilling fear and control into domestic people and enemies was HUMAN SACRIFICE, which was often nominally for the purpose of appeasing Sun Gods and keeping the cycle of the earth going.
CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe Dar-Al-Islam 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?
- Culturally unified! (Ibn Battuta traveled throughout easily!)
The Abbasid political authority fell but the beliefs continued to be spread (the empire was to big so they lost the control, but the belief thrived) -conquered by Turks and Mongols
Mongol armies came through Eurasia with violence which actually led to the spread of Islam across Mongol territory.
Dar al-Islam's golden age was the rise in religion and culture, not politics
Turkics conquered much of the Empire and later converted to Islam, making the culture and religion rise even more
The Mongols conquered the Turks and destroyed the House of Learning putting an end to Abbasid Caliphate, however converted to Islam later (more religious rise)
CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe South/South East 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?

CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe East Asia (China/Japan) 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?
Song China = highly politically & culturally centralized (civil service exams; strong emperor with Mandate of Heaven, etc.)
Feudal Japan = highly decentralized (feudal system with shogun, daimyos, samurai doing whatever they wanted. etc.)
CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe Europe 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?
Relatively decentralized! Feudalism existed largely because there were not huge centralized empires dominating Europe at this time.
CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe Africa 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?
Relatively decentralized because of different kinds of places: 
CONTEXTUALIZATION:
Overall, would you describe the Americas 1200-1450 as politically or culturally unified?
 etzcoco, and Tlacopan)
etzcoco, and Tlacopan)
Incas
VOCAB REVIEW:
1) What is a caliphate?
2) Who was the Abbasid Caliphate eventually conquered by?
1) A Muslim state headed by a "Caliph" or descendant of the prophet Muhammad
2) The Mongols! (Who became the Ottoman Turks in the Ottoman Empire!)
VOCAB REVIEW:
In Hinduism, what is 1) a brahmin and 2) moksha?
1) Brahmin = hindu priest
2) state of liberation, bliss and awareness, escaping the cycle of samsara (afterlife/reincarnation) and karma.
VOCAB REVIEW:
1) What was the mandate of heaven?
2) When the Song Dynasty was toppled, who did the mandate of heaven pass to?
1) The idea that the Chinese emperor had the divine right to rule from God.
2) The Yuan Dynasty (the Mongols!)
VOCAB REVIEW:
1) Describe the Medieval Climate Anomaly and Little Ice Age.
2) What effect did this have on State control?
1) MCA (Medieval Climate Anomaly) = period of warm stable weather with easier farming; LIA (Little Ice Age) = cold, wet & unstable
2) Effects = During MCA = expansion; During LIA changes in agriculture (to feudal manorial system) and political fragmentationVOCAB REVIEW:
Explain the difference between a city-state, chieftancy, and confederation.
City-State = a state based around a city
Chieftancy = one individual has a lot of power over others
Confederation = an alliance of many states, often arising for collective security
VOCAB REVIEW:
1) _______ were floating gardens in the _____ capital city of _________, which was created in the center of Lake __________. These gardens provided a agricultural space for a growing population.
1) Chinampas were floating gardens in the Aztec capital city of Tenotichtitlan, which was created in the center of Lake Texcoco.
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in Dar-Al-Islam, and describe where they were found.
The Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258; Present Day Middle East)
The House of Wisdom (in Baghdad)
The Mali Empire (in Northern Africa, headed by Mansa Musa).
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in South & SouthEast Asia, and describe where they were found.
Delhi Sultanate in India
Đại Việt Empire in Vietnam
Champa Empire in Myanmar
Angkor Empire in Cambodia
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in East Asia, and describe where they were found.
Feudal Japan
Song Dynasty China Empire
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in Europe, and describe where they were found.
Holy Roman Empire (in decline)
Feudal Kingdoms
France
England
Etc.
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in Africa, and describe where they were found.
Mali Empire
Kingdom of Ile Ife
Swahili City-States
Greater Zimbabwe
Various Chieftancies and Confederations
STATE STRUCTURES:
Name at least 2-3 places that were found in the Americas, and describe where they were found.
Mayans & Aztec Empire (Mexica)
Inca Empire (present day Peru)
Mississippi Civilization (North America)